Tests
1st tests to order
prolactin
Test
Measurement of a fasting sample is desirable. In laboratories that do not use a 2-step assay for prolactin measurement, serial dilution in people with large pituitary macroadenomas (>3 cm) should be considered, to exclude the "hook effect" caused by very high prolactin levels. An elevated level should normally be repeated prior to further evaluation, which should include exclusion of pregnancy, and review of medications and comorbidities. Systemic disorders such as hypothyroidism, liver disease, and renal insufficiency may be associated with hyperprolactinemia. A serum prolactin level below 100 nanograms/mL in the presence of a pituitary macroadenoma is usually due to stalk effect. Hyperprolactinemia has been described where monomeric prolactin is bound to immunoglobulin or polysaccharides (macroprolactinemia). It is detected in the laboratory as hyperprolactinemia in the absence of symptoms of hyperprolactinemia. The monomeric prolactin levels, if measured accurately, will be normal.
Result
may be elevated; levels >200 nanograms/mL in the absence of drugs such as metoclopramide and antipsychotics are almost always diagnostic of a prolactinoma
insulin-like growth factor 1
Test
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels are reported as age- and sex-specific. The presence of 3 or more anterior pituitary hormone deficiencies in the presence of low IGF-1 usually indicates the presence of growth hormone (GH) deficiency and thus may obviate the need for further testing. However, an age- and sex-matched normal IGF-1 may be seen in up to 65% of patients with GH deficiency. Measurement of IGF- 1 also serves to screen for acromegaly (GH excess from a pituitary tumor) especially in mild or early cases that may not be clinically apparent.
Result
low or normal levels are consistent with GH deficiency; elevated levels with GH excess.
luteinising hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone
Test
Low serum testosterone in men (estradiol in women) accompanied by normal/low follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinising hormone (LH) levels are consistent with gonadotropin deficiency in males and amenorrheic premenopausal women. Failure to elevate FSH and LH in postmenopausal women is also consistent with gonadotropin deficiency. Measurement of gonadotropins and estradiol in reproductive age women with irregular menstruation is usually not informative. The presence of normal menstruation is the best indicator of the integrity of gonadotropin axis in women of reproductive age.
Result
low or normal LH and FSH levels in postmenopausal women, in reproductive-age women with amenorrhea and low estradiol, and in men with low testosterone levels (<200 nanograms/dL)
alpha subunit of human pituitary glycoprotein hormones
Test
Over 45% of clinically nonfunctional pituitary adenomas (CNFPAs) are in fact gonadotrope cell adenomas that can produce intact FSH and LH, but more commonly produce varying combinations of either FSH beta subunit and/or LH beta subunit along with the common alpha subunit.[37]
The alpha subunit may be elevated in up to 20% of patients with CNFPAs, but it is not a reliable tumor marker as it does not correlate with residual tumor size for follow-up of gonadotroph adenomas after surgery.[49]
Result
normal or elevated
testosterone
Test
Testosterone is best measured first thing in the morning. It tends to be higher earlier and lower later in the day. Two to 3 measurements may be necessary in those with borderline levels (200-300 nanograms/dL).
Result
low in men with gonadotropin deficiency, rarely high in LH-secreting adenomas
estradiol
Test
Measurement of gonadotropins and estradiol in reproductive-age women with irregular menstruation is usually not informative. The presence of normal menstruation is the best indicator of the integrity of gonadotropin axis in women of reproductive age.
Result
low in amenorrheic, premenopausal women with gonadotropin deficiency
thyroid-stimulating hormone, free thyroxine
Test
Concurrent evaluation of free thyroxine and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is required for the diagnosis of central hypothyroidism. Hospitalized patients with severe acute illness may have the euthyroid sick syndrome, which can resemble central hypothyroidism. Such patients usually have significantly lower T3 levels along with a history of an acute illness. In such circumstances, measurement of free T3 along with TSH and free T4 is recommended. In rare cases, TSH may be slightly elevated in patients with central hypothyroidism. Here the TSH is immunogenic but not biologically active.
Result
free T4 and free T4 index are low in secondary hypothyroidism and TSH may be low or normal
morning cortisol
Test
Early morning cortisol level >15 micrograms/dL makes the diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency unlikely. An early morning serum cortisol <3 micrograms/dL is usually diagnostic for adrenal insufficiency. However, it is not uncommon to see a morning cortisol in the range between 3 to 15 micrograms/dL. Such patients should be further evaluated by an adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulation test, which can be performed anytime during the day.
Result
morning (8 am) cortisol <3 micrograms/dL indicates adrenal insufficiency
adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulation test
Test
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulation test can be performed any time during the day. The optimal cortisol values need to be individualized depending on the assay used, as newer assays (e.g., monoclonal antibody immunoassays or mass spectrometry) may have a lower threshold and result in a false positive test.[45] The value of <18 micrograms/dL to indicate adrenal insufficiency is derived from polyclonal antibody assays; a serum cortisol cutoff of less than 14-15 micrograms/dL is suggested for the new specific monoclonal antibody immunoassays.[45]
Cut-off values also need to be individualized according to whether high-dose or low-dose cosyntropin is used for the ACTH stimulation test used.[46] Patients with mild, partial, or recent-onset pituitary ACTH or hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone deficiency (e.g., within 2 to 4 weeks after pituitary surgery) may have a normal response to ACTH stimulation test because the adrenal glands have not undergone sufficient atrophy and still respond to very high concentrations of ACTH stimulation. The ability of the test to detect mild adrenal insufficiency improves when low dose cosyntropin (1 microgram) is used.[46]
Result
low in adrenal insufficiency, e.g., cortisol <18 micrograms/dL at 30 minutes following 250 micrograms cosyntropin, administered via intramuscular or intravenous injection
adrenocorticotropic hormone
Test
Adrenocorticotropic hormone levels are not reliable for diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency but can be used to differentiate primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency in those with low cortisol levels.
Result
low or within the normal reference range in patients with secondary adrenal insufficiency
insulin tolerance test for cortisol
Test
Insulin tolerance test (ITT) is generally used for the evaluation of patients suspected to have secondary adrenal insufficiency to evaluate the integrity of the whole hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. ITT is considered the definitive test for evaluation of the HPA axis. However, it is usually not necessary because the adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulation test is much easier to perform and, except within 2 to 4 weeks after an acute pituitary event, correlates well with ITT. A serum cortisol level above 18 micrograms/dL during an ITT is usually considered a normal response. The test needs to be done by an experienced clinician and is usually not needed for the evaluation of adrenal function in day-to-day practice.
Result
cortisol <18 micrograms/dL considered abnormal
basic metabolic panel
Test
Patients with secondary adrenal insufficiency are not hyperkalemic because adrenocorticotropic hormone has a minor role in aldosterone regulation.
Result
hyponatremia may be seen in hypothyroidism and adrenal insufficiency
CBC
Test
Anemia may be a feature in patients with longstanding hypogonadism, hypothyroidism, and adrenal insufficiency.
Result
anemia
MRI pituitary with gadolinium enhancement
Test
Pituitary MRI is preferred over CT scan.[40] It delineates the characteristics of the tumor including any invasion of cavernous sinuses and sphenoid sinus, in addition to chiasmal compression. It can help with exclusion of other diagnoses.[39] MRI is contraindicated in patients with permanent pacemakers and should be avoided in patients with end-stage kidney disease on dialysis.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Precontrast coronal (A) and sagittal (B) MR images of a patient with a pituitary macroadenoma (arrow, A). The pituitary mass extends toward the optic chiasm with some pressure effectFrom the collection of Dr Amir Hamrahian [Citation ends].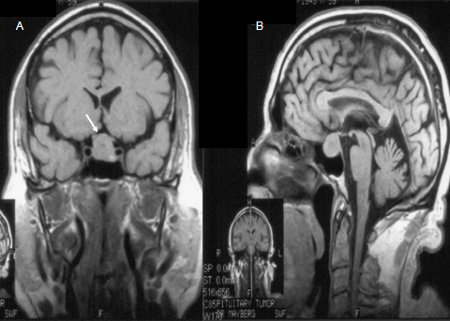 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Precontrast (A) and postcontrast (B) coronal MR images of a patient with a small pituitary microadenoma. The pituitary lesion enhances less than the normal pituitary gland following gadolinium and appears hypodense compared with the normal pituitary gland (arrow, B)From the collection of Dr Amir Hamrahian [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Precontrast (A) and postcontrast (B) coronal MR images of a patient with a small pituitary microadenoma. The pituitary lesion enhances less than the normal pituitary gland following gadolinium and appears hypodense compared with the normal pituitary gland (arrow, B)From the collection of Dr Amir Hamrahian [Citation ends].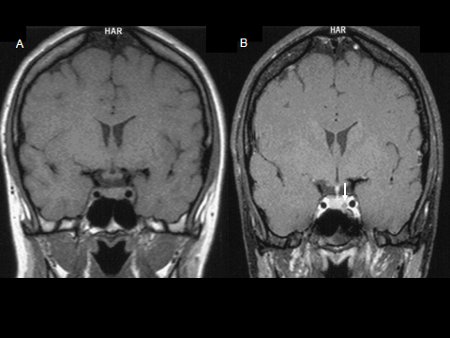
Result
sellar mass
contrast-enhanced CT pituitary
Test
Where MRI scan is unavailable or contraindicated, it may be used to demonstrate the tumor.
Result
sellar mass
Tests to consider
growth hormone stimulation test
Test
Growth hormone (GH) deficiency is best evaluated with dynamic testing including either an insulin tolerance test (ITT), glucagon stimulation test, growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)/arginine stimulation test, or macimorelin test. ITT is considered the most specific and sensitive test for evaluation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-growth hormone axis. However, it needs to be performed by experienced clinicians and is usually not needed for everyday clinical practice.
Result
stimulated peak GH levels:<3 nanograms/mL (ITT or glucagon stimulation); <11 nanograms/mL (GHRH/arginine stimulation; BMI <25kg/m²); <8 nanograms/mL (GHRH/arginine stimulation; BMI 25-30 kg/m²); <4 nanograms/mL (GHRH/arginine stimulation; BMI >30 kg/m²); GH level <2.8 nanograms/ml (macimorelin)
lipid panel
Test
Hyperlipidemia may occur in growth hormone deficiency and hypogonadism.
Result
hyperlipidemia
Humphrey or Goldmann formal visual fields test
Test
Eye examination and formal visual field testing (Humphrey or Goldmann visual field test) are indicated if imaging shows the adenoma is causing pressure on, or has contact with, the optic chiasm, in order to document visual acuity and field deficits.
Result
visual field deficits
immunohistochemical staining
Test
May help to establish the functional status of the tumor after resection.
Result
positive staining for any of anterior pituitary hormones and alpha subunit
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer