Criteria
Rule-in criteria
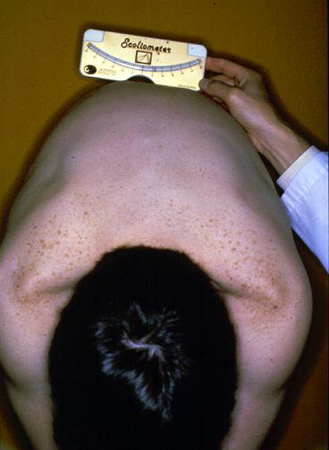
Scoliometer measurement of >5°[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Scoliometer measurement of a right thoracic prominenceWeinstein SL, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Lancet. 2008;371:1527-1537. Used with permission [Citation ends].
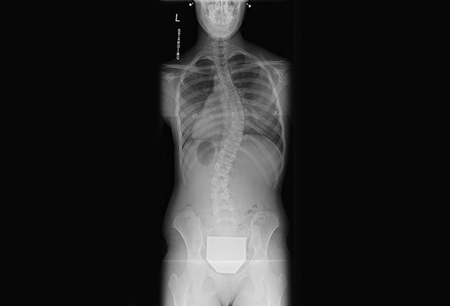
Cobb angle measurement, of a major structural curve, of >10° (cut-off based on natural history studies and evaluation of curve progression rates)[1][15][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Posteroanterior scoliosis radiograph of a 13-year-old girl with a 49° right thoracic curvature with apex at the T9-T10 disc spaceFrom the collection of Stuart Weinstein, MD, University of Iowa; used with permission [Citation ends].
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Lateral scoliosis radiograph of a 13-year-old girl with a 49° right thoracic curvatureFrom the collection of Stuart Weinstein, MD, University of Iowa; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Lateral scoliosis radiograph of a 13-year-old girl with a 49° right thoracic curvatureFrom the collection of Stuart Weinstein, MD, University of Iowa; used with permission [Citation ends].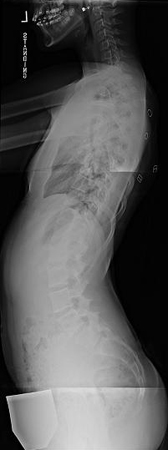
Absence of other possible cause for the spinal deformity.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer