Investigations
1st investigations to order
vaginal pH
Test
The normal vaginal pH in women of childbearing age is 4.5.
In postmenopausal women, the vaginal pH is generally in the 6.0 to 7.0 range.
Elevated pH is seen in bacterial infections, including trichomoniasis, and in atrophic vaginitis.
Generally, Candida infections will present with a normal range pH.
Result
elevated/normal
amine 'whiff' test of vaginal secretions
Test
The presence of volatile amines (fishy odour) is not encountered in normal vaginal fluids.
The presence of a fishy odour following addition of 10% potassium hydroxide to the vaginal sample is suggestive of bacterial vaginosis when accompanied by at least two other Amsel criteria.[4][31]
Result
suggestive of bacterial vaginosis
wet mount microscopy of vaginal secretions
Test
Vaginal samples are added to two different slides, one with saline solution and one with potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution.
Bacterial vaginosis: clue cells (vaginal epithelial cells with distinctive stippled appearance by being covered with bacteria) are present and are seen as vaginal epithelial cells covered with many rods and cocci, with a granular appearance. The numbers of lactobacilli are decreased and WBCs are absent.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Photomicrograph revealing bacteria adhering to vaginal epithelial cells, known as clue cellsCDC Image Library; M. Rein [Citation ends].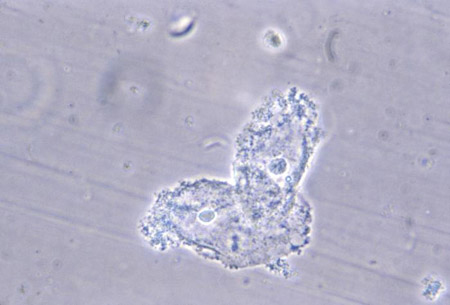
Candidiasis: hyphae and budding yeast are better seen with the KOH preparation microscopy.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Vaginal smear identifying Candida albicans using a wet mount techniqueCDC Image Library; Dr Stuart Brown [Citation ends].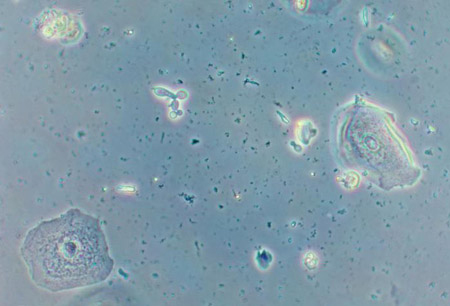
Trichomoniasis: a significant number of WBCs and epithelial cells are observed. The parasite is a motile oval or fusiform-shaped protozoan 15 micrometres long. The sensitivity of wet mount is low in vaginal specimens (51% to 65%). Sensitivity declines quickly with time, so clinicians should aim to evaluate slides immediately.[4][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Phase contrast wet mount micrograph of a vaginal discharge revealing the presence of Trichomonas vaginalis protozoa CDC Image Library [Citation ends].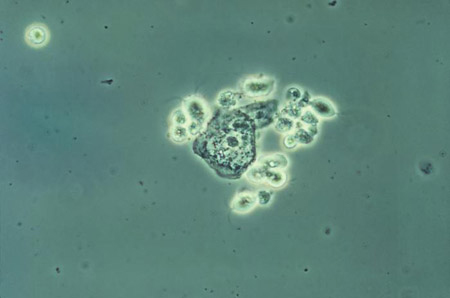
Result
identification of bacteria and yeast infections
Gram stain of vaginal secretions
Test
Scored in accordance to Nugent classification, which involves counting the bacterial morphotypes. Reduced or absent lactobacilli are indicative of bacterial vaginosis.[32]
Result
Lactobacillus morphotype reduced or absent
HIV test
Test
Routine to rule out HIV. Time to HIV seropositivity with a third-generation enzyme immune assay can be >21 days.
Recommended in individuals with recurrent infections and/or those who are at risk of exposure to STIs (e.g., unprotected intercourse).
Bacterial vaginosis and candidiasis are not typically sexually transmitted; however, they may occur concomitantly with STIs (e.g., gonorrhoea and chlamydial infections) and therefore it is recommended to screen for STIs in all women with infective vaginitis.
Result
may be positive
nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT)
Test
Recommended for diagnosis of chlamydial infection and gonorrhoea.[4]
Highly sensitive for trichomoniasis, often detecting 3 to 5 times more infections than wet mount microscopy.[4]
Recommended in individuals with recurrent infections and/or those who are at risk of exposure to STIs (e.g., unprotected intercourse).
Bacterial vaginosis and candidiasis are not typically sexually transmitted; however, they may occur concomitantly with STIs (e.g., gonorrhoea and chlamydial infections) and therefore it is recommended to screen for STIs in all women with infective vaginitis.
Result
may be positive
venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) test
Test
Routine to exclude syphilis.
Recommended in individuals with recurrent infections and/or those who are at risk of exposure to STIs (e.g., unprotected intercourse).
Bacterial vaginosis and candidiasis are not typically sexually transmitted; however, they may occur concomitantly with STIs (e.g., gonorrhoea and chlamydial infections) and therefore it is recommended to screen for STIs in all women with infective vaginitis.
Result
may be positive
serum rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test
Test
Routine to exclude syphilis.
Recommended in individuals with recurrent infections and/or those who are at risk of exposure to STIs (e.g., unprotected intercourse).
Bacterial vaginosis and candidiasis are not typically sexually transmitted; however, they may occur concomitantly with STIs (e.g., gonorrhoea and chlamydial infections) and therefore it is recommended to screen for STIs in all women with infective vaginitis.
Result
may be positive
Investigations to consider
culture of vaginal secretions
Test
Trichomoniasis results take approximately 3 days. Although this is the most specific and sensitive test for trichomoniasis, wet mount preparation remains the most commonly used test as it is quicker and less expensive.
May aid diagnosis in treatment-resistant cases of Candida and trichomoniasis.
Result
positive for trichomoniasis/candidiasis infections
polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for trichomoniasis on vaginal secretions
Test
PCR targeting the beta-tubulin genes of Trichomonas vaginalis.[33]
Result
positive if trichomoniasis
rapid enzyme tests of vaginal secretions
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer