Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- typical age group (<15 years or >25 years)
- exposure to infected individual
- travel from epidemic or endemic regions
- unvaccinated/incompletely vaccinated individuals
- sore throat
- dysphagia or dysphonia
- dyspnoea
- croupy cough
- pseudomembrane formation
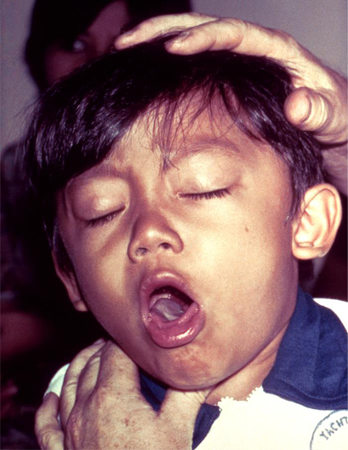
- swelling of the neck
- skin lesions
- respiratory compromise
Risk factors
- unvaccinated individuals
- inadequately vaccinated individuals
- exposure to an infected individual
- travel from endemic areas
- skin breakdown
- poor hygiene, overcrowding, and poverty
Diagnostic investigations
Investigations to consider
- Elek test for toxigenicity
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- diphtheria antibodies
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Derek Sloan, FRCP, PhD
Reader & Consultant Physician in Infectious Diseases
University of St Andrews & NHS Fife
Scotland
Infectious Diseases Referent
UK-Med
UK
Disclosures
DS declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Derek Sloan would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Walid Abuhammour, Dr Sarmad Farook Yahya Alhamdani, and Dr Nida Yousef, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
WA, SFYA, and NY declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
William A. Petri, Jr, MD, PhD, FACP
Chief and Professor of Medicine
Division of Infectious Diseases and International Health
University of Virginia Health System
Charlottesville
VA
Disclosures
WAP declares that he has no competing interests.
George Y. Wu, MD, PhD
Professor of Medicine
University of Connecticut Health Center
Farmington
CT
Disclosures
GYW is on the medical advisory boards of the following: Gilead Sciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AbbVie, and Intercept.
Linda S. Nield, MD
Associate Professor of Pediatrics
West Virginia University School Of Medicine
Morgantown
WV
Disclosures
LSN declares that she has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer