History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
presence of risk factors
Key risk factors include: childhood (especially male children); previous sinus infection; lack of Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccination.
recent sinus infection
recent eyelid injury
Eyelid injury can lead to a secondary skin infection and peri-orbital and/or orbital cellulitis.
redness and swelling of eye
Peri-orbital cellulitis usually presents as redness around the eyelid.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Swollen and red left eyelidFrom the personal collections of H. Jane Kim, MD, and Robert Kersten, MD, UCSF; used with permission [Citation ends].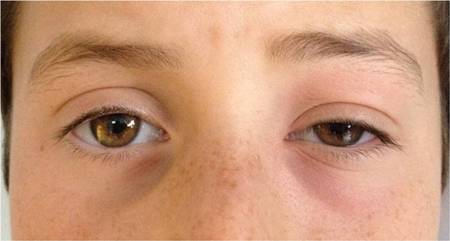
Orbital cellulitis usually presents as a severe redness around a swollen eyelid with ptosis.
ocular pain
decreased vision
Visual disturbance is a key symptom of orbital cellulitis. Rarely present in peri-orbital cellulitis.
Rapidly declining vision may be a sign of developing orbital compartment syndrome, and is an indication for hospital admission.[1][9][10][11]
Visual loss is a sign of orbital cellulitis; occurs in up to 11% of cases.[10][18]
proptosis
eyelid oedema
insect bite on eyelid
An insect bite on the eyelid or surrounding area is one of the more common causes of this condition. Insect bites can become infected with common pathogens and lead to peri-orbital cellulitis.
stye or chalazion
A stye or chalazion (or even a papule) on the eyelid or surrounding skin can rupture and become infected, leading to peri-orbital cellulitis.
uncommon
ophthalmoplegia and diplopia
Key factor for orbital cellulitis. Rarely present in peri-orbital cellulitis.
Decreased eye mobility can be difficult to evaluate, so index of suspicion needs to be high.
Severe ophthalmoplegia is an indication for hospital admission as it may be a sign of cavernous sinus thrombosis.
Diplopia is not a common symptom, but may be present in orbital cellulitis.
Other diagnostic factors
common
orbital trauma
skin infection
Can be a cause, especially when preceded by an insect bite or inoculation from a penetrating injury.
chemosis
Occurs more commonly in orbital cellulitis, but cannot be used as a differentiating sign.
fever
eyelid erythema
One of the early signs in both conditions.
elevated intra-ocular pressure
headache
Can be one of the earliest signs, present mostly in orbital cellulitis.
malaise
Some patients may have constitutional symptoms such as malaise, but this mostly occurs in orbital cellulitis.
uncommon
previous dental infection or dental work
A dental problem can be the source of sinusitis, which in turn is the most common cause of orbital cellulitis.[27]
orbital fracture
Can be the cause of orbital cellulitis.
foreign body in eye or orbit
Can be a cause of trauma, which can lead to infection.[1]
drowsiness
Late sign, and indicates meningeal involvement.[10]
nasal discharge
May be purulent, especially late in disease.
Risk factors
strong
sinusitis
male sex
lack of Hib vaccine in children
Standard use of the Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine has significantly decreased the risk of pre-septal and orbital cellulitis in children.[4]
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer