Images and videos
Images
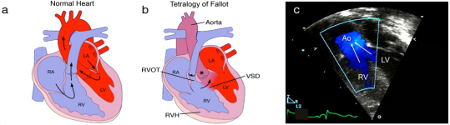
Tetralogy of Fallot
Anatomy and pathophysiology of tetralogy of Fallot (TOF): normal heart structure (a) promotes unidirectional flow of de-oxygenated blood (blue) into the lungs and oxygenated blood (red) into the aorta; in TOF (b) pulmonary stenosis and narrowing of the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) impedes the flow of de-oxygenated blood into the lungs, and both the ventricular septal defect (VSD) and overriding aorta (*) promote the flow of de-oxygenated blood into the systemic circulation, to produce cyanosis (sometimes referred to as 'blue baby' syndrome), right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) is also present; (c) a Doppler echocardiogram shows mixing of de-oxygenated blood from the right ventricle (RV) and oxygenated blood from the left ventricle (LV) as blood is pumped out the over-riding aorta (Ao) in a patient with TOF (RA=right atrium, LA=left atrium)
Multimedia Library of Congenital Heart Disease, Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA, editor Robert Geggel, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Tetralogy of Fallot
ECG in tetralogy of Fallot showing right ventricular hypertrophy
From the collection of Dr Jeffrey Gossett; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer