Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
The results suggest an infectious process but are non-specific.
Result
leukocytosis, elevated neutrophil count, anaemia
serum LFTs
Test
Elevated serum alkaline phosphatase (alk phos) level is the most common finding in liver abscess and is present in approximately two-thirds of patients.[4] Typically, the aminotransferases and bilirubin levels are only mildly elevated except in severe disease or with concomitant biliary obstruction.[3][4][8][18]
A falling serum albumin level is common.
Result
elevated alk phos, mildly elevated aminotransferases and bilirubin, hypoalbuminaemia
blood cultures
Test
Positive in approximately one half of patients with liver abscess.[36] Sensitivity decreases with prior antibiotics.
Result
pyogenic: may be positive for causative bacterial organism; fungal: may be positive for causative fungal species
prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time
Test
Indicated to check that blood clotting is within normal limits before aspiration is performed. Aspiration is contraindicated in the presence of abnormal clotting.
If an abnormality is detected, the cause would need to be investigated and the coagulation defect corrected before aspiration could take place.
Result
usually normal
liver ultrasound
contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan
Test
Only a few lesions display rim enhancement.[39] Gas within the lesion is highly suggestive of a pyogenic abscess.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A non-contrast abdominal CT scan showing a huge gas-containing liver abscess (arrow)Adapted from BMJ Case Reports 2009 (doi:10.1136/bcr.08.2008.0638). Copyright 2009 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd [Citation ends].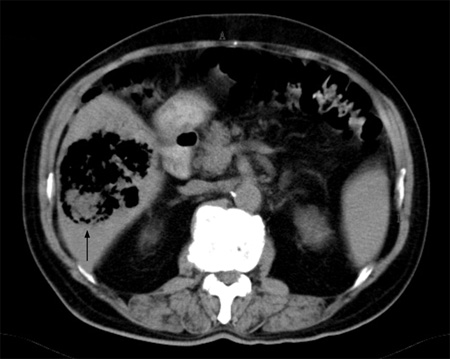
CT scan permits examination of the surrounding structures and can be used to guide aspiration of the abscess.
Sensitivity >95%.[38][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan showing a liver abscess (7 cm x 5 cm) in a 46-year-old man who presented with fever, fatigue, and coughFrom the collection of Massachusetts General Hospital radiology images [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan (coronal view) showing liver abscess in a 46-year-old man who presented with fever, fatigue, and coughFrom the collection of Massachusetts General Hospital radiology images [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan (coronal view) showing liver abscess in a 46-year-old man who presented with fever, fatigue, and coughFrom the collection of Massachusetts General Hospital radiology images [Citation ends].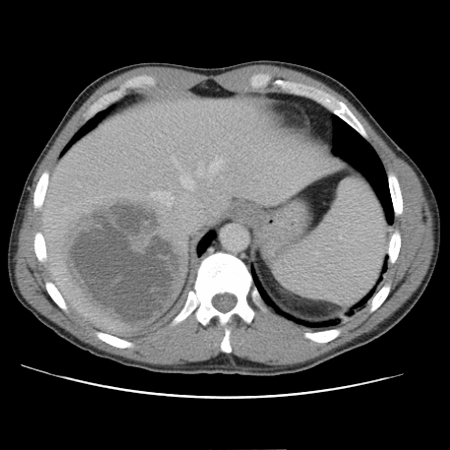
Result
demonstrates hypodense liver lesions
Gram stain and culture of aspirated abscess fluid
Test
Sampling should be avoided if there is evidence of abnormal coagulation or if hydatid is suspected.
Culture of abscess material is positive in around two-thirds of the patients with liver abscess.[3][4][15][18] Direct culture of aspirated material is preferred to culture obtained through a drainage catheter.[35]
Result
pyogenic: positive for causative bacterial organism; fungal: may be positive for causative fungal species
Investigations to consider
CXR
Test
Indicated only if there are any chest symptoms or signs on examination (e.g., symptoms suggestive of diaphragmatic irritation or signs of pleural effusion).
Result
in the presence of pleural effusion: blunting of the costophrenic angles
serum antibody test for Entamoeba histolytica
Test
Performed if amoebiasis is suspected.
Test remains positive for years after an infection.
Result
positive in amoebiasis
stool Entamoeba histolytica antigen detection test
Test
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) performed in people with suspected amoebiasis with diarrhoea.
Result
positive in amoebiasis
antigen testing or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of aspirated abscess fluid
Test
Aspiration of the lesion confirms the diagnosis of amoebic abscess, but it may not be necessary. The aspirate is typically a red-brown viscous fluid ('anchovy paste' or 'chocolate sauce').[20]
Antigen detection or positive PCR on liver abscess pus is definitive for diagnosis of amoebic liver abscess.
Molecular diagnostic tests are typically performed at reference laboratories.
Result
positive for antigen or amplification of amoebic DNA
liver MRI
Test
More sensitive than abdominal CT for detecting small abscesses.[20]
Expensive test, requiring intravenous administration of gadolinium, and may be limited in availability.
Result
low signal intensity on T1-weighted images; high signal intensity lesions on T2-weighted images
CRP
Test
Elevated CRP suggests an inflammatory process but is non-specific.[28]
Result
can be used to monitor adequate response to therapy
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer