Investigations
1st investigations to order
immunoglobulin A-tissue transglutaminase (IgA-tTG)
Test
Order an IgA-tTG test in any patient with suspected coeliac disease.[68]
Higher titres have increased positive predictive value. Serological testing should be done on a gluten-containing diet.[110][111]
Result
titre above normal range for laboratory; however, a normal titre does not exclude coeliac disease, as seronegative coeliac disease occurs in a minority of patients
quantitative IgA
IgG DGP (deamidated gliadin peptide)
Test
Test of choice for individuals with IgA deficiency.[73]
Result
elevated titre; however, normal titres do not rule out coeliac disease
FBC
Test
Iron deficiency anaemia is a common clinical presentation in adults.
Folate (and rarely vitamin B12) deficiency may lead to macrocytic anaemia.[87]
Result
low Hb and microcytic hypochromic red cells
endomysial antibody (EMA)
Test
EMA is an alternative to IgA-tTG with greater specificity but lower sensitivity.
Perform initially if IgA-tTG is unavailable.
Result
elevated titre
skin biopsy
Test
Order this test initially in any patient with skin lesions suggestive of dermatitis herpetiformis.
Both sensitivity and specificity are high, if normal-appearing skin adjacent to a lesion is biopsied.
Result
granular deposits of IgA at the dermal papillae of lesional and perilesional skin by direct immunofluorescence
small bowel endoscopy
Test
The endoscopic appearance is not sensitive for diagnosis and may be normal in up to one third of cases at diagnosis.[113][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Scalloping of the duodenal mucosa in a patient with coeliac diseaseFrom the personal collection of DA Leffler; used with permission [Citation ends].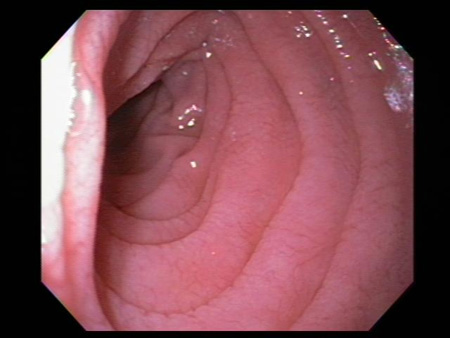 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Scalloping of the duodenal mucosa in a patient with coeliac diseaseFrom the personal collection of DA Leffler; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Scalloping of the duodenal mucosa in a patient with coeliac diseaseFrom the personal collection of DA Leffler; used with permission [Citation ends].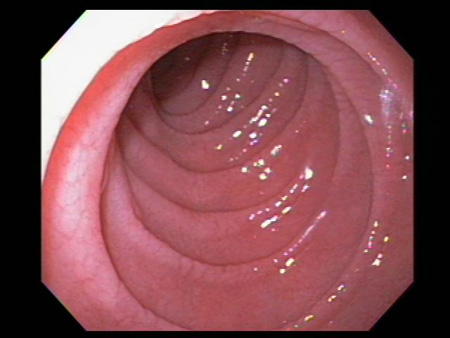
Result
atrophy and scalloping of mucosal folds; nodularity and mosaic pattern of mucosa
small bowel histology
Test
Small bowel histology is essential and the gold-standard test to confirm the diagnosis.
Biopsies should be performed while on a gluten-containing diet. Patients with an elevated IgA-tTG level should be referred for duodenal biopsy. Small intestinal biopsies should be obtained regardless of the IgA-tTG result in patients with a high clinical index of suspicion.[75]
Two biopsies of the duodenal bulb and at least four biopsies of the distal duodenum should be submitted for histological analysis.
A single biopsy specimen should be collected with each pass of the forceps, to improve the diagnostic quality of the specimens.[34]
Biopsy results are commonly graded using the Marsh criteria.
Result
presence of intra-epithelial lymphocytes, villous atrophy, and crypt hyperplasia
Investigations to consider
human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing
Test
May be used to rule out coeliac disease in patients already on a gluten-free diet or in patients with an idiopathic coeliac-like enteropathy but is only helpful for diagnosis in select cases, such as when there is discrepancy between serological and histological findings.[73]
Result
positive HLA-DQ2 or HLA-DQ8
gluten challenge
Test
People with coeliac disease on a gluten-free diet prior to evaluation cannot be differentiated from healthy controls. In these patients, gluten challenge is necessary. In a gluten challenge, the person is placed back on a gluten-containing diet (at least two slices of wheat bread daily), and serological tests and small bowel histology assessed after 2-8 weeks on the gluten-containing diet.[81][82]
Result
increase in coeliac serological tests and presence of intra-epithelial lymphocytes, villous atrophy, and crypt hyperplasia on small intestinal biopsy
video capsule endoscopy
Test
Video capsule endoscopy enables imaging of the entire small intestine and has good sensitivity for the detection of macroscopical features of coeliac disease. In 3% of cases, villous atrophy is only found in the jejunum, reducing the yield of upper endoscopy and duodenal biopsies for diagnosis.[114]
Capsule endoscopy is, however, typically used to detect complications of coeliac disease, such as ulcerative jejunitis or lymphoma.[79][80]
Video capsule endoscopy is not recommended when a stricture is suspected.
Result
atrophy and scalloping of mucosal folds; nodularity and mosaic pattern of mucosa; sensitive for the detection of villous atrophy
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer