Investigations
1st investigations to order
plain x-rays (anteroposterior [AP] pelvis and AP and lateral hip)
Test
First-line imaging study.
Should be obtained following initial evaluation for most acute and chronic presentations of hip pain.
Result
signs of femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) or dysplasia, including cam and pincer impingement; abnormal bone morphology; also shows fracture; dislocation, degenerative joint space narrowing, arthritic changes, lytic or destructive bony lesions
Investigations to consider
ultrasound of the hip
Test
Real-time examination, making it possible to combine imaging with movement, palpation, and tenderness. Very helpful with therapeutic or diagnostic injections.
Result
soft-tissue injuries and other changes, inflammation (with Doppler), bursitis, tendinopathy, enthesopathy, snapping tendon, hip joint effusion, pathology in or around the inguinal canal
MRI of the hip
Test
Study of choice for diagnosing or excluding stress fractures, osteomyelitis, or early-stage osteonecrosis. The reported sensitivity of this modality varies widely (47% to 91%).[17][19]
Clinical correlation is vital.
Labral pathology may be incidental finding.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI demonstrating inferior right femoral neck stress fracture (compression-sided)From the collection of Cedric J. Ortiguera, MD [Citation ends].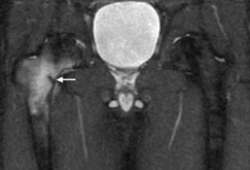 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Osteonecrosis of the right femoral head seen on MRIFrom the collection of Cedric J. Ortiguera, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Osteonecrosis of the right femoral head seen on MRIFrom the collection of Cedric J. Ortiguera, MD [Citation ends].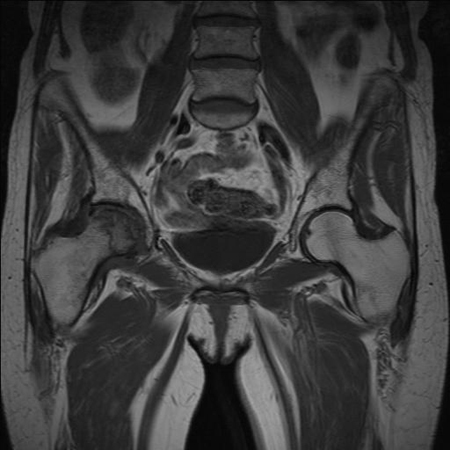
Result
soft-tissue injuries, bone abnormalities including malignancy, and stress fracture
MRI arthrogram of the hip
Test
Most sensitive non-invasive test available to identify labral tears.[17]
Result
intra-articular pathology including labral, cartilage, and ligamentum teres pathology
CT of the hip
Test
Study of choice for demonstrating bony anatomy of the pelvis and proximal femur in the setting of fracture, dislocation, or osseous lesion. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Metastatic lesion of the femoral neck seen on CTFrom the collection of Cedric J. Ortiguera, MD [Citation ends].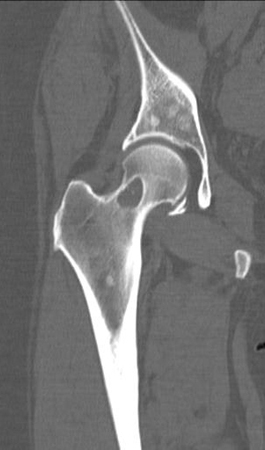
Result
fractures, dislocation, or infiltrative bone lesions
isotope bone scan of the hip
Test
Sensitive but non-specific measure of abnormal metabolic activity in the setting of infectious, repair, inflammatory, or malignant process.
Can in some cases be used as an alternative to MRI or CT if these are contraindicated or not available.
Result
increased uptake of isotope in case of increased metabolic uptake, reflecting a number of entities
intra-articular injection corticosteroid ± local anaesthetic agent
Test
Only intra-articular lesions will have relief from this therapeutic trial.
Should only be performed under image guidance by trained radiologist or orthopaedic surgeon.
Result
subjective pain relief
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer