Investigations
1st investigations to order
plain x-ray
Test
The radiographs of affected pagetoid bone have a classical appearance, with coarsened trabecular pattern, thinned cortices, and disruption of the trabecular/cortical interface. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: X-ray of Paget's disease of proximal femurFrom the collection of Camilo Restrepo, Rothman Institute, Philadelphia, PA [Citation ends].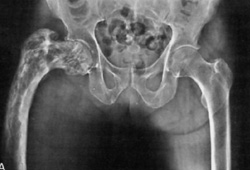 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: X-ray of Paget's disease of the tibiaFrom the collection of Camilo Restrepo, Rothman Institute, Philadelphia, PA [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: X-ray of Paget's disease of the tibiaFrom the collection of Camilo Restrepo, Rothman Institute, Philadelphia, PA [Citation ends].
Pelvis, long bones, and skull are most common sites of abnormal bone.
Complete fractures are unusual unless there has been a slight trauma on an already compromised bone.
X-rays are used for initial evaluation and for follow-up.[28]
Result
early stage: mostly lytic changes, commonly seen in the skull; advancing V-shaped lytic lesion in the long bones; occasional fractures, mostly incomplete; later stage: sclerotic picture predominates over osteolytic
bone scan
Test
Bone scans (e.g., scintigram) are non-specific.
Technetium (Tc-bisphosphonate) scans are most commonly used as a screening tool to identify additional asymptomatic areas of involved bone during the evaluation of patients with PDB diagnosed by plain films.[3][30] However, in the first osteolytic stage, bone scans may be negative because of the low uptake of isotope.[29]
Serial Tc-bisphosphonate scans are not recommended except to monitor response to treatment, though treatment reduces radionuclide uptake in pagetic lesions.[28][31]
Result
areas of intense uptake in pagetoid bone; may identify all areas involved and often picks up non-symptomatic regions
total serum alkaline phosphatase
bone-specific alkaline phosphatase
Test
Is a more sensitive blood test for diagnosis, and can also be used as an index for treatment response.[34]
Result
>40 international units/L
serum calcium
Test
Usually normal but, rarely, hypercalcaemia (>2.75 mmol/L [11 mg/dL]) may be encountered in patients with PDB, particularly after prolonged bed rest. Most commonly, hypercalcaemia is associated with primary hyperparathyroidism.
Result
normal (2.20 to 2.57 mmol/L [8.8 to 10.3 mg/dL])
serum procollagen 1 N-terminal peptide (P1NP)
Test
Used as a marker of bone formation, as well as an index for treatment response.
Result
initially elevated; treatment may normalise values
serum C-terminal propeptide of type 1 collagen (CTX)
Test
Used as a marker of bone resorption, as well as an index for treatment response.
Result
initially elevated; treatment may normalise values
liver function tests
Test
Monitor for liver disease possibly causing an increased alkaline phosphatase.
Result
normal
serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D
Test
Used to exclude vitamin D deficiency and osteomalacia as a potential cause for increased alkaline phosphatase.
Result
normal
Investigations to consider
CT scan or MRI
bone biopsy
Test
The most sensitive and specific test for diagnosis.
In weight-bearing long bones like the femur, diagnostic biopsy should be avoided because of the risk of fracture in an already compromised bone.[36]
Result
presence of osteoclasts with multiple nuclei; wide canaliculi with disorganised matrix in bone; a mosaic pattern of poorly organised lamellar bone
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer