Investigations
1st investigations to order
nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT)
Test
Non-culture testing using NAATs is generally considered the most robust method for testing, but clinicians should use the approved local diagnostic method.[26][51] In the US, the Association of Public Health Laboratories and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend NAATs for the detection of genital tract infections with gonorrhoea without routine repeat testing for positive results.[26][50][53]
Useful for urine, urethral, cervical, and vaginal specimens. However, in the US it is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in non-genital sites (pharyngeal and rectum). Individual laboratories can perform NAATs at non-genital sites if they satisfy regulations for Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments compliance before reporting results.[50][53]
Most sensitive method to detect gonorrhoea but has less than 100% specificity, particularly with pharyngeal and rectum specimens.
Samples for NAATs can be collected by the clinician/healthcare provider or the patient (self-collected).[26][52] Self-collected specimens sent for NAATs have been found to be non-inferior to clinician-collected specimens, although local laboratory validation of this collection method should be conducted.[54][55]
A NAAT for chlamydial infection is also recommended.[26]
Result
positive for gonorrhoea
culture
Test
Urethral, endocervical, rectal, pharyngeal, blood, synovial fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, or conjunctival specimen can be used.
Definitive diagnostic test but has deficiencies in sensitivity with pharyngeal and rectal sites: sensitivity of culture for the pharynx is about 50%.[63]
It is the only available method to test for antimicrobial sensitivities.
In the US, culture had been the only Food and Drug Administration-approved method for testing rectum and pharyngeal specimens, and it may be the only available option in some regions, but some NAAT platforms are now approved for these non-genital sites.[26]
Culture of swabs for chlamydial infection may also be requested.
Result
positive chocolate agar culture
urinalysis in men
Test
Useful if the patient has no urethral discharge.
Provides a presumptive diagnosis of urethritis and guides differential and further investigation.[26]
Result
positive leukocyte esterase
Gram stain of urine sediment
Test
Useful if the patient has no urethral discharge.
Confirms urethritis and guides differential and further investigation.
Strongly suggests gonorrhoea if organism seen. But does not rule out gonorrhoea if organisms not seen.[64]
Result
≥10 WBC per high-power field or ≥2 WBC per oil immersion field; intracellular gram-negative diplococci in polymorphonuclear leukocytes
Gram stain of urethral discharge
Test
Confirms urethritis and guides differential and further investigation.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Photomicrograph revealing the histopathology in an acute case of gonococcal urethritis using gram-stain techniqueUS Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/ Joe Millar [Citation ends].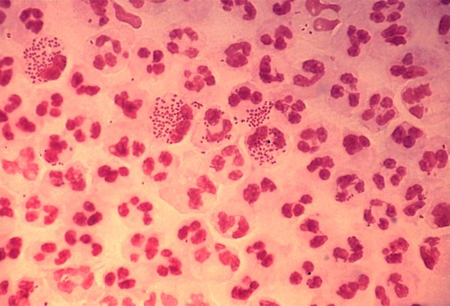
Strongly suggests gonorrhoea if organism seen. But does not rule out gonorrhoea if organisms not seen.[64]
Result
intracellular gram-negative diplococci in polymorphonuclear leukocytes
HIV test
Test
Routine to rule out HIV. Time to HIV seropositivity with a third-generation enzyme immunoassay can be >21 days.
Result
may be positive
syphilis test
Test
Routine to rule out syphilis. A Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test or serum rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test can take up to 3 months to become positive. Some laboratories may perform a reverse sequence screening algorithm that uses a serological test before the RPR.
Result
may be positive
Investigations to consider
transvaginal ultrasound
Test
Highly specific for pelvic inflammatory disease. Useful in presence of chronic ascending infection resulting in tubo-ovarian abscess.
Result
thickening of endometrium or tubes; fluid in the tubes or abscess
pelvic CT/MRI
Test
Highly specific for pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). When diagnosis of PID is uncertain or ultrasound is equivocal, either a CT or MRI may be performed, if available.
Result
inflammatory changes of fallopian tubes and ovaries; abnormal fluid collection; thickened ligaments
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer