Differentials
Your Organisational Guidance
ebpracticenet urges you to prioritise the following organisational guidance:
Acute KeelpijnPublished by: Werkgroep Ontwikkeling Richtlijnen Eerste Lijn (Worel)Last published: 2017Mal de gorge aiguPublished by: Groupe de Travail Développement de recommmandations de première ligneLast published: 2017Epiglottitis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Severe and acute onset of sore throat and fever.
Notable change in the quality of the voice to a muffled texture.
Drooling of saliva from the mouth.
Tripod or sniffing posture in children.
INVESTIGATIONS
Direct visualisation of the epiglottis (under controlled circumstances in the operating room, with the immediate capability of intubation should the airway close), or lateral neck x-rays.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Lateral neck film demonstrating epiglottitisFrom Dr Petri's personal collection; used with permission [Citation ends].
Retropharyngeal, peritonsillar, and lateral abscess
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Sore throat, fever, neck pain, and muffled voice.
Most common in children aged 2-4 years.
May be associated with history of oral or pharyngeal trauma in older children.
INVESTIGATIONS
Imaging studies of the neck may be required to visualise the abscess.
Infectious mononucleosis
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Pharyngitis of longer than several days' duration.
Adenopathy and splenomegaly.
INVESTIGATIONS
Serum monospot positive for Epstein-Barr virus infection.
Atypical lymphocytes in peripheral blood.
Diphtheria
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Pharyngitis with grey membrane adherent to the pharynx.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Typical pseudomembrane of diphtheria pharyngitisCopyright Department of Paediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, Princess Margaret Hospital, Hong Kong; used with permission [Citation ends].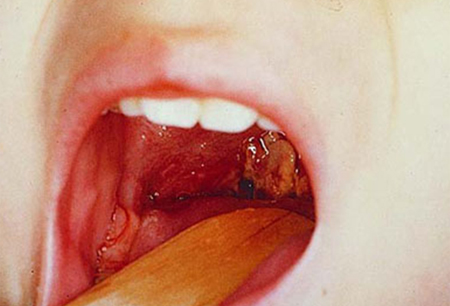
Rarely seen except in low- and middle-income countries or unvaccinated populations.
INVESTIGATIONS
Culture recovery of organism.
Lemierre's syndrome
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Thrombophlebitis of the jugular vein, with a mixed anaerobic abscess.
Typically present in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) or sepsis.
INVESTIGATIONS
Imaging studies of the neck demonstrate abscess.
Measles
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Systemic infection with conjunctivitis, rhinorrhoea, cough, and characteristic exanthema (maculopapular rash).
Pharyngitis appears during the exanthematous phase.
Koplik spots (bluish-white, raised lesions on an erythematous base on the buccal mucosa) are pathognomonic.
INVESTIGATIONS
Anti-measles IgM, viral culture, or polymerase chain reaction: positive.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Close contact with a confirmed or probable case of COVID-19, in the 14 days prior to symptom onset.
May have other symptoms including cough, gastrointestinal symptoms, or systemic symptoms including fever.
However, patients may present with mild symptoms or sore throat in isolation.
INVESTIGATIONS
Real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR): positive for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA.
Behcet syndrome
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Vesicles on the pharynx, genital ulcers, skin lesions, and eye lesions.
INVESTIGATIONS
Laboratory testing and imaging are not useful in making the diagnosis of Behcet syndrome, but do play a role in ruling out alternative diagnoses.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Preceding drug history of anticonvulsant use, recent infections, seizures, or new medications.
Vesicles on the pharynx along with more pronounced mucosal changes.
INVESTIGATIONS
Diagnosis is made by clinical presentation and confirmed with skin biopsy.
Kawasaki disease
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Typical signs include fever longer than 5 days, polymorphic rash, injected eyes (conjunctivitis), large unilateral cervical adenopathy, and mucosal erythema with strawberry tongue.
Diffuse inflammation of oral mucosa.
INVESTIGATIONS
Diagnosis is made by clinical presentation.
Coronary artery aneurysms may be present on echocardiography.
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Common childhood viral infection caused most often by coxsackievirus A16.
Usually a mild illness characterised by low-grade fever, painful oral ulcers, and vesicles on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
INVESTIGATIONS
Elevated WBC count, atypical lymphocytes.
Polymerase chain reaction molecular assay is an emerging diagnostic modality.
Oropharyngeal cancer
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Hoarseness, dysphonia, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, vocal cord lesions on indirect laryngoscopy, and neck mass or adenopathy.
INVESTIGATIONS
CT of the neck may be diagnostic and is essential to evaluate the extent of disease.
Cytological analysis of fine needle aspirate may establish the diagnosis, although biopsy is usually required.
Aphthous ulcers
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Multiple recurrent small, erythematous, round or ovoid ulcers with circumscribed margins, typically presenting first in childhood or adolescence.
INVESTIGATIONS
Diagnosis is based on the history and clinical examination, with exclusion of a systemic aetiology; there are no specific laboratory findings.
Periodic Fever, Aphthous Stomatitis, Pharyngitis, and Adenitis (PFAPA) syndrome
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Recurrent fevers associated with pharyngitis, aphthous ulcers, and adenitis.
INVESTIGATIONS
History of frequent recurrence (every 2-6 weeks) with spontaneous resolution.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer