Investigations
1st investigations to order
CXR
Test
Most patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis have an abnormal CXR at presentation.[44]
Some patients may present with mild or even absent symptoms subsequent to a CXR obtained for other reasons.
CXR is of use in evaluating alternative diagnoses, especially in acute exacerbations.[47][48]
Result
basilar, peripheral, bilateral, asymmetrical, reticular opacities
high-resolution CT (HRCT) chest
Test
Should be ordered in all patients with a suspected diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).[47][48][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest computed tomography scan image of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosisFrom the collection of Jeffrey C. Munson, MD, MS; used with permission [Citation ends].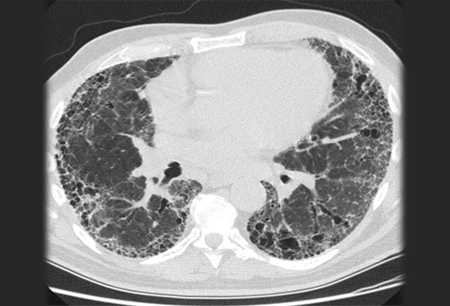
Can increase the level of diagnostic confidence for IPF and, in certain situations, obviate the need for surgical lung biopsy.[5]
HRCT should be categorised by the certainty that findings represent an underlying pathology of usual interstitial pneumonia.[1][5][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest computed tomography scan image of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosisFrom the collection of Jeffrey C. Munson, MD, MS; used with permission [Citation ends].
If honeycombing is absent but other features are present, the HRCT represents probable usual interstitial pneumonia.[5] The diagnostic sensitivity (71% to 90%), specificity (64% to 95%), and positive predictive value (79% to 100%) of HRCT for IPF depend on the level of certainty reported by the interpreting radiologist.[1]
Diagnosis usually requires multi-disciplinary evaluation.[44]
Result
basilar- and subpleural-predominant areas of increased reticulation, honeycombing, and possible traction bronchiectasis or bronchiolectasis
pulmonary function tests
Test
Can support the diagnosis by showing a restrictive pattern of reduced forced vital capacity and reduced total lung capacity.
An isolated decrease in the lung diffusion capacity test may be seen early in the disease or if there is concomitant airway disease (i.e., COPD).
Result
restrictive changes
Investigations to consider
surgical lung biopsy
Test
A crucial component in the evaluation of patients in whom the history, clinical evaluation, and high-resolution CT findings do not support a clear diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Pathology slide of usual interstitial pneumonia, the characteristic biopsy appearance of a patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosisFrom the collection of Gregory Tino, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].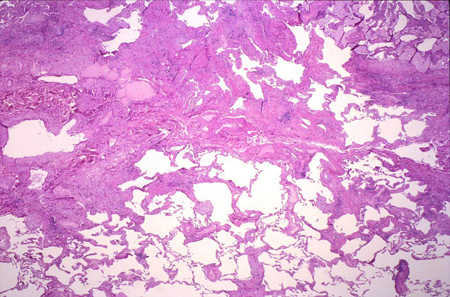
Usually by video-assisted thoracoscopy.
Although all patients with IPF should have changes typical of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) on biopsy, not all patients with UIP on biopsy have IPF.
Multiple samples, preferably from at least two distinct anatomical sites, are typically required to confidently diagnose UIP.
Result
fibrosis of varying ages; areas of normal lung next to areas of honeycombing; areas of more active scar formation, including fibroblastic foci; interstitial inflammation typically mild to moderate and patchy
bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)
Test
The diagnostic value of BAL in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is limited. It is not recommended in patients with a high-resolution CT that demonstrates a usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) pattern.[5]
If a confident UIP pattern cannot be identified on high-resolution CT imaging, BAL for differential cell count may be a useful adjunct, as specific patterns such as an isolated elevation of lymphocytes (>40%) are unusual in IPF and suggest alternate diagnoses such as chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis.[5][50]
Result
normal
trans-bronchial lung biopsy and cryobiopsy
Test
Trans-bronchial lung biopsy (TBLB) may have a role when the clinical evaluation suggests an alternative diagnosis, centrilobular zones are involved, or the pathology is not complex (e.g., carcinomatous lymphangitis, sarcoidosis, organising pneumonia, and diffuse alveolar damage).[51]
Although traditional TBLB has a poor diagnostic yield due to small specimens, sampling errors, and crush artefacts, the use of genomic classifiers on TBLB specimens may improve its clinical utility.[52][53]
Trans-bronchial lung cryobiopsy (TBLC) is an acceptable alternative, provided there is clinical expertise in both performing and interpreting the investigation.[5][51]
Diagnostic yields are estimated at 80% with trans-bronchial biopsy compared with 90% for surgical biopsy; risks of pneumothorax and bleeding are similar.[58]
Result
fibrosis of varying ages; areas of normal lung next to areas of honeycombing; areas of more active scar formation, including fibroblastic foci; interstitial inflammation typically mild to moderate and patchy
CRP
Test
Although commonly observed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), elevations in CRP are rarely practice-changing.
Use of CRP in the management of IPF merits further investigation.
Result
normal or mildly elevated
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Test
Although commonly observed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), elevations in ESR are rarely practice-changing.
Use of ESR in the management of IPF merits further investigation.
Result
normal or mildly elevated
anti-nuclear antibody immunofluorescence
Test
Mildly elevated titres may occur in 10% to 20% of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Titres of >1:160 suggest the possibility that a collagen vascular disease might be responsible for the interstitial lung disease.
Result
normal or mildly elevated
rheumatoid factor
Test
Mildly elevated titres may occur in 10% to 20% of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Titres of >1:160 suggest the possibility that a collagen vascular disease might be responsible for the interstitial lung disease.
Result
normal or mildly elevated
anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide
Test
The presence of circulating anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies suggests that a collagen vascular disease might be responsible for the interstitial lung disease.
Result
normal
myositis panel
Test
The presence of myositis-specific antibodies suggests that a collagen vascular disease might be responsible for the interstitial lung disease.
Result
normal
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer