Investigations
1st investigations to order
12-lead ECG
Test
ECG should be recorded in any patients with suspected supraventricular arrhythmia. Intermittent pre-excitation is defined by the electrocardiographic presence of QRS complexes with pre-excitation intermingled with narrow QRS complexes due to conduction solely via the atrioventricular (AV) node (without pre-excitation). Sometimes, pre-excited QRS complexes alternate with the narrow QRS complex because of a long refractory period of the accessory pathway (AP). Intermittent pre-excitation indicates that the AP is incapable of conduction to the ventricle fast enough to pose a risk for ventricular fibrillation during rapid atrial arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation or flutter. An algorithm of delta wave polarity in 12-lead ECG or during antidromic tachycardia has been developed.
Twelve-lead ECG at baseline shows no delta waves and short RP tachycardia during the clinical arrhythmia in AV nodal re-entrant tachycardia.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A simplified algorithm for localising an accessory pathwayFrom the collection of Dr Mithilesh K. Das [Citation ends].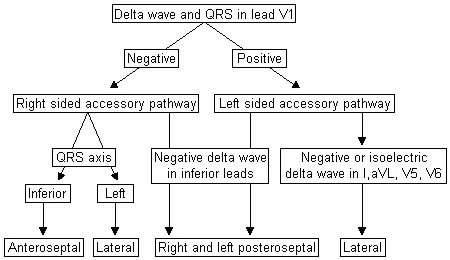 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Intermittent pre-excitationFrom the collection of Dr Mithilesh K. Das [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Intermittent pre-excitationFrom the collection of Dr Mithilesh K. Das [Citation ends].
Result
delta waves signify presence of an antegradely conducting AP; no delta waves can mean a concealed retrograde-only AP or an AP with intermittent pre-excitation
Investigations to consider
echocardiogram
Test
Risk of associated heart disease is 7% to 20%.
Result
associated structural heart disease such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Ebstein's anomaly and other congenital heart disease
treadmill exercise test
Test
An indicator of a low risk of sudden cardiac death is the disappearance of pre-excitation during exercise due to a long anterograde refractory period of the accessory pathway (AP).[17] Sympathetic stimulation occurring during exercise shortens the refractory period of the AP and if the refractory period of the AP is reached, then the conduction down the AP is blocked. This indicates that during atrial fibrillation, conduction down the AP will not be fast enough to cause ventricular fibrillation.
Result
intermittent pre-excitation or sudden disappearance of pre-excitation
electrophysiology study
Test
Risk stratification is performed invasively by programmed electrical stimulation with intracardiac recordings or with semi-invasive atrial stimulation by trans-oesophageal route.[17][18][19]
Result
location and physiology of the accessory pathway (AP); number of APs; antegrade conduction properties of the AP; presence or absence of inducible tachycardia
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer