History and exam
Your Organisational Guidance
ebpracticenet urges you to prioritise the following organisational guidance:
Cliquez ici pour les guides de pratique clinique sur l'otite moyenne aiguë et leur mise en œuvre dans le contexte belgePublished by: ebpracticenet adminLast published: 2024Acute otitis media (NL versie)Published by: ebpracticenet adminLast published: 2024Key diagnostic factors
common
presence of risk factors
Key factors include young age, possible exposure to respiratory viruses (e.g., day care attendance, older siblings), positive family history, and Native American or Native Alaskan ethnicity.
otalgia
preceding upper respiratory symptoms
Upper respiratory infection symptoms may be ongoing or resolving and are non-specific.
bulging tympanic membrane
A purulent middle ear effusion and a tympanic membrane with a loss of landmarks, splayed or attenuated light reflex, and characteristic bagel or doughnut appearance (evidence of positive pressure) is pathognomonic.[19][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Otoscopy appearance of a bulging, erythematous tympanic membrane and absent landmarksFrom the personal collection of Dr Armengol [Citation ends].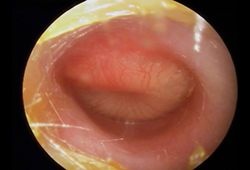 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Purulent middle ear effusion and tympanic membrane with a loss of landmarks and characteristic bagel or doughnut appearanceFrom the personal collection of Dr Armengol [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Purulent middle ear effusion and tympanic membrane with a loss of landmarks and characteristic bagel or doughnut appearanceFrom the personal collection of Dr Armengol [Citation ends].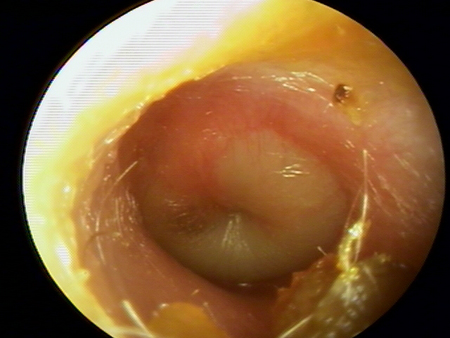
myringitis
Erythema of the tympanic membrane is non-specific and may be present with crying, fever, and other otological conditions such as otitis media with effusion, otitis externa, and tympanic membrane retraction.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Otoscopy of myringitis, showing erythema and injection of the tympanic membrane in the neutral positionFrom the personal collection of Dr Armengol [Citation ends].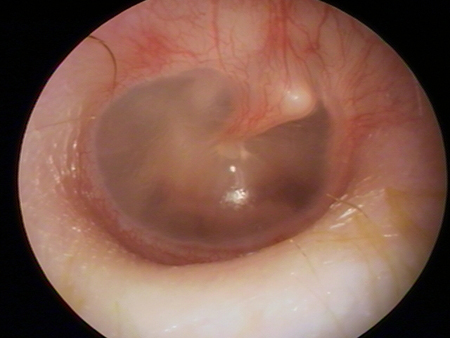
Other diagnostic factors
common
irritability
Irritability is a non-specific symptom common in younger children. Younger patients may cry inconsolably.
sleep disturbance
Restless sleep is a non-specific symptom.
fever
Fever is a non-specific sign.
uncommon
decreased appetite
Decreased appetite is a non-specific symptom.
Risk factors
strong
day care attendance
older siblings
young age
family history
Observational studies have linked this non-modifiable risk factor to the development of the condition.
Native American or Native Alaskan
Observational studies have linked this non-modifiable risk factor to the development of the condition.[17]
absence of breastfeeding
supine feedings (bottle propping)
Observational studies have linked supine feeding to the development of AOM.[1] It is not clear whether modifying this risk factor would decrease the risk of developing the condition.
lower socioeconomic status
craniofacial anomaly
Children with anatomical anomalies (e.g., cleft palate, cleft uvula) encounter more AOM than their peers.
immunological deficiency
Children with immunological deficiencies encounter more AOM than their peers.
weak
male sex
dummy use
Observational studies have linked dummy use to the development of AOM.[18] It is not clear whether modifying this risk factor would decrease the risk of developing the condition.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer