Criteria
Flow convergence method or proximal isovelocity surface area (PISA)
Flow convergence method or PISA involves looking at the colour images on the left ventricular side of the mitral regurgitant images.[17][18][19] This flow convergence zone is the location where the blood is accelerating to go across the regurgitant orifice, as it undergoes a pressure drop from left ventricular pressure to left atrial pressure. With this area of flow acceleration, colour Doppler tracks the location of increases in velocity and shows this as a proximal zone of colour aliasing. Analysis of this convergence zone when its shape is hemispheric allows estimation of the surface area of the hemisphere, which is derived from a measurement of the radius (R) and the aliasing velocity (V), numerically extracted from the colour bar reflecting machine settings. When this is combined with the maximum velocity, the size of the regurgitant orifice can be calculated according to the formula 2PiR²V divided by maximum velocity through the valve obtained by continuous-wave Doppler. The advantage of this formula is that it calculates the actual size of the regurgitant lesion, a fundamental parameter of valve integrity, which may be less load-dependent than other methods.
Severity
A regurgitant orifice area >0.4 cm² is indicative of severe regurgitation, whereas <0.2 cm² is considered mild.
A regurgitant fraction of <30% is considered mild and >50% is considered severe.
A regurgitant volume of <30 mL is considered mild and >60 mL is considered severe.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Apical 4-chamber view of 1-2+ posteriorly directed mitral regurgitationFrom the collection of Samir Kapadia and Mehdi H. Shishehbor [Citation ends].
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Apical 4-chamber view of 4+ (severe) mitral regurgitation and a large proximal isovelocity surface areaFrom the collection of Samir Kapadia and Mehdi H. Shishehbor [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Apical 4-chamber view of 4+ (severe) mitral regurgitation and a large proximal isovelocity surface areaFrom the collection of Samir Kapadia and Mehdi H. Shishehbor [Citation ends].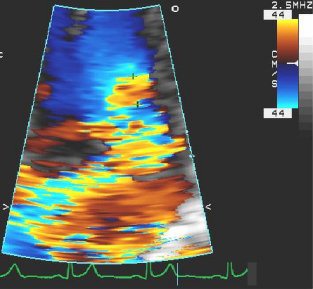 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Apical 4-chamber view of severe MR with proximal isovelocity surface areaFrom the collection of Samir Kapadia and Mehdi H. Shishehbor [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Apical 4-chamber view of severe MR with proximal isovelocity surface areaFrom the collection of Samir Kapadia and Mehdi H. Shishehbor [Citation ends].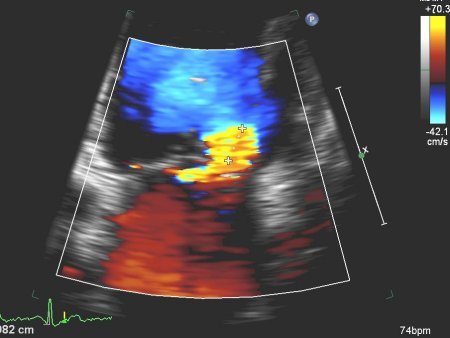
Colour Doppler jet area
Small central jet <4 cm² or <20% of the left atrial area is considered mild.
Vena contracta width >0.7 cm with large central jet is considered severe.
Doppler vena contracta width
<0.3 cm is considered mild.
>0.7 cm is considered severe.
Severity of symptoms: New York Heart Association classification
I - No symptoms and no limitation in ordinary physical activity (e.g., shortness of breath when walking, stair climbing).
II - Mild symptoms (mild shortness of breath and/or angina pain) and slight limitation during ordinary activity.
III - Marked limitation in activity due to symptoms, even during less than ordinary activity (e.g., walking short distances; 20-100 m). Comfortable only at rest.
IV - Severe limitations. Experiences symptoms even while at rest; mostly bed-bound patients.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer