Investigations
1st investigations to order
12-lead ECG
CXR
Test
Should be ordered immediately in any person presenting with shortness of breath.
Result
frequently reveals bilateral pulmonary infiltrates in the setting of myocarditis-induced CHF
serum CK
Test
Should be ordered immediately when evaluating anyone with suspected myocardial injury.
Result
often mildly elevated
serum CK-MB
Test
Should be ordered immediately when evaluating anyone with suspected myocardial injury.
Result
often mildly elevated
serum troponin (I or T)
serum B-type natriuretic peptide
Test
May be helpful in distinguishing primary cardiac from primary pulmonary aetiologies of dyspnoea when the physical examination and initial work-up is unclear or non-specific.[57] Is best used to support the history and physical examination.
Result
elevated in response to ventricular distention, such as occurs in CHF due to myocarditis
two-dimensional echocardiogram
Test
Should be ordered in every patient suspected of having myocarditis.[15][16][56][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Apical 4-chamber transthoracic echocardiogram in a patient with myocarditis. The right ventricle is dilated with hypokinesis. Triscupid regurgitation is present with a reduced continuous wave Doppler gradient indicating right ventricular failureFrom: Rasmussen TB, Dalager S, Andersen NH, et al. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.09.2008.0997 [Citation ends].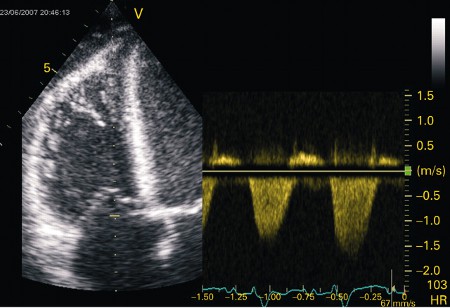 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Apical 4-chamber echocardiogram in a patient presenting with myocarditis showing a slightly dilated left ventricle with spontaneous ultrasonic contrast indicating severely impaired left ventricular systolic functionFrom: Rasmussen TB, Dalager S, Andersen NH, et al. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.09.2008.0997 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Apical 4-chamber echocardiogram in a patient presenting with myocarditis showing a slightly dilated left ventricle with spontaneous ultrasonic contrast indicating severely impaired left ventricular systolic functionFrom: Rasmussen TB, Dalager S, Andersen NH, et al. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.09.2008.0997 [Citation ends].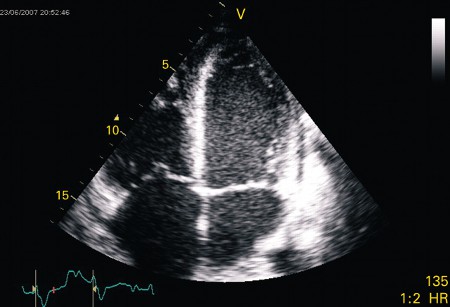
Result
global and regional left ventricular motion abnormalities and dilatation
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography (18F-FDG PET-CT)
Test
Helps diagnose myocarditis by providing metabolic information of inflammation as increased FDG uptake. The role of 18F-FDG PET-CT is useful in chronic myocarditis, where CMR does not have the same accuracy as in acute myocarditis.[68]
Result
detection of inflammation
Investigations to consider
endomyocardial biopsy (EMB)
Test
There is no general consensus on which aldult patients should undergo EMB; recommendations vary and local guidelines should be consulted.[5][55][57][58][59][63][64] A statement on dilated cardiomyopathies from the American Heart Association (AHA) recommends biopsy 'in those patients with clinically suspected unexplained acute myocarditis who require inotropic support or mechanical circulatory support and those with Mobitz type 2 second-degree or higher heart block, sustained or symptomatic ventricular tachycardia, or failure to respond to guideline-based medical management within 1-2 weeks'.[55] The 2022 AHA/American College of Cardiology/Heart Failure Society of America (HFSA) heart failure (HF) guidelines state 'endomyocardial biopsy may be advantageous in patients with heart failure in which a histological diagnosis, such as myocarditis, may influence treatment decisions'.[57] A joint statement from Heart Failure Association of European Society of Cardiology (ESC), HFSA, and Japanese HF Society recommends EMB 'in patients with fulminant/acute myocarditis presenting with cardiogenic shock or acute HF and left ventricular (LV) dysfunction, with or without malignant ventricular arrhythmias and/or conduction abnormalities'. They also recommend considering EMB in 'haemodynamically stable patients with clinical symptoms and diagnostic criteria (electrocardiographic abnormalities, elevated troponin levels, imaging findings) suggestive of myocarditis, in the absence of significant coronary artery disease'.[59]
The potential risks and benefits of EMB should always be carefully assessed, particularly during the acute presentation, as the risk of arrhythmia or ventricular perforation is highest at this time.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histological findings in a patient with giant cell myocarditis. A: severe myocardial necrosis and fibrotic replacement of the cardiomyocytes with granulation tissue and fibrosis is present in a section from the anterolateral left ventricular wall; B: a sharp demarcating border between vital and necrotic myocardium is seen, confirmed by additional immunohistochemical staining for myoglobin; C: at the inflammatory border, cells consisting of prominent multi-nucleated giant cells, macrophages, lymphocytes, and eosinophilic granulocytes are seen in close proximity to vital myocardium; D: immunohistochemical staining for complement 4d is positive in all vessels, suggestive of complement cascade activationFrom: Rasmussen TB, Dalager S, Andersen NH, et al. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.09.2008.0997 [Citation ends].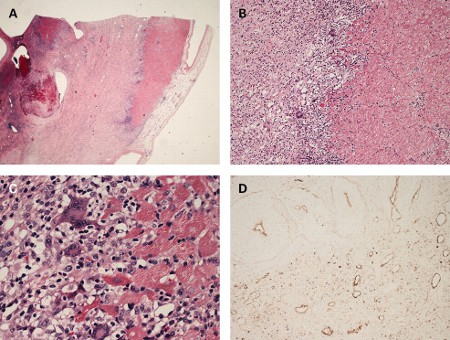 In children, AHA guidelines continue to mark biopsies as the reference test for myocarditis diagnosis.[15] It is important to note that with immunohistochemistry, the ability to assess for inflammatory cells has greatly increased. Additionally, the biopsies can be used for viral polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing to diagnose viral myocarditis with specificity, and to analyse immune-mediated injury and potentially inflammatory markers at a molecular level.[65]
In children, AHA guidelines continue to mark biopsies as the reference test for myocarditis diagnosis.[15] It is important to note that with immunohistochemistry, the ability to assess for inflammatory cells has greatly increased. Additionally, the biopsies can be used for viral polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing to diagnose viral myocarditis with specificity, and to analyse immune-mediated injury and potentially inflammatory markers at a molecular level.[65]
Result
histopathological findings of myocardial cellular infiltrates ± myocardial necrosis
coronary angiography
Test
Should be performed when the presenting symptoms and findings are indistinguishable from the acute coronary syndromes.
Result
normal or insignificant findings on coronary angiography are common in myocarditis and rule out MI
cardiac MRI
Test
Can be performed when trying to distinguish between myocarditis and ischaemic heart disease using typical findings on MRI.[16][56][60] In some cases, findings from cardiac MRI can also be useful in determining the aetiology of myocarditis.[66]
Lake Louise consensus criteria were updated in 2018 to propose that presence of both T2 and T1 findings provide strong evidence for myocardial inflammation.[67] The primary purpose of cardiac MRI in children is to identify myocardial injury, and to differentiate acute myocarditis from non-inflammatory cardiomyopathies.[15]
Result
global early enhancement suggests myocarditis where late gadolinium enhancement suggests myocardial ischaemia or scar; presence of concurrent pericardial thickening or inflammation
viral polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Test
Endomyocardial biopsies can be used for viral PCR testing to diagnose viral myocarditis with specificity.[65]
Result
positive for causative viral agent
Emerging tests
MRI-guided EMB
Test
Still in the developmental phase and requires validation in larger studies.
MRI-guided EMB is a promising new technology that appears to significantly increase the sensitivity of EMB in the diagnosis of myocarditis.[69]
Result
histopathological findings of myocardial cellular infiltrates ± myocardial necrosis
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer