Complications
Patient develops worsening nausea and vomiting.
Abdominal x-ray shows small bowel dilation.
Nasogastric tube insertion and supportive therapy is indicated until ileus resolves. Important to be watchful for perforation, peritonitis, and toxic megacolon.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the abdomen showing gross thickening of the large bowel wall and obliteration of the lumenYates B, Murphy CM, et al. Pseudomembranous colitis in four patients with cystic fibrosis following lung transplantation. BMJ Case reports. 2009; doi: 10.1136/bcr.11.2008.1218 [Citation ends].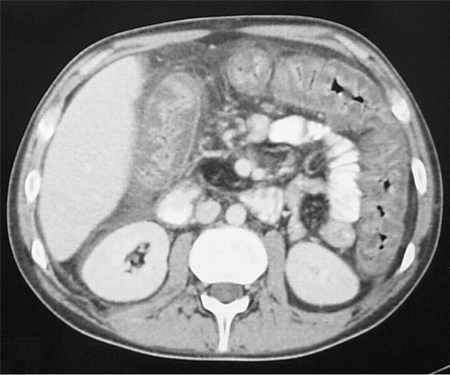 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the abdomen showing diffuse bowel thickening suggestive of colitisFrom the collection of Dr Ali Hassoun [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the abdomen showing diffuse bowel thickening suggestive of colitisFrom the collection of Dr Ali Hassoun [Citation ends].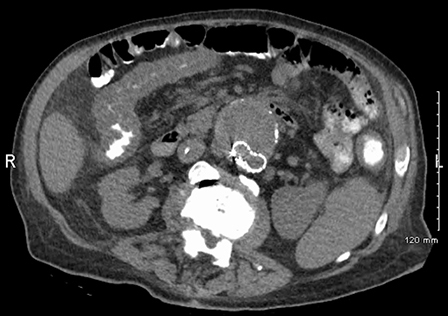
Patients present with acute abdomen, pain, and rebound tenderness. They have high fever and have hypotension and tachycardia.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the abdomen showing gross thickening of the large bowel wall and obliteration of the lumenYates B, Murphy CM, et al. Pseudomembranous colitis in four patients with cystic fibrosis following lung transplantation. BMJ Case reports. 2009; doi: 10.1136/bcr.11.2008.1218 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the abdomen showing diffuse bowel thickening suggestive of colitisFrom the collection of Dr Ali Hassoun [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the abdomen showing diffuse bowel thickening suggestive of colitisFrom the collection of Dr Ali Hassoun [Citation ends].
Supportive therapy, intravenous metronidazole, and rectal or nasogastric vancomycin should be given.
Laparotomy with colectomy may be required as an emergency.
Increased abdominal pain and distension, hypotension, tachycardia with significant colonic dilation.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the abdomen showing gross thickening of the large bowel wall and obliteration of the lumenYates B, Murphy CM, et al. Pseudomembranous colitis in four patients with cystic fibrosis following lung transplantation. BMJ Case reports. 2009; doi: 10.1136/bcr.11.2008.1218 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the abdomen showing diffuse bowel thickening suggestive of colitisFrom the collection of Dr Ali Hassoun [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the abdomen showing diffuse bowel thickening suggestive of colitisFrom the collection of Dr Ali Hassoun [Citation ends].
Patients may require intravenous, nasogastric, or rectal therapy with either metronidazole or vancomycin (or both).
In severe cases, colectomy may be necessary.[21]
Post-infection irritable bowel syndrome affects approximately 21% of patients. Diarrhoea-predominant and mixed were the most common subtypes.[144]
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer