Last reviewed: 16 Mar 2025
Last updated: 06 Feb 2025
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Other diagnostic factors
- fever
- abdominal tenderness
- nausea and vomiting
- abdominal distension
- symptoms of shock
Risk factors
- antibiotic exposure
- advanced age
- hospitalisation or residence in a nursing home
- exposure to infected family member
- history of Clostridioides difficile-associated disease
- use of acid-suppressing drugs
- inflammatory bowel disease
- solid organ transplant recipients
- haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients
- chronic kidney disease
- HIV infection
- immunosuppressive agents or chemotherapy
- gastrointestinal surgery
- vitamin D deficiency
- consumption of C difficile contaminated food
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- FBC
- stool guaiac (faecal occult blood test)
- stool polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- stool immunoassay for glutamate dehydrogenase
- stool immunoassay for toxins A and B
- abdominal x-ray
Investigations to consider
- cell culture cytotoxicity neutralisation assay
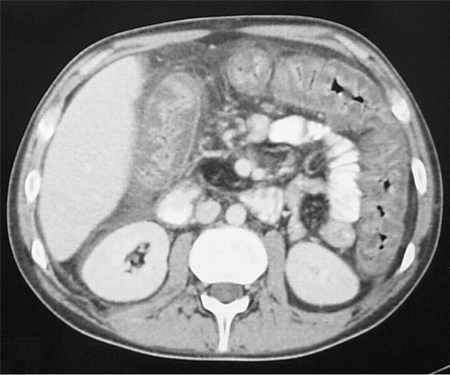
- CT abdomen
- sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Ali Hassoun, MD, FACP, FIDSA, AAHIVS
Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
Alabama Infectious Diseases Center
Huntsville
AL
Disclosures
AH declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Gregory R. Madden, MD, MSDS
Assistant Professor
Division of Infectious Diseases and International Health
University of Virginia School of Medicine
Charlottesville
VA
Disclosures
GRM declares that he has no competing interests.
Satish Keshav, MBBCh, DPhil, FRCP
Consultant Gastroenterologist
Department of Gastroenterology
John Radcliffe Hospital
Oxford
UK
Disclosures
SK declares that he has no competing interests.
Ian Beales, MD, FRCP
Clinical Reader and Consultant Gastroenterologist
Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital
Norwich
UK
Disclosures
IB declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer