Diagnosis of genital warts is made based on the clinical presentation of lesions located on the genital area, perianal region, or adjacent areas such as the mons pubis, with a tendency for genital wart formation to occur on areas of high friction.[3]Wiley DJ, Douglas J, Beutner K, et al. External genital warts: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Clin Infect Dis. 2002 Oct 15;35(Suppl 2):S210-24.
https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/35/Supplement_2/S210/316436
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12353208?tool=bestpractice.com
[17]Ahmed AM, Madkan V, Tyring SK. Human papillomaviruses and genital disease. Dermatol Clin. 2006 Apr;24(2):157-65.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16677964?tool=bestpractice.com
[40]Brodell LA, Mercurio MG, Brodell RT. The diagnosis and treatment of human papillomavirus-mediated genital lesions. Cutis. 2007 Apr;79(4 Suppl):5-10.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17508490?tool=bestpractice.com
[41]Steinberg JL, Cibley LJ, Rice PA. Genital warts: diagnosis, treatment, and counseling for the patient. Curr Clin Top Infect Dis. 1993;13:99-122.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7691082?tool=bestpractice.com
Biopsy is generally not performed for the diagnosis of genital warts.
Clinical presentation
Genital warts are usually 1 to 3 mm, discrete, sessile, smooth-surfaced exophytic papillomas or they may coalesce into larger plaques. These plaques may be extensive, with expansion into the urethra, or into the anal or vaginal canals.[3]Wiley DJ, Douglas J, Beutner K, et al. External genital warts: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Clin Infect Dis. 2002 Oct 15;35(Suppl 2):S210-24.
https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/35/Supplement_2/S210/316436
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12353208?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Venereal warts in the anal region of the perineumCDC/Dr Wiesner [Citation ends].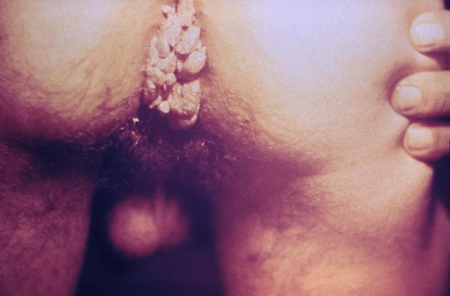 Colour varies from flesh-coloured to whitish to hyperpigmented. Maceration may occur, particularly in moist areas lacking the thick horny cell layer found in cutaneous warts.[5]Kirnbauer R, Lenz P, Okun MM. Human papillomavirus. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Rapini RP, eds. Dermatology Vol 1. London: Mosby; 2003:1217-33.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Wart on shaft of penisFrom Dr Tyring's personal collection; used with permission [Citation ends].
Colour varies from flesh-coloured to whitish to hyperpigmented. Maceration may occur, particularly in moist areas lacking the thick horny cell layer found in cutaneous warts.[5]Kirnbauer R, Lenz P, Okun MM. Human papillomavirus. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Rapini RP, eds. Dermatology Vol 1. London: Mosby; 2003:1217-33.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Wart on shaft of penisFrom Dr Tyring's personal collection; used with permission [Citation ends].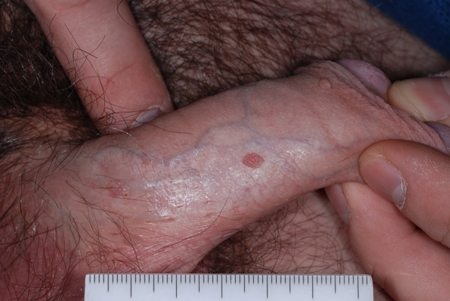 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Close-up of penile wartFrom Dr Tyring's personal collection; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Close-up of penile wartFrom Dr Tyring's personal collection; used with permission [Citation ends].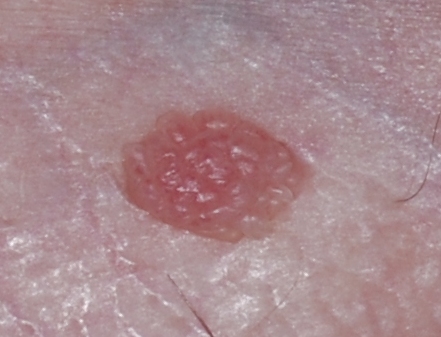 External genital warts may be diagnosed using direct visual inspection aided by bright light and magnification.[3]Wiley DJ, Douglas J, Beutner K, et al. External genital warts: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Clin Infect Dis. 2002 Oct 15;35(Suppl 2):S210-24.
https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/35/Supplement_2/S210/316436
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12353208?tool=bestpractice.com
Lesions are generally asymptomatic, but may be painful, friable, or pruritic.[5]Kirnbauer R, Lenz P, Okun MM. Human papillomavirus. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Rapini RP, eds. Dermatology Vol 1. London: Mosby; 2003:1217-33.[6]Beutner KR, Reitano MV, Richwald GA, et al. External genital warts: report of the American Medical Association consensus conference. Clin Infect Dis. 1998 Oct;27(4):796-806.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9798036?tool=bestpractice.com
Bleeding may occur due to local trauma or maceration of the area. Urinary symptoms such as terminal haematuria or abnormal stream of urine may be present.
External genital warts may be diagnosed using direct visual inspection aided by bright light and magnification.[3]Wiley DJ, Douglas J, Beutner K, et al. External genital warts: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Clin Infect Dis. 2002 Oct 15;35(Suppl 2):S210-24.
https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/35/Supplement_2/S210/316436
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12353208?tool=bestpractice.com
Lesions are generally asymptomatic, but may be painful, friable, or pruritic.[5]Kirnbauer R, Lenz P, Okun MM. Human papillomavirus. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Rapini RP, eds. Dermatology Vol 1. London: Mosby; 2003:1217-33.[6]Beutner KR, Reitano MV, Richwald GA, et al. External genital warts: report of the American Medical Association consensus conference. Clin Infect Dis. 1998 Oct;27(4):796-806.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9798036?tool=bestpractice.com
Bleeding may occur due to local trauma or maceration of the area. Urinary symptoms such as terminal haematuria or abnormal stream of urine may be present.
Investigations
A biopsy may be indicated if the genital warts appear fixed to underlying structures or are refractory to standard therapy.[42]Beutner KR, Wiley DJ, Douglas JM, et al. Genital warts and their treatment. Clin Infect Dis. 1999 Jan;28 Suppl 1:S37-56.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10028109?tool=bestpractice.com
Additional indications for biopsy include ulceration of the lesions or an individual wart larger than 1 cm.[6]Beutner KR, Reitano MV, Richwald GA, et al. External genital warts: report of the American Medical Association consensus conference. Clin Infect Dis. 1998 Oct;27(4):796-806.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9798036?tool=bestpractice.com
Should a biopsy be indicated, the following histological features are seen: epidermal hyperplasia, parakeratosis, koilocytosis, and papillomatosis.[17]Ahmed AM, Madkan V, Tyring SK. Human papillomaviruses and genital disease. Dermatol Clin. 2006 Apr;24(2):157-65.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16677964?tool=bestpractice.com
Compared with common warts, the papillomatosis seen in genital warts tends to be more rounded. Not all of these histological features are necessarily seen in every genital wart. In patients with recurrent perianal warts, evaluation for intra-anal warts by anoscopy is recommended.[6]Beutner KR, Reitano MV, Richwald GA, et al. External genital warts: report of the American Medical Association consensus conference. Clin Infect Dis. 1998 Oct;27(4):796-806.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9798036?tool=bestpractice.com
Urinary symptoms such as terminal haematuria or abnormal stream of urine should prompt a referral for urethroscopy to evaluate the distal urethra and meatus.[6]Beutner KR, Reitano MV, Richwald GA, et al. External genital warts: report of the American Medical Association consensus conference. Clin Infect Dis. 1998 Oct;27(4):796-806.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9798036?tool=bestpractice.com
 Colour varies from flesh-coloured to whitish to hyperpigmented. Maceration may occur, particularly in moist areas lacking the thick horny cell layer found in cutaneous warts.[5][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Wart on shaft of penisFrom Dr Tyring's personal collection; used with permission [Citation ends].
Colour varies from flesh-coloured to whitish to hyperpigmented. Maceration may occur, particularly in moist areas lacking the thick horny cell layer found in cutaneous warts.[5][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Wart on shaft of penisFrom Dr Tyring's personal collection; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Close-up of penile wartFrom Dr Tyring's personal collection; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Close-up of penile wartFrom Dr Tyring's personal collection; used with permission [Citation ends]. External genital warts may be diagnosed using direct visual inspection aided by bright light and magnification.[3] Lesions are generally asymptomatic, but may be painful, friable, or pruritic.[5][6] Bleeding may occur due to local trauma or maceration of the area. Urinary symptoms such as terminal haematuria or abnormal stream of urine may be present.
External genital warts may be diagnosed using direct visual inspection aided by bright light and magnification.[3] Lesions are generally asymptomatic, but may be painful, friable, or pruritic.[5][6] Bleeding may occur due to local trauma or maceration of the area. Urinary symptoms such as terminal haematuria or abnormal stream of urine may be present.