Images and videos
Images
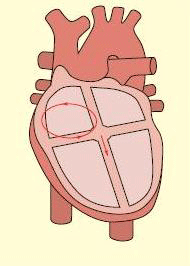
Atrial flutter
Atrial flutter typically involves a circuit in the right atrium
From: Cox D, Dougall H. Student BMJ. 2001;9:399-442; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
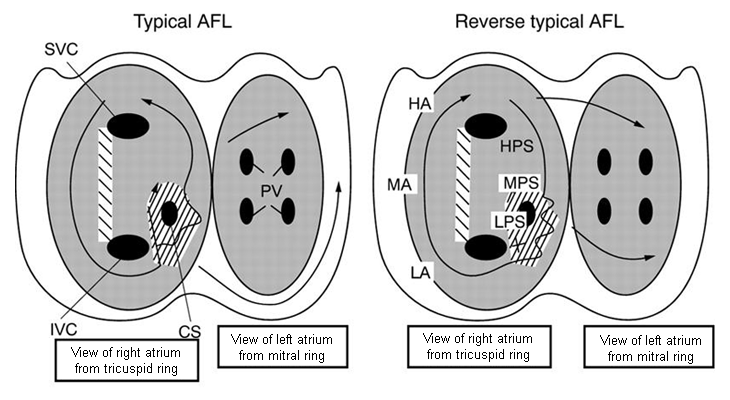
Atrial flutter
Left panel: atrial activation in typical atrial flutter (AFL). Right panel: activation in reverse typical AFL. The atria are represented schematically in a left anterior oblique view, from the tricuspid (left) and mitral rings. The endocardium is shaded and the openings of the superior (SVC) and inferior vena cava (IVC), coronary sinus (CS), and pulmonary veins (PV) are shown. The direction of activation is shown by arrows. Dashed areas mark approximate location of zones of slow conduction and block. Lettering on the right-hand panel marks the low (LPS), mid (MPS), and high (HPS) posteroseptal wall, respectively
From: Waldo AL. Heart. 2000;84:227-227; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Atrial flutter
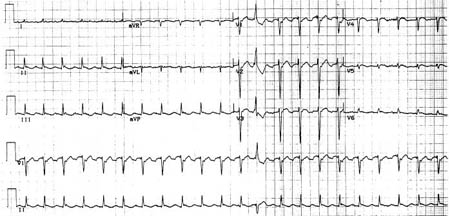
Atypical flutter with right bundle branch block
From the collection of Dr K.C. Wu
See this image in context in the following section/s:
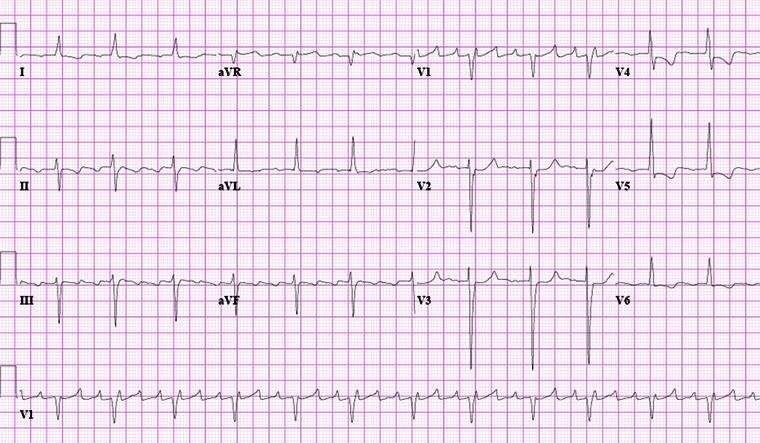
Atrial flutter
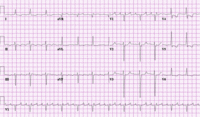
Typical atrial flutter with variable (3 to 4:1) block
From the collection of Dr K.C. Wu
See this image in context in the following section/s:
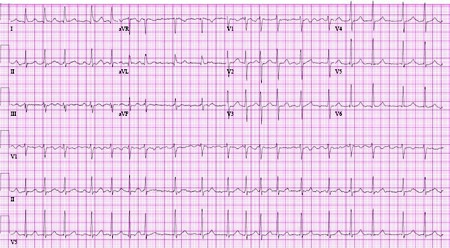
Atrial flutter
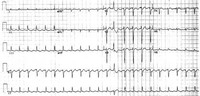
Atrial fibrillation
From the collection of Dr K.C. Wu
See this image in context in the following section/s:
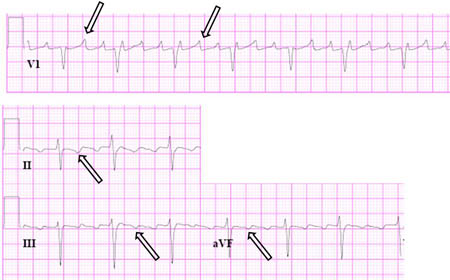
Atrial flutter
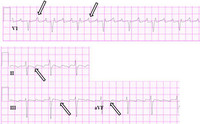
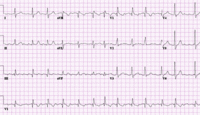
Close-up images of leads V1, II, III, aVF demonstrating the features of typical atrial flutter: positive saw-tooth deflections in lead V1 and negative deflections in leads II, III, aVF (arrows)
From the collection of Dr K.C. Wu
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Atrial flutter
Reverse typical atrial flutter
From: Waldo AL. Heart. 2000 Aug;84(2):227-32; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
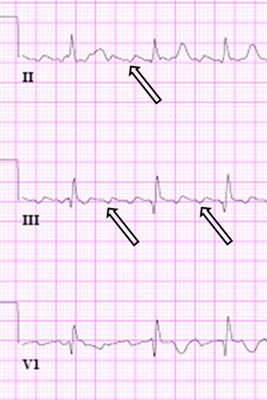
Atrial flutter
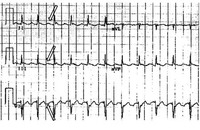
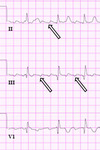
Close up of leads II, III, V1 showing the continuously undulating pattern of atrial deflections not fitting the criteria for typical or reverse typical atrial flutter
From the collection of Dr K.C. Wu
See this image in context in the following section/s:
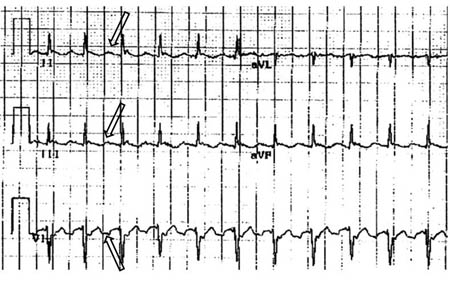
Atrial flutter
Selected leads from a patient with reverse typical atrial flutter confirmed at electrophysiological study. The atrial deflections are negative in lead V1 and positive in leads II, III, aVF (arrows)
Adapted from: Waldo AL. Heart. 2000 Aug;84(2):227-32; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Videos
 Electrical (direct current) cardioversion animated demonstration
Electrical (direct current) cardioversion animated demonstrationHow to perform electrical (direct current) cardioversion using a defibrillator.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer