Gout is clinically suspected in patients with typical history and examination findings.
A clinical diagnosis can be made with a good degree of certainty in patients with a reliable history of recurrent acute monoarthritis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint (podagra).[53]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gout: diagnosis and management. Jun 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng219
Rapid onset of severe pain, redness or swelling of joints other than the first metatarsophalangeal (e.g., midfoot, ankle, knee, hand, wrist, elbow) may also indicate a diagnosis of gout.[53]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gout: diagnosis and management. Jun 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng219
Arthrocentesis showing monosodium urate crystals confirms the diagnosis of gout.[54]Qaseem A, McLean RM, Starkey M, et al. Diagnosis of acute gout: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2017 Jan 3;166(1):52-7.
https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/full/10.7326/M16-0569
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27802479?tool=bestpractice.com
In the UK, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends performing a serum urate level as the first investigation to confirm the clinical diagnosis in patients with signs and symptoms of gout.[53]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gout: diagnosis and management. Jun 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng219
NICE recommends that arthrocentesis (with microscopy of synovial fluid) should be considered when the diagnosis of gout remains uncertain or unconfirmed following measurement of serum urate level.[53]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gout: diagnosis and management. Jun 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng219
Alternatively, diagnosis may be based upon fulfilment of ≥6 of the following criteria from the American College of Rheumatology (ACR):[55]Wallace SL, Robinson H, Masi AT, et al. Preliminary criteria for the classification of the acute arthritis of primary gout. Arthritis Rheum. 1977;20:895-900.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/856219?tool=bestpractice.com
More than one attack of acute arthritis
Maximum inflammation developed within 1 day
Monoarthritis attack, redness observed over joints
First metatarsophalangeal joint painful or swollen
Unilateral first metatarsophalangeal joint attack
Unilateral tarsal joint attack
Tophus (confirmed or suspected)
Hyperuricaemia
Asymmetrical swelling within a joint on x-ray film
Subcortical cyst without erosions on x-ray film
Joint culture negative for organism during attack.
In 2015 the ACR published new classification criteria; however, these criteria are intended to identify people who may be eligible for entry into a clinical study and they are not intended to be used to diagnose gout.[56]Neogi T, Jansen TL, Dalbeth N, et al. 2015 gout classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:2557-2568.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/art.39254
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26352873?tool=bestpractice.com
[57]Neogi T, Jansen TL, Dalbeth N, et al. 2015 gout classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:1789-1798.
https://ard.bmj.com/content/74/10/1789.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26359487?tool=bestpractice.com
History
Gout is more common in men and rare in pre-menopausal women.[2]Safiri S, Kolahi AA, Cross M, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and years lived with disability due to gout and its attributable risk factors for 195 countries and territories 1990-2017: a systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2017. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Nov;72(11):1916-27.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/art.41404
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32755051?tool=bestpractice.com
[3]Kuo CF, Grainge MJ, Zhang W, et al. Global epidemiology of gout: prevalence, incidence and risk factors. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015 Nov;11(11):649-62.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26150127?tool=bestpractice.com
[5]Chen-Xu M, Yokose C, Rai SK, et al. Contemporary prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the United States and decadal trends: the National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007-2016. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Jun;71(6):991-9.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6536335
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21800283?tool=bestpractice.com
[8]Hak AE, Curhan GC, Grodstein F, et al. Menopause, postmenopausal hormone use and risk of incident gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010 Jul;69(7):1305-9.
https://www.doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.109884
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19592386?tool=bestpractice.com
[37]Singh JA, Reddy SG, Kundukulam J. Risk factors for gout and prevention: a systematic review of the literature. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23:192-202.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21285714?tool=bestpractice.com
A history of previous attacks that are self-limiting (7-14 days) supports the diagnosis. Medications, dietary habits, and family history should be assessed.
The most common presentation is acute monoarticular arthritis characterised by sudden-onset severe pain and swelling.[53]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gout: diagnosis and management. Jun 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng219
[58]Hainer BL, Matheson E, Wilkes RT. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of gout. Am Fam Physician. 2014 Dec 15;90(12):831-6.
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2014/1215/p831.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25591183?tool=bestpractice.com
Symptoms often develop overnight.[53]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gout: diagnosis and management. Jun 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng219
The disease may be oligoarticular (<4 joints involved) or, to a lesser degree, polyarticular (e.g., in older people, where it may be associated with marked oedema and swelling of the hands and feet). The most commonly affected joints are the first metatarsophalangeal, tarsometatarsal, ankle, and knee joints, but almost any other joint may be affected.[58]Hainer BL, Matheson E, Wilkes RT. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of gout. Am Fam Physician. 2014 Dec 15;90(12):831-6.
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2014/1215/p831.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25591183?tool=bestpractice.com
Physical examination
Involved joints are warm, red, and swollen.[53]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gout: diagnosis and management. Jun 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng219
Usually, there is considerable tenderness and limited range of movement due to pain.
All joints should be examined, as others may be affected in a more subtle fashion.
Hard subcutaneous nodules (tophi) over the extensor surface of the joint, especially over the elbows, knees, and Achilles tendons, may be present.[53]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gout: diagnosis and management. Jun 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng219
[58]Hainer BL, Matheson E, Wilkes RT. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of gout. Am Fam Physician. 2014 Dec 15;90(12):831-6.
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2014/1215/p831.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25591183?tool=bestpractice.com
Tophi may also be evident over the dorsal aspects of hands and feet, and in the helix of the ears. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chronic tophaceous gout showing nodules in periarticular structures and arthritisAdapted from BMJ Case Reports 2009 [doi:10.1136/bcr.03.2009.1668] Copyright © 2009 by the BMJ Group Ltd [Citation ends].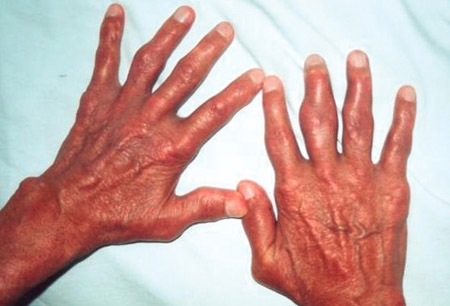 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chronic tophaceous gout showing nodules in the hands, elbows, legs, buttocks, and abdominal wall (arrows)Adapted from BMJ Case Reports 2009 [doi:10.1136/bcr.03.2009.1668] Copyright © 2009 by the BMJ Group Ltd [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chronic tophaceous gout showing nodules in the hands, elbows, legs, buttocks, and abdominal wall (arrows)Adapted from BMJ Case Reports 2009 [doi:10.1136/bcr.03.2009.1668] Copyright © 2009 by the BMJ Group Ltd [Citation ends].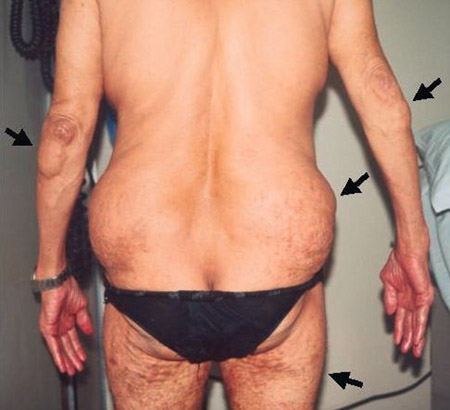
Investigations
The following tests may be considered in people with symptoms typical of gout.
Arthrocentesis with synovial fluid analysis
Provides definitive diagnosis.[54]Qaseem A, McLean RM, Starkey M, et al. Diagnosis of acute gout: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2017 Jan 3;166(1):52-7.
https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/full/10.7326/M16-0569
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27802479?tool=bestpractice.com
The synovial fluid white blood cell count usually exceeds 2.0 x 10⁹/L (2000/mm³ or 2000/microlitre), and the cells are mostly polymorphonuclear neutrophils type. Monosodium urate crystals (intracellular and/or extracellular needle-shaped crystals strongly negative for birefringence under polarised light) confirm the diagnosis. Synovial fluid analysis should be considered in most patients, but the diagnosis can often be made clinically.
In the UK, NICE recommends that arthrocentesis (with microscopy of synovial fluid) should be considered when the diagnosis of gout remains uncertain or unconfirmed following measurement of serum urate level.[53]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gout: diagnosis and management. Jun 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng219
Serum uric acid level
May be low, normal, or high during an acute gout attack. This test becomes more reliable when done at least 2 weeks after the attack resolves.[59]Bădulescu M, Macovei L, Rezuş E. Acute gout attack with normal serum uric acid levels. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2014 Oct-Dec;118(4):942-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25581951?tool=bestpractice.com
In the UK, NICE recommends performing a serum urate level as the first investigation to confirm the clinical diagnosis in patients with signs and symptoms of gout. A serum urate level 360 micromol/L (6 mg/dL) or more confirms a diagnosis of gout. If the serum urate level is below 360 micromol/L (6 mg/dL) during a gout flare, and gout is suspected, the test should be repeated at least two weeks after the flare has settled.[53]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gout: diagnosis and management. Jun 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng219
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is more sensitive than x-rays in detecting erosions, tophi, and the gout-specific double contour sign (linear urate deposits over hyaline cartilage). Ultrasound findings, including tophi and erosion beside a double contour sign, have a sensitivity of 65% and specificity approaching 90%.[60]Lee YH, Song GG. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound in patients with gout: a meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2018 Apr;47(5):703-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29054295?tool=bestpractice.com
[61]Zhang Q, Gao F, Sun W, et al. The diagnostic performance of musculoskeletal ultrasound in gout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2018 Jul 6;13(7):e0199672.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6034830
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29979706?tool=bestpractice.com
Ultrasound is recommended for patients in the UK if joint aspiration can't be performed, or if the diagnosis of gout is uncertain.[53]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gout: diagnosis and management. Jun 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng219
Dual energy computed tomography (DECT)
Could be helpful in the diagnosis of gout when it is in question, or for patients with contraindications for, or who refuse to have joint aspiration.[53]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gout: diagnosis and management. Jun 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng219
[62]Ogdie A, Taylor WJ, Weatherall M, et al. Imaging modalities for the classification of gout: systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:1868-1874.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24915980?tool=bestpractice.com
[63]American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: chronic extremity joint pain - suspected inflammatory arthritis. 2016 [internet publication].
https://acsearch.acr.org/docs/3097211/Narrative
[64]Carotti M, Salaffi F, Filippucci E, et al. Clinical utility of dual energy computed tomography in gout: current concepts and applications. Acta Biomed. 2020 Jul 13;91(8-s):116-24.
https://www.doi.org/10.23750/abm.v91i8-S.9942
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32945286?tool=bestpractice.com
Evidence suggests that DECT is valid and reliable, more sensitive than radiographs and computed tomography, and at least comparable to ultrasound for the diagnosis of gout.[65]Ramon A, Bohm-Sigrand A, Pottecher P, et al. Role of dual-energy CT in the diagnosis and follow-up of gout: systematic analysis of the literature. Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Mar;37(3):587-95.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29350330?tool=bestpractice.com
[66]Chen J, Liao M, Zhang H, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of dual-energy CT and ultrasound in gouty arthritis: a systematic review. Z Rheumatol. 2017 Oct;76(8):723-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28058498?tool=bestpractice.com
[67]Yu Z, Mao T, Xu Y, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of dual-energy CT in gout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Skeletal Radiol. 2018 Dec;47(12):1587-93.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29725712?tool=bestpractice.com
One meta-analysis concluded that DECT has a high diagnostic accuracy in established gout, but low sensitivity for recent-onset gout.[64]Carotti M, Salaffi F, Filippucci E, et al. Clinical utility of dual energy computed tomography in gout: current concepts and applications. Acta Biomed. 2020 Jul 13;91(8-s):116-24.
https://www.doi.org/10.23750/abm.v91i8-S.9942
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32945286?tool=bestpractice.com
[68]Gamala M, Jacobs JWG, van Laar JM. The diagnostic performance of dual energy CT for diagnosing gout: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 Dec 1;58(12):2117-21.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31089688?tool=bestpractice.com
Radiography
Radiographs are of limited diagnostic utility.[52]Sivera F, Andrés M, Carmona L, et al. Multinational evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis and management of gout: integrating systematic literature review and expert opinion of a broad panel of rheumatologists in the 3e initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 Feb;73(2):328-35.
https://ard.bmj.com/content/73/2/328.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23868909?tool=bestpractice.com
In late/severe gout, radiographic changes may help to differentiate between chronic gout and other joint conditions.[69]Zhang W, Doherty M, Bardin T, et al. EULAR evidence based recommendations for gout. Part I: diagnosis. Report of a task force of the Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:1301-1311.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16707533?tool=bestpractice.com
X-ray findings suggestive of gout include soft-tissue opacifications with densities between soft tissue and bone, articular and periarticular bone erosions, and osteophytes at the margins of opacifications or erosions.[70]Rettenbacher T, Ennemoser S, Weirich H, et al. Diagnostic imaging of gout: comparison of high-resolution US versus conventional X-ray. Eur Radiol. 2008 Mar;18(3):621-30.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17994238?tool=bestpractice.com
The hands are an optimal place to look for gouty erosions.
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chronic tophaceous gout showing nodules in the hands, elbows, legs, buttocks, and abdominal wall (arrows)Adapted from BMJ Case Reports 2009 [doi:10.1136/bcr.03.2009.1668] Copyright © 2009 by the BMJ Group Ltd [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chronic tophaceous gout showing nodules in the hands, elbows, legs, buttocks, and abdominal wall (arrows)Adapted from BMJ Case Reports 2009 [doi:10.1136/bcr.03.2009.1668] Copyright © 2009 by the BMJ Group Ltd [Citation ends].