Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC with differential
panoramic radiograph
Test
Extra-oral screening dental radiograph, which allows quick overall screening to rule out more advanced pathology, fractures, and assessment for impacted teeth. May also show cysts or granulomas and more advanced tooth decay.
Not as detailed as a periapical radiograph and, therefore, not as good at assessing for early decay or periodontal bone loss. However, will show full mouth with one film.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Panoramic radiograph showing periapical abscess related to the lower-left second molarFrom the personal collection of Melanie S. Lang and Thomas B. Dodson [Citation ends].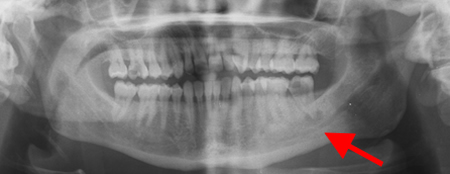 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Panoramic radiograph showing generalised advanced horizontal periodontal bone loss with periapical radiolucency (see arrow) related to left mandibular first molar consistent with combined endodontic/periodontal abscessFrom the personal collection of Melanie S. Lang and Thomas B. Dodson; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Panoramic radiograph showing generalised advanced horizontal periodontal bone loss with periapical radiolucency (see arrow) related to left mandibular first molar consistent with combined endodontic/periodontal abscessFrom the personal collection of Melanie S. Lang and Thomas B. Dodson; used with permission [Citation ends].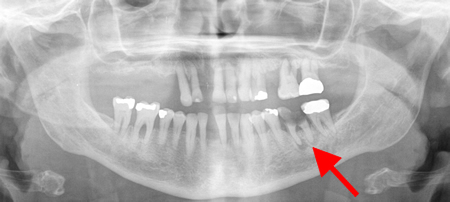
Result
periapical radiolucency (with larger abscesses); advanced horizontal periodontal bone loss (periodontal disease)
Investigations to consider
periapical radiograph
Test
Intra-oral dental radiograph that captures the entire tooth and surrounding bone with good detail. Shows areas of decay and relationship to dental pulp, as well as early periapical bone changes.
Helpful in determining the source of pain in a specific tooth and potential need for endodontic (root canal) treatment.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Periapical radiograph showing large periapical radiolucency related to root canal-treated lateral incisor; final pathology was consistent with a periapical cystFrom the personal collection of Melanie S. Lang and Thomas B. Dodson [Citation ends].
Result
periapical radiolucency (chronic periapical abscess); decrease in alveolar bone levels (periodontal disease); early tooth decay
CT head and neck (with contrast)
Test
May be ordered in the accident and emergency department if panoramic or periapical radiographs are not available.
Helpful in planning an operative approach and determining whether there is drainable local pus or fluid collection versus cellulitic changes only.
May also be useful to assess drain placement or residual areas of fluid/pus collection. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Sagittal CT scan with contrast showing submandibular space abscessFrom the personal collection of Melanie S. Lang and Thomas B. Dodson [Citation ends].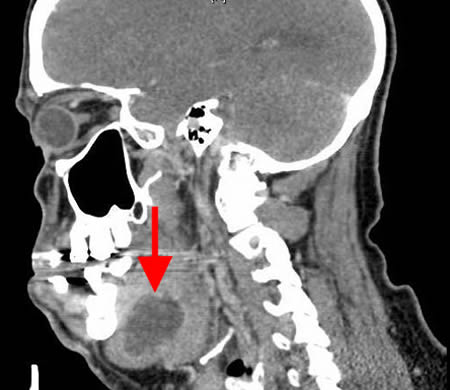
Result
infection/pus deposits in lateral pharyngeal space, retropharyngeal space, orbit, brain, neck, or mediastinum
infection site aspiration Gram stain/culture and sensitivity
Test
Check both aerobic and anaerobic cultures. In certain conditions, may consider fungal or viral testing in addition to bacterial cultures.
Results often take several days; therefore, often not helpful with mild infections, as patient has often recovered from the infection before culture results are final. However, may be beneficial to guide antibiotic choice in unresponsive infections with resistant organisms.
Result
variable
CRP
Test
Usually elevated in the presence of inflammation.
Useful in determining disease progression and effectiveness of treatment.
More sensitive and accurate in acute phase inflammatory response compared with ESR.
Returns to normal more quickly than ESR.
Rising level on the second day after surgical incision and drainage has been found to be predictive of the need for re-operation.[12]
Result
elevated
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Test
Usually elevated in the presence of inflammation.
Useful in determining disease progression and effectiveness of treatment.
Less sensitive and accurate in acute phase inflammatory response compared with CRP.
Result
elevated
serum electrolytes
Test
Typically normal with mild infection; however, electrolyte abnormalities often develop with decreased oral intake with aggressive infection or sepsis, or may be related to comorbid conditions.
Result
typically normal; often deranged with severe infection
plasma fibrinogen level
Test
Acute phase protein that may be elevated in any form of inflammation.
Result
elevated
MRI head and neck
Test
Rarely indicated. Although an MRI has superior contrast resolution, it is rarely of benefit with an acute infection, except for patients with an ocular/orbital infection. For these patients it is useful to assess the optic nerve for developing ischaemia/infarction. It may also be helpful in differentiating between inflammatory and neoplastic lesions.
Not suitable in the case of potential airway compromise, as it takes more time to perform compared with other imaging modalities. Also not suitable in patients with claustrophobia, or those with a pacemaker or implanted metallic device in the area (particularly if it is made of stainless steel).
Result
infection/pus deposits in lateral pharyngeal space, retropharyngeal space, orbit, brain, neck, or mediastinum
ultrasound of fascial spaces
Test
Relatively inexpensive, non-invasive, portable, and effective diagnostic tool.
Predictable in detecting infection stage and confirming abscess formation in the superficial fascial spaces.
More widely used in Europe and some other countries than in the US.[42]
Result
abscess formation
electric pulp testing
Test
Performed by a dental professional to verify vitality of a tooth.
Result
non-responsive secondary to pulpal necrosis with a periapical abscess
thermal testing
Test
Performed by a dental professional to verify vitality of a tooth.
Result
non-responsive secondary to pulpal necrosis with a periapical abscess
blood cultures
Test
May be positive if patient develops sepsis.
Rarely directs management of odontogenic infections.
Positive blood culture should direct the clinician to broaden the differential.
Result
negative in mild infection
C-terminal cross-linking telopeptide (CTX)
Test
Biological index to measure bone remodelling and resorption. Used as a screening tool to assess for possible drug-induced (e.g., bisphosphonates, denosumab) osteonecrosis of the jaw in conjunction with the history and examination.[35][36][37][38][39]
Decreased level may indicate moderate risk for drug-related osteonecrosis of the jaw.
Result
may be used in setting of bisphosphonate use
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer