Investigations
1st investigations to order
stool microscopy
Test
Stool samples should be collected for microscopy as part of the initial investigation in all patients with suspected Campylobacter infection.
Red blood cells and neutrophils are present in stool in the majority of patients with Campylobacter infection.[4][34][35]
Result
presence of red blood cells and neutrophils
stool culture
Test
Stool samples should be collected for microscopy and culture as part of the initial investigation in all patients with suspected Campylobacter infection. A positive stool culture for Campylobacter is diagnostic.[14] Current Canadian guidelines for investigating suspected infectious diarrhoea suggest that stool testing is not required in cases of acute (≤7 days) or resolving diarrhoea.[36]
The guideline recommends that the Infectious Diarrhea Panel, a new stool test that combines stool cultures, ova and parasites, and Clostridium difficile, should be requested if diarrhoea is severe of any duration or prolonged >7 days.[36]
Isolation techniques and special media (Campy-BAP or Skirrow) are used to reduce the growth of other enteric organisms. Specific selective media and raised incubation temperatures are required to isolate Campylobacter species.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Campylobacter cultures grown on Skirrow's and Butzler's mediumSheila Mitchell, Image Library, US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Citation ends].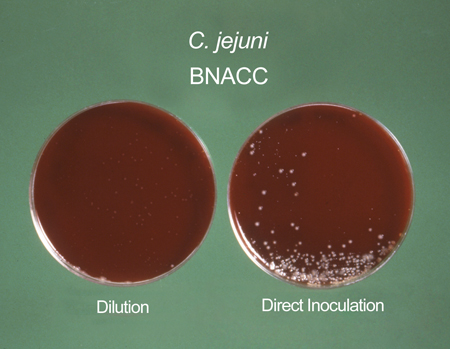
Result
Campylobacter isolated from stool
white blood cell count
Test
Performed to detect leukocytosis or leukopenia.[39]
Result
often normal, but a left shift (increase in neutrophil predominance) may occur; may show lymphopenia
Investigations to consider
serum Campylobacter serology
Test
Used to detect previous infection in patients with late-onset complications from Campylobacter infection (e.g., bacteraemia, cardiac complications, extraintestinal manifestations, reactive arthritis, and Guillain-Barre syndrome).
Result
positive
blood culture
Test
Bacteraemia can transiently occur in the early stages of infection.[38] Blood culture is not recommended as an initial test in people with features of Campylobacter infection because the diagnosis can usually be made by stool culture alone. Symptoms of bacteraemia or other extraintestinal manifestations do warrant additional investigation with blood cultures.
Result
positive
intestinal biopsy
Test
Rarely used to make the diagnosis but can help distinguish between infectious and inflammatory causes of diarrhoea.
Result
histological findings can include oedema, inflammatory changes, cryptitis, or crypt abscess formation
faecal microscopy
Test
Although rarely performed, examination by darkfield or phase-contrast microscopy can assist with presumptive diagnosis.[4]
Result
microscopy demonstrates the characteristic darting motility of organisms
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer