Investigations
1st investigations to order
x-ray of the face
Test
Useful in injuries involving the mid-facial bones. Views should be occipitomental 10° or 15° and 30°, and anteroposterior.
The presence of a polypoid mass (teardrop sign) protruding from the floor of the orbit into the maxillary antrum is a classic radiographic finding in blow-out fractures. The teardrop represents the herniated orbital contents, peri-orbital fat, and inferior rectus muscle. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Right orbital blow-out fracture; teardrop sign on occipitomental 15° x-rayFrom the personal collection of Dr Alistair Cobb [Citation ends].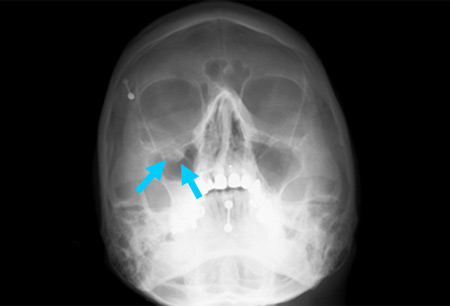
A teardrop sign may be unreliable in some cases and may be caused by an artifact or benign pathology such as a polyp.[24]
Antral fluid may be evident as a fluid level. This is likely to be blood but merely represents bleeding from traumatised antral mucosa, and is not necessarily a hard tissue injury.
Result
teardrop sign, may show fluid
CT scan of the orbit
Test
Fine-cut spiral CT with coronal and sagittal reconstructions. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Right orbital blow-out fracture on CT-scan; coronal reformatFrom the personal collection of Dr Alistair Cobb [Citation ends].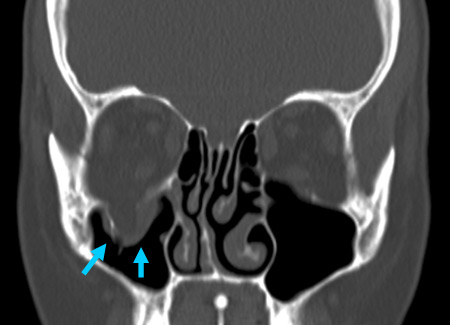 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Right orbital blow-out fracture on CT-scan; sagittal reformatFrom the personal collection of Dr Alistair Cobb [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Right orbital blow-out fracture on CT-scan; sagittal reformatFrom the personal collection of Dr Alistair Cobb [Citation ends].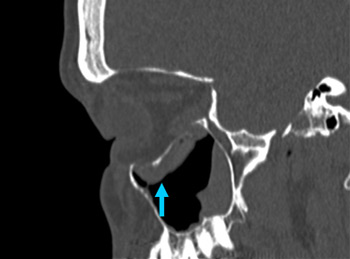 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: No evidence of fracture on the left orbit as seen on CT-scan; sagittal reconstructionFrom the personal collection of Dr Alistair Cobb [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: No evidence of fracture on the left orbit as seen on CT-scan; sagittal reconstructionFrom the personal collection of Dr Alistair Cobb [Citation ends].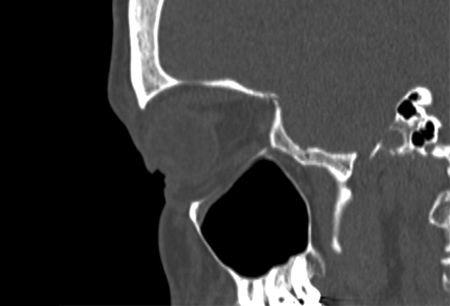
Result
fracture, may show herniation of orbital contents into adjacent paranasal sinuses
Investigations to consider
MRI of the orbit
Test
Soft tissue herniation and entrapment may be demonstrated more clearly by MRI than by CT scanning. However, MRI may underestimate the incidence of soft tissue injuries.[23]
Result
soft tissue injury
forced duction test
Test
This test is performed by an ophthalmology/maxillofacial specialist in comatose patients to determine whether the absence of movement of the eye is due to a neurological disorder or a mechanical restriction. A fine pair of ophthalmic forceps is used to gently grasp the inferior-most conjunctiva and used to attempt to elevate the eye. If there is mechanical restriction the eye will not move.
Result
mechanical or neurological restriction of eye movement
orthoptic test
Test
All cases of orbital injury, real or suspected, should undergo orthoptic assessment. This includes Hess chart, cover test, binocular fixation test, and binocular fields of vision. All patients should be referred to an orthoptist.
Result
may show vision or eye movement abnormalities
Emerging tests
ultrasonographic orbital scanning
Test
There may be a role for rapid ultrasonographic scanning for immediate assessment of orbital fractures in the accident and emergency department.
Result
fracture; may show herniation of orbital contents into adjacent paranasal sinuses
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer