Summary
Definition
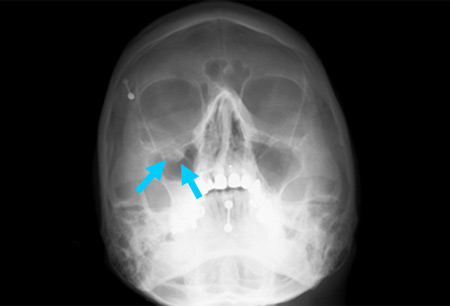
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- diplopia on upward gaze
- derangement of globe position
- intercanthal distance increased
- oculovagal symptoms (bradycardia, hypotension, nausea/vomiting)
Other diagnostic factors
- visual disturbance
- peri-orbital ecchymosis
- peri-orbital oedema
- nerve sensory loss
- subconjunctival haemorrhage
- step defect infra-orbital rim
- loss of colour vision
- impaired pupillary light reflex
- decreased visual acuity
Diagnostic investigations
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Alistair R.M. Cobb, MBBS, BDS, FRCS (OMFS), FDSRCS (Eng), MFSEM (UK)
Consultant Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon
South West Cleft Service
United Hospitals Bristol NHS Trust
Bristol
UK
Disclosures
ARMC is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Acknowledgements
Mr Alistair Cobb would like to gratefully acknowledge Mr Timothy Lloyd, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
TL declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Andrew Parfitt, MBBS, FFAEM
Clinical Director
Acute Medicine
Associate Medical Director
Consultant Emergency Medicine
Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust
Clinical Lead and Consultant
Accident Emergency Medicine
St Thomas' Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
AP declares that he has no competing interests.
Mark I. Neuman, MD
Assistant Professor of Pediatrics
Children's Hospital Boston
Harvard Medical School
Boston
MA
Disclosures
MIN declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer