Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
In acute Chagas disease, leukocytosis (mild or moderate) is common, but normal or low levels may be observed. Lymphocytosis with atypical lymphocytes is a significant marker.
Result
leukopenia or leukocytosis with a left shift and lymphocytosis; hypochromic anaemia; reduced platelets; low platelets
LFTs
Test
Helpful in acute Chagas disease (especially with suspected ingestion of contaminated food or drink) to assess for hepatic lesions. May be altered in some cases of chronic-phase disease with cardiac involvement due to congestive hepatopathy.
Result
elevated aspartate transaminase and alanine transaminase; elevated bilirubin
serum electrolytes, urea nitrogen, and creatinine
Test
Useful for assessing renal function. May be abnormal in acute Chagas disease and in some cases of complicated chronic-phase disease.
Result
normal or elevated sodium and potassium; normal or elevated urea nitrogen and creatinine
microscopy: fresh blood
Test
Useful in acute Chagas disease.
Detected by microscopy of fresh preparations of anticoagulated blood. The trypomastigotes are translucent, and are usually detected by the corresponding movement of red blood cells. A fast, simple, accurate test of low cost.[13][24] Sensitivity is increased if the patient is febrile during blood collection. Parasitaemia decreases within 90 days of infection, even without treatment, and is undetectable by microscopy in the chronic phase.[34]
First-line diagnostic method in case of reactivation.
Result
mobile trypomastigotes
microscopy: concentration methods applied to fresh blood
Test
Useful in acute Chagas disease.
Parasites are detected by microscopy of fresh preparations of buffy coated blood (quantitative buffy coat test). Concentration methods (Strout's, microhaematocrit) are an alternative. The use of microhaematocrit tubes focuses the test for congenital Chagas disease in infants born to chronically infected mothers.
These tests are more sensitive (80% to 90%), but more complicated to perform.[13][24]
The parasitaemia decreases within 90 days of infection, even without treatment, and parasites are undetectable by microscopy in the chronic phase.
First-line diagnostic method in case of reactivation.
Result
mobile trypomastigotes
microscopy: thick blood smear
Test
Useful in acute Chagas disease.
Stained thin and thick blood smears may be examined for diagnosis. However, these methods have lower sensitivity than other microscopy methods.[13][24]
The parasitaemia decreases within 90 days of infection, even without treatment, and is undetectable by microscopy in the chronic phase.[34]
Commonly used in association with malaria control measures in malaria-endemic areas.[13]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Trypanosoma cruzi metacyclic trypomastigotes on a peripheral blood smear prepared with Giemsa stainCenters for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA, USA: Public Health Image Library ID # 3013 (Dr Mae Melvin, 1977) [Citation ends].
Result
trypomastigote forms
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on parasite lysate
Test
Used for chronic-phase disease.
This method has better sensitivity than conventional parasitological methods, due to low parasitaemia in chronic disease.[13][24]
Serological methods detect almost 100% of cases.[13][134] However, no single assay has sufficient sensitivity and specificity to be relied on alone. At least two subsequent tests based on different antigens or techniques are used in parallel, to increase the accuracy of diagnosis. When results are discordant, an additional assay may be used to confirm the diagnosis, or repeat sampling may be required.[34]
Result
antibody titre above locally validated threshold
immunofluorescent antibody test
Test
Used for chronic-phase disease.
No single assay has sufficient sensitivity and specificity to be relied on alone. At least two subsequent tests based on different methods or antigens must be used in association, to increase the accuracy of the laboratory diagnosis.
In cases of discordant results, a third assay may be used to confirm the diagnosis.[34]
Result
antibody titre above locally validated threshold
indirect haemagglutination antibody test
Test
Diagnostic option for chronic-phase disease.
No single assay has sufficient sensitivity and specificity to be relied on alone. At least two subsequent tests based on different methods or antigens must be used in association, to increase the accuracy of the laboratory diagnosis.
In cases of discordant results, a third assay may be used to confirm the diagnosis.[34]
Result
antibody titre above locally validated threshold
chemiluminescence
Test
Diagnostic option for chronic-phase disease. No single assay has sufficient sensitivity and specificity to be relied on alone. At least two subsequent tests based on different methods or antigens must be used in association, to increase the accuracy of the laboratory diagnosis.[143]
In cases of discordant results, a third assay may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Result
antibody titre above locally validated threshold
radio-immunoprecipitation assay
Test
Serological screening option in the US to confirm reactive blood screening tests. Also used in the diagnosis of chronic-phase disease. No single assay has sufficient sensitivity and specificity to be relied on alone. At least two subsequent tests based on different methods or antigens must be used in association, to increase the accuracy of the laboratory diagnosis.[143]
In cases of discordant results, a third assay may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Result
antibody titre above locally validated threshold
western blot
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Test
PCR, when available, is a highly sensitive test in acute infection, and may show rising parasite loads before the parasites are detectable by microscopy. It is not recommended for diagnosis of chronic disease, but may be used for early detection of reactivation in immunocompromised patients.[2]
Result
evidence of Trypanosoma cruzi DNA
urinalysis
Test
In acute Chagas disease, urine sediment examination is useful to assess renal function.
Result
active sediment
serum or urine beta-hCG
Test
Pregnancy status determines the selection of antiparasitic drugs. All women of childbearing age should be tested prior to treatment.
Result
positive or negative
ECG with a 30-second lead II rhythm strip
Test
Acute-phase disease: sinus tachycardia, low QRS voltage, prolonged PR and/or QT intervals, and primary alterations of the T wave are common abnormalities. Ventricular extrasystoles, atrial fibrillation, or complete right bundle branch block may indicate a fatal outcome.
Chronic-phase disease: conduction disorders (especially right bundle branch block associated with left-anterior hemiblock), sinus bradycardia, primary and non-specific repolarisation alterations, Q waves, atrioventricular block, low QRS voltage, ventricular premature beats, and atrial fibrillation are common.
ECG normalises in some months with specific treatment or with disease progression, and may be normal for many years in the indeterminate form of the disease.[62]
In asymptomatic patients with non-specific ECG changes, further evaluation should be decided on an individual basis.
Major predictors of sudden death are ventricular dysfunction, non-sustained or sustained ventricular tachycardia on resting ECG or ambulatory monitoring, severe sinus node dysfunction, and high-degree heart block.[135][136][137][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ECG with complete right bundle branch block and left anterior hemiblockGrupo de Estudo em Correlalacao Anatomo-Clinica, Clínica Médica, Pontificia Universidade Catolica de Campinas, Sao Paulo, Brazil; used with permission [Citation ends].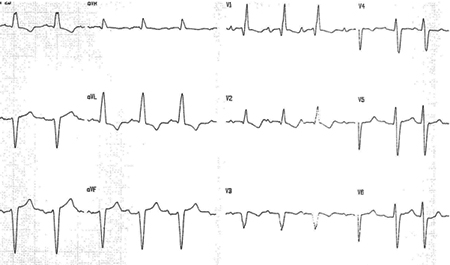
Result
abnormal
chest x-ray
Test
The cardiac area is normal in at least half of cases. Mild or moderate global increase of the cardiac area is common, as a result of cardiac involvement. The pleuro-pulmonary areas are generally clean, but pleural effusion can occur in cases of cardiac failure. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray: cardiomyopathy, heart enlargementGrupo de Estudo em Correlalacao Anatomo-Clinica, Clínica Médica, Pontificia Universidade Catolica de Campinas, Sao Paulo, Brazil; used with permission [Citation ends].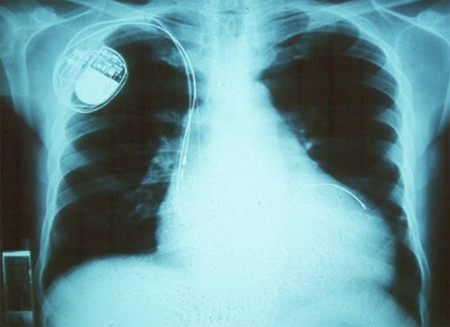
Result
enlargement of cardiac area, pleural effusion
barium swallow
Test
Only indicated in cases with gastrointestinal symptoms. Following barium swallow, x-rays should be taken at 10 seconds, and at 5 and 10 minutes.[146][147][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barium swallow showing dilation of oesophagusGrupo de Estudo em Correlalacao Anatomo-Clinica, Clínica Médica, Pontificia Universidade Catolica de Campinas, Sao Paulo, Brazil; used with permission [Citation ends].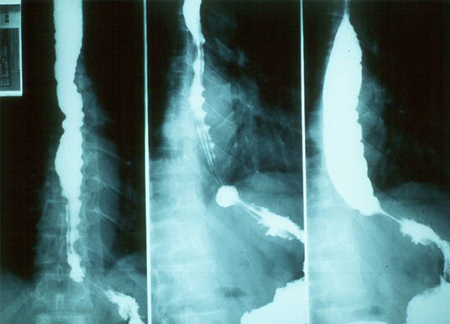
Result
achalasia
barium enema
Test
Only indicated in cases with gastrointestinal symptoms. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barium enema showing excessive dilation of sigmoid colonGrupo de Estudo em Correlalacao Anatomo-Clinica, Clínica Médica, Pontificia Universidade Catolica de Campinas, Sao Paulo, Brazil; used with permission [Citation ends].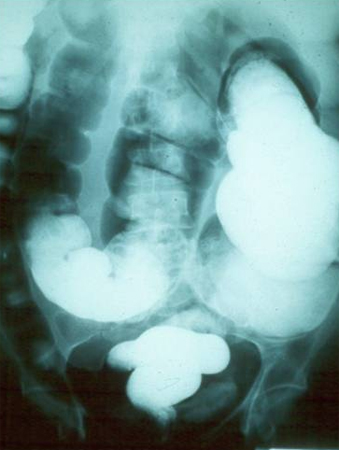
Result
megacolon
Investigations to consider
culture (blood and cerebrospinal fluid)
Test
An indirect parasitological method. The sensitivity of this method is limited by the level of parasitaemia, and false negative results are common, but specificity is high. Involves the use of a specialised liquid culture medium that is not available commercially.
Result
epimastigote forms of Trypanosoma cruzi
xenodiagnosis
Test
Indirect parasitological method. 30 to 40 laboratory-reared insects are allowed to feed directly (or indirectly) on the blood of a person suspected to have Chagas disease. After 1 month, the intestinal contents of the insects are extracted and examined microscopically for the presence of parasites.
The sensitivity of this method is limited by the level of parasitaemia, and false negative results are common, but specificity is high (up to 100%), and allows differentiation of T. cruzi from T rangeli.
Results are not available in time for short-term clinical management decisions.
Result
epimastigote forms of Trypanosoma cruzi
cerebrospinal fluid analysis
Test
These results occur in cases of meningoencephalitis with no mass effect signs (reactivation).
Result
microbiological: motile trypomastigote forms of Trypanosoma cruzi; cytological/biochemical assay: elevated cells, normal levels of glucose and protein
coagulation profile
Test
Indicated in cases with hepatic failure or haemorrhagic manifestations.
Result
prolonged prothrombin time
ambulatory 24-hour ECG
Test
Patients with cardiac symptoms suggestive of arrhythmias (e.g., palpitations, presyncope, or syncope) or ECG changes consistent with heart disease must be monitored to detect arrhythmias.
Principal predictors of sudden death are indicators of ventricular dysfunction, ventricular tachycardia on resting ECG or on ambulatory monitoring, sinus node dysfunction, and high-degree heart block.[34][148]
Result
bradyarrhythmias (atrioventricular block, sinoatrial block, sinus node dysfunction); tachyarrhythmias (non-sustained or sustained ventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, or atrial flutter)
exercise testing
Test
Patients with cardiac symptoms or ECG changes consistent with heart disease must be monitored to identify exercise-induced arrhythmias and to assess functional capacity and chronotropic response.
Principal predictors of sudden death are indicators of ventricular dysfunction, ventricular tachycardia on resting ECG or on ambulatory monitoring, sinus node dysfunction, and high-degree heart block.[34][148]
Result
acute phase: T wave alteration, prolonged PR interval, sinus tachycardia, low QRS voltage; chronic phase: bradycardia, sinus node dysfunction, paired ventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, left bundle branch block, low QRS voltage, Q waves, right bundle branch block
echocardiography
Test
Indicated in patients with clinical, radiological, or ECG evidence of functional cardiac disturbance. An important test considering the high frequency of pericardial effusion in patients with acute Chagas disease, and myocardial dysfunction in patients with chronic Chagas-related cardiomyopathy.
May show impaired biventricular function and abnormal wall motion and cardiac structures.[4][14]
Result
acute phase: pericardial effusion and transitory myocardial dysfunction; chronic phase: biventricular dysfunction with diffuse or segmental pattern (more frequent), with characteristic aneurysm
oesophageal manometry
upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
Test
Used in cases with intense epigastric pain refractory to specific treatment. Also useful for investigation of haematemesis, persistent vomiting, dysphagia, or anaemia. Upper digestive endoscopy is not indicated for diagnosis of mega-oesophagus.
Patients with impaired oesophageal motility are at increased risk of reflux oesophagitis and oesophageal carcinoma, and screening for these conditions may be indicated, especially if a change of symptoms has occurred.[34]
Result
inflammation, bleeding
cranial CT/MRI
Test
Used in cases of suspected meningoencephalitis in severe acute-phase disease or reactivation disease in immunosuppressed patients.
May also be used to evaluate for cardioembolic ischaemic stroke in patients with chronic-phase disease with cardiac involvement.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI brain in a patient with AIDS and reactivation of Chagas disease in CNSGrupo de Estudos em Doenca de Chagas (GEDoCH), Departamento de Clínica Médica, Faculdade de Ciências Médicas, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Sao Paulo, Brazil; used with permission [Citation ends].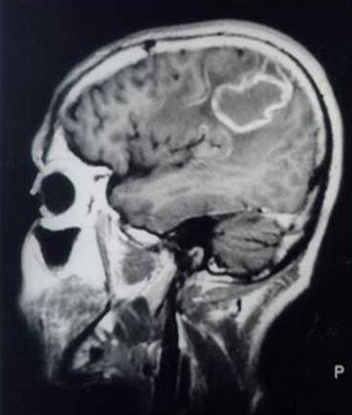 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI brain in a patient with AIDS and reactivation of Chagas disease in CNSGrupo de Estudos em Doenca de Chagas (GEDoCH), Departamento de Clínica Médica, Faculdade de Ciências Médicas, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Sao Paulo, Brazil; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI brain in a patient with AIDS and reactivation of Chagas disease in CNSGrupo de Estudos em Doenca de Chagas (GEDoCH), Departamento de Clínica Médica, Faculdade de Ciências Médicas, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Sao Paulo, Brazil; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
singular or multiple hypodensic pseudo tumour-like lesions (meningoencephalitis); hypodense lesions (cardioembolic ischaemic stroke)
cardiac MRI
Test
Indicated in select patients with Chagas cardiomyopathy to assess the extent of fibrosis, if available.[2]
Result
fibrosis
nuclear medicine testing
Test
Indicated to assess biventricular function when echocardiography is inadequate if available, and when it is desirable to evaluate myocardial perfusion or sympathetic innervation.[2]
Result
myocardial dysfunction
cardiac catheterisation and coronary angiography
Test
May be required in patients with disabling, angina-like symptoms to rule out concomitant coronary artery disease. Right cardiac catheterisation must be performed in patients with advanced heart failure to assess the feasibility of cardiac transplantation.[2]
Result
coronary vessel anomalies
Emerging tests
immunochromatography
Test
Immunochromatography tests for Chagas disease, such as rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) or lateral flow assays, are emerging investigations that have been developed and used for Chagas disease diagnosis.[140]
RDTs were developed as an easy-to-use alternative to conventional tests. Although they have high validity for diagnosing chronic Chagas disease, they are not yet used for this purpose.[141] RDT use is limited to diagnostic screening in the field. If the test is positive, confirmation with other serological tests is necessary.
Result
antibody titre above locally validated threshold
commercial polymerase chain reaction (PCR) kits
Test
Commercial PCR kits for the detection and quantification of T. cruzi in blood samples are available.[142] The kits may become a standard test for molecular diagnosis in endemic countries in the future.
Result
evidence of Trypanosoma cruzi DNA
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer