Management of congenital (physiological) phimosis is expectant until the age of puberty (typically around 12 years of age). Parents and patients should be counselled on good hygiene practices and avoidance of forcible preputial retraction.[42]Dave S, Afshar K, Braga LH, et al. Canadian Urological Association guideline on the care of the normal foreskin and neonatal circumcision in Canadian infants (full version). Can Urol Assoc J. 2018 Feb;12(2):E76-99.
https://www.cua.org/guidelines
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29381458?tool=bestpractice.com
After puberty, definitive treatment (e.g., topical corticosteroid cream or circumcision) may be recommended.[11]European Association of Urology; European Society for Paediatric Urology. EAU guidelines on paediatric urology. Apr 2024 [internet publication].
https://uroweb.org/guidelines/paediatric-urology
Paraphimosis is a urological emergency. If the foreskin is not immediately reducible by manual technique (or other conservative therapeutic measure), paraphimosis requires surgical intervention to release the constricting foreskin.
Surgery should be discussed as an option for patients with hypospadias and congenital penile curvature >30 degrees.
Concealed penis usually resolves over time as children age and pre-pubertal fat recedes. If concealed penis persists into puberty or adulthood, treatment may include weight loss or phalloplasty. In severe cases, earlier surgical intervention may be appropriate.
Phimosis
Expectant management for congenital (physiological) phimosis is preferred up to the time of puberty (typically around 12 years of age).[11]European Association of Urology; European Society for Paediatric Urology. EAU guidelines on paediatric urology. Apr 2024 [internet publication].
https://uroweb.org/guidelines/paediatric-urology
[46]The Royal Children's Hospital Melbourne. Clinical practice guidelines: the penis and foreskin. Jul 2018 [internet publication].
https://www.rch.org.au/clinicalguide/guideline_index/The_penis_and_foreskin
Reassurance to parents and child about normal penile anatomy and proper hygiene (without the need to forcibly retract the foreskin) will generally suffice. Routine cleaning of the external skin is desirable, but it is not necessary to retract the phimotic foreskin for cleaning until natural separation of the foreskin occurs.[42]Dave S, Afshar K, Braga LH, et al. Canadian Urological Association guideline on the care of the normal foreskin and neonatal circumcision in Canadian infants (full version). Can Urol Assoc J. 2018 Feb;12(2):E76-99.
https://www.cua.org/guidelines
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29381458?tool=bestpractice.com
Persistent phimosis
Phimosis persisting after puberty and into adulthood is generally treated with topical corticosteroid.[11]European Association of Urology; European Society for Paediatric Urology. EAU guidelines on paediatric urology. Apr 2024 [internet publication].
https://uroweb.org/guidelines/paediatric-urology
[47]Webster TM, Leonard MP. Topical steroid therapy for phimosis. Can J Urol. 2002 Apr;9(2):1492-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12010594?tool=bestpractice.com
[48]Monsour MA, Rabinovitch HH, Dean GE. Medical management of phimosis in children: our experience with topical steroids. J Urol. 1999 Sep;162(3 Pt 2):1162-4.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10458456?tool=bestpractice.com
[49]Ghysel C, Vander Eeckt K, Bogaert GA. Long-term efficiency of skin stretching and a topical corticoid cream application for unretractable foreskin and phimosis in prepubertal boys. Urol Int. 2009;82(1):81-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19172103?tool=bestpractice.com
Results from one systematic review (that included adolescents up to age 17 years) indicate that topical corticosteroid may resolve phimosis (low-quality evidence).[50]Moreno G, Ramirez C, Corbalán J, et al. Topical corticosteroids for treating phimosis in boys. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jan 25;1(1):CD008973.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38269441?tool=bestpractice.com
Acquired or pathological phimosis (e.g., cicatrix or balanitis xerotica obliterans [BXO] / lichen sclerosis) requires treatment regardless of age.
Phimosis: indications for surgery
Patients with phimosis who do not respond to or cannot tolerate a course of properly applied topical corticosteroid are managed with circumcision.[11]European Association of Urology; European Society for Paediatric Urology. EAU guidelines on paediatric urology. Apr 2024 [internet publication].
https://uroweb.org/guidelines/paediatric-urology
[35]McGregor TB, Pike JG, Leonard MP. Pathologic and physiologic phimosis: approach to the phimotic foreskin. Can Fam Physician. 2007 Mar;53(3):445-8.
http://www.cfp.ca/content/53/3/445.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17872680?tool=bestpractice.com
If the patient or carer wishes to avoid the cosmetic effect of circumcision but needs surgical intervention, they may be offered a preputioplasty.[11]European Association of Urology; European Society for Paediatric Urology. EAU guidelines on paediatric urology. Apr 2024 [internet publication].
https://uroweb.org/guidelines/paediatric-urology
A preputioplasty consists of limited dorsal slit(s) with transverse closure made along the constricting band of skin. Preputioplasty can be an effective alternative to full circumcision in most children; however, patients with BXO should undergo standard circumcision.[51]Cuckow PM, Rix G, Mouriquand PD. Preputial plasty: a good alternative to circumcision. J Pediatr. Surg. 1994 Apr;29(4):561-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8014816?tool=bestpractice.com
[52]British Association of Paediatric Surgeons. Management of foreskin conditions. Jun 2006 [internet publication].
https://www.baps.org.uk/resources/management-foreskin-conditions
Paraphimosis
Paraphimosis should be managed with immediate manual reduction. The goal of treatment is prompt reduction of the foreskin to its normal anatomical position (distal to the glans penis).
To perform manual reduction, adequate anaesthesia is administered in the form of dorsal penile nerve block or ring block with local anaesthetic. Children may require conscious sedation and/or general anaesthesia. Circumferential pressure around the oedematous ring of foreskin for several minutes may help to reduce the oedema. Both thumbs are placed on the glans with the fingers wrapped around the shaft of the penis proximal to the foreskin. Gentle pressure is applied to pull the foreskin with the fingers and push the glans with the thumbs until the foreskin is reduced to its anatomical position.[53]Little B, White M. Treatment options for paraphimosis. Int J Clin Pract. 2005 May;59(5):591-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15857356?tool=bestpractice.com
Water-based lubrication may facilitate preputial reduction.[54]American Urological Association. Urologic emergencies. Nov 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.auanet.org/meetings-and-education/for-medical-students/medical-students-curriculum/urologic-emergencies
Paraphimosis: difficulty with manual reduction
Several therapeutic measures can be considered if manual reduction is difficult. Compression wrap, application of granulated sugar, hyaluronidase injection, and puncture technique are options.[55]Mackway-Jones K, Teece S. Best evidence topic reports. Ice, pins, or sugar to reduce paraphimosis. Emerg Med J. 2004 Jan;21(1):77-8.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1756379
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14734388?tool=bestpractice.com
However, reduction of the paraphimotic prepuce is a surgical emergency, and additional therapeutic measures may require time to be effective.
Applying granulated sugar to the area of oedema, or wrapping a glucose-soaked gauze around the penis for 10 to 20 minutes before attempted manual reduction, may help to extract some of the oedema by osmosis.[56]Cahill D, Rane A. Reduction of paraphimosis with granulated sugar. BJU Int. 1999 Feb;83(3):362.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10375281?tool=bestpractice.com
Note that in some cases topical administration of granulated sugar may take 1 to 2 hours to be effective.[53]Little B, White M. Treatment options for paraphimosis. Int J Clin Pract. 2005 May;59(5):591-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15857356?tool=bestpractice.com
[57]Kerwat R, Shandall A, Stephenson B. Reduction of paraphimosis with granulated sugar. Br J Urol. 1998 Nov;82(5):755.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9839597?tool=bestpractice.com
Needle puncture may be employed if paraphimosis cannot be treated with more conservative measures.[52]British Association of Paediatric Surgeons. Management of foreskin conditions. Jun 2006 [internet publication].
https://www.baps.org.uk/resources/management-foreskin-conditions
Pressure is applied following needle puncture to facilitate reduction of oedema before manual reduction is attempted.[58]Reynard JM, Barua JM. Reduction of paraphimosis the simple way - the Dundee technique. BJU Int. 1999 May;83(7):859-60.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10368214?tool=bestpractice.com
Injection of hyaluronidase into the oedematous tissue may break down hyaluronic acid and its subsequent osmotic gradient.[52]British Association of Paediatric Surgeons. Management of foreskin conditions. Jun 2006 [internet publication].
https://www.baps.org.uk/resources/management-foreskin-conditions
[59]Litzky GM. Reduction of paraphimosis with hyaluronidase. Urology. 1997 Feb;50(3):160.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9218042?tool=bestpractice.com
Wrapping the phallus with a tight bandage may help to reduce oedema.[60]Pohlman GD, Phillips JM, Wilcox DT. Simple method of paraphimosis reduction revisited: point of technique and review of the literature. J Pediatr Urol. 2013 Feb;9(1):104-7.
https://www.jpurol.com/article/S1477-5131(12)00170-2/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22827972?tool=bestpractice.com
Autoreduction of the foreskin has been reported, but manual reduction may be required when the compression wrap is removed.
If conservative measures fail, definitive management in terms of either dorsal slit or circumcision may be performed.[33]Choe JM. Paraphimosis: current treatment options. Am Fam Physician. 2000 Dec 15;62(12):2623-6, 2628.
http://www.aafp.org/afp/2000/1215/p2623.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11142469?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ParaphimosisFrom the collection of Nicol Corbin Bush, MD [Citation ends].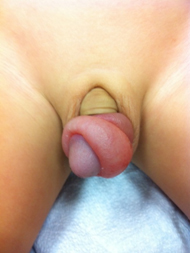
Hypospadias
Although some minor forms of hypospadias do not require surgical intervention, infants with hypospadias should be referred to a specialist for further evaluation to determine the severity of the condition. The goals of treatment are to restore normal urinary function, sexual function, and cosmesis.
Surgical intervention can be performed in most patients on an outpatient basis as early as 3 months of age.[61]Bush NC, Holzer M, Zhang S, et al. Age does not impact risk for urethroplasty complications after tubularized incised plate repair of hypospadias in prepubertal boys. J Pediatr Urol. 2013 Jun;9(3):252-6.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22542204?tool=bestpractice.com
The patient may need a postoperative urethral stent for up to 2 weeks after surgery depending upon the complexity of the repair.
Boys with an incomplete prepuce should not undergo circumcision in the neonatal period and should instead be referred to a specialist. The foreskin can be reconstructed or a circumcision can be performed at the time of urethroplasty with similar outcomes in distal hypospadias.[62]Snodgrass W, Dajusta D, Villanueva C, et al. Foreskin reconstruction does not increase urethroplasty or skin complications after distal TIP hypospadias repair. J Pediatr Urol. 2013 Aug;9(4):401-6.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22854388?tool=bestpractice.com
If megameatus with intact prepuce (a mild variant of distal hypospadias) is discovered during routine neonatal circumcision, the circumcision should be completed and the patient referred electively for urological evaluation thereafter.[63]Snodgrass WT, Khavari R. Prior circumcision does not complicate repair of hypospadias with an intact prepuce. J Urol. 2006 Jul;176(1):296-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16753427?tool=bestpractice.com
Not all patients with hypospadias will benefit from preoperative administration of topical oestrogen or testosterone, and use of topical corticosteroids should be considered for each individual patient.[64]Godlewski KF, Mittal S, Hyacinthe N, et al. Does preoperative testosterone administration decrease complications in distal hypospadias repair with urethroplasty? J Urol. 2023 Aug;210(2):352-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37195856?tool=bestpractice.com
[65]Thanneeru SK, Gupta A, Chanchlani R, et al. Preoperative topical estrogen application in the management of hypospadias: a systematic review. Pediatr Surg Int. 2024 May 13;40(1):132.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38739164?tool=bestpractice.com
[66]Wright I, Cole E, Farrokhyar F, et al. Effect of preoperative hormonal stimulation on postoperative complication rates after proximal hypospadias repair: a systematic review. J Urol. 2013 Aug;190(2):652-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23597451?tool=bestpractice.com
[67]Netto JM, Ferrarez CE, Schindler Leal AA, et al. Hormone therapy in hypospadias surgery: a systematic review. J Pediatr Urol. 2013Dec;9(6 Pt B):971-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23602841?tool=bestpractice.com
Congenital penile curvature and/or torsion
Surgery to straighten the penis should be offered for congenital penile curvature >30 degrees or torsion >90 degrees. This can be done in conjunction with a circumcision or with foreskin preservation.
Surgery for curvature can be deferred until after puberty.[68]European Association of Urology. EAU guidelines on sexual and reproductive health. Apr 2024 [internet publication].
https://uroweb.org/guidelines/sexual-and-reproductive-health/chapter/penile-curvature
Concealed penis
Need for, and timing of, management for concealed penis remains controversial. Although some advocate early intervention, most paediatric urologists feel that observation may be warranted up until the age of toilet training (2-3 years of age).[1]Radhakrishnan J, Razzaq A, Manickam K, et al. Concealed penis. Pediatr Surg Int. 2002 Dec;18(8):668-72.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12598960?tool=bestpractice.com
[69]Borsellino A, Spagnoli A, Vallasciani S, et al. Surgical approach to concealed penis: technical refinements and outcome. Urology. 2007 Jun;69(6):1195-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17572214?tool=bestpractice.com
In this age group, re-distribution of body fat often leads to spontaneous resolution of the buried penis.
If resolution has not occurred by 3 years of age, improvement without surgical intervention is unlikely. In cases of congenital concealed penis (congenital megaprepuce) that are associated with an excess of inner preputial skin with a relative paucity of shaft skin, surgical intervention is warranted at an earlier date. In cases of concealed penis related to trauma or postoperative scarring, surgery is also indicated.
Older boys and adults with concealed penis are unlikely to have spontaneous resolution. Weight loss is recommended primarily, with urological surgical options also available. Although weight loss may help in adolescents and adults, the psychological impact of the condition and the low rate of improvement may warrant surgical referral. Several operative techniques have been described, although treatment preferences vary among patient populations and surgeons.[1]Radhakrishnan J, Razzaq A, Manickam K, et al. Concealed penis. Pediatr Surg Int. 2002 Dec;18(8):668-72.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12598960?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Tang SH, Kamat D, Santucci RA. Modern management of adult-acquired buried penis. Urology. 2008 Jul;72(1):124-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18343486?tool=bestpractice.com
[25]Jones SA, Flynn RJ. An unusual (and somewhat piercing) cause of paraphimosis. Br J Urol. 1996 Nov;78(5):803-4.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8976792?tool=bestpractice.com
[26]Higgins SP. Painful swelling of the prepuce occurring during penile erection. Genitourin Med. 1996 Dec;72(6):426.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1195731/pdf/genitmed00012-0040.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9038639?tool=bestpractice.com
[32]Kiss A, Kiraly L, Kutasy B, et al. High incidence of balanitis xerotica obliterans in boys with phimosis: prospective 10-year study. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005 Jul-Aug;22(4):305-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16060864?tool=bestpractice.com
[33]Choe JM. Paraphimosis: current treatment options. Am Fam Physician. 2000 Dec 15;62(12):2623-6, 2628.
http://www.aafp.org/afp/2000/1215/p2623.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11142469?tool=bestpractice.com
[41]Maizels M, Zaontz M, Donovan J, et al. Surgical correction of the buried penis: description of a classification system and a technique to correct the disorder. J Urol. 1986 Jul;136(1 Pt 2):268-71.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2873259?tool=bestpractice.com
[59]Litzky GM. Reduction of paraphimosis with hyaluronidase. Urology. 1997 Feb;50(3):160.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9218042?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Congenital buried penisFrom the collection of Nicol Corbin Bush, MD [Citation ends].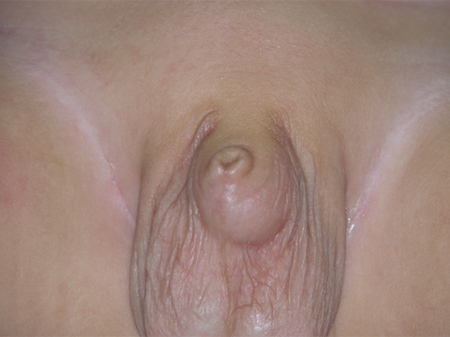 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Congenital buried penis: abundant inner preputial skin with paucity of shaft skinFrom the collection of Nicol Corbin Bush, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Congenital buried penis: abundant inner preputial skin with paucity of shaft skinFrom the collection of Nicol Corbin Bush, MD [Citation ends].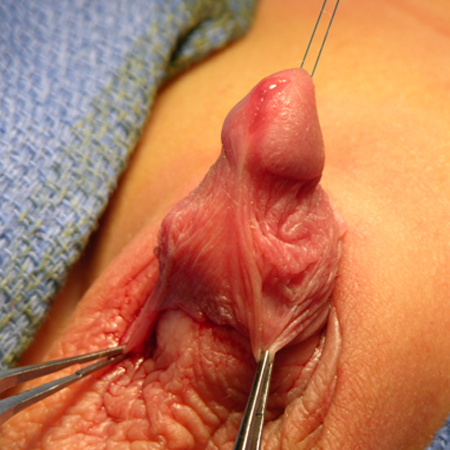 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Congenital buried penisFrom the collection of Warren T. Snodgrass, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Congenital buried penisFrom the collection of Warren T. Snodgrass, MD [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Repaired congenital buried penis (with bilateral hernia repair and scrotoplasty)From the collection of Warren T. Snodgrass, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Repaired congenital buried penis (with bilateral hernia repair and scrotoplasty)From the collection of Warren T. Snodgrass, MD [Citation ends].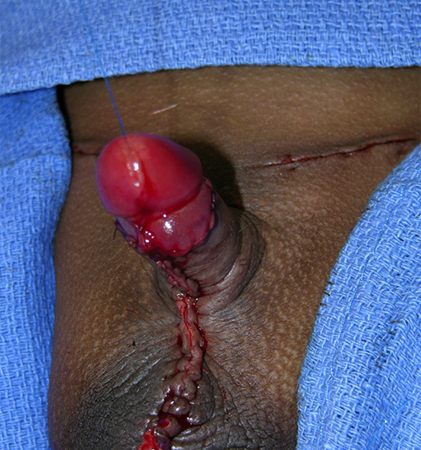
Micropenis
In true cases of micropenis (stretched penile length that is 2.5 or more standard deviations less than the mean for age), endocrine evaluation by a specialist is recommended.[45]Hatipoğlu N, Kurtoğlu S. Micropenis: etiology, diagnosis and treatment approaches. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2013;5(4):217-23.
https://jcrpe.org/jvi.aspx?un=JCRPE-01058
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24379029?tool=bestpractice.com

 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Congenital buried penis: abundant inner preputial skin with paucity of shaft skinFrom the collection of Nicol Corbin Bush, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Congenital buried penis: abundant inner preputial skin with paucity of shaft skinFrom the collection of Nicol Corbin Bush, MD [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Congenital buried penisFrom the collection of Warren T. Snodgrass, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Congenital buried penisFrom the collection of Warren T. Snodgrass, MD [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Repaired congenital buried penis (with bilateral hernia repair and scrotoplasty)From the collection of Warren T. Snodgrass, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Repaired congenital buried penis (with bilateral hernia repair and scrotoplasty)From the collection of Warren T. Snodgrass, MD [Citation ends].