Images and videos
Images

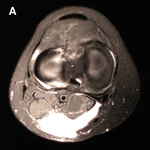
Popliteal cyst
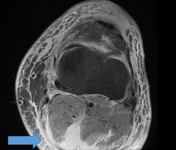
MRI depicting cyst in interval of medial gastrocnemius and semimembranosus
From the collection of Dr John D. Kelly IV; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Popliteal cyst
A ruptured haemorrhagic popliteal cyst extending in the calf
Stony Brook University Medical Center private collection; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
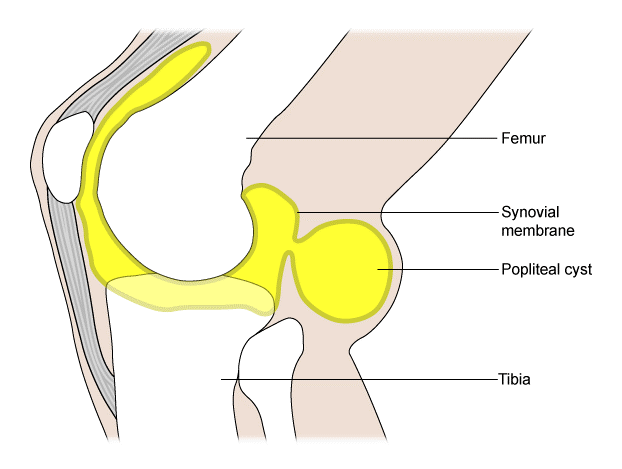
Popliteal cyst
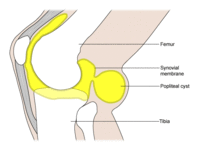
Popliteal cyst
Created by BMJ Publishing Group
See this image in context in the following section/s:
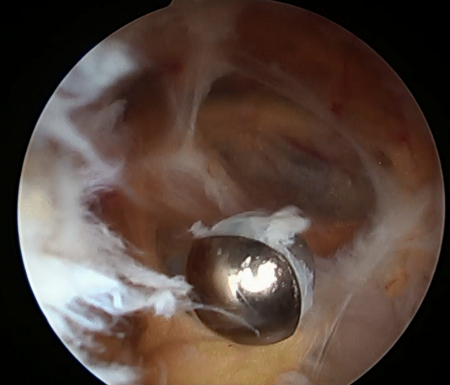
Popliteal cyst
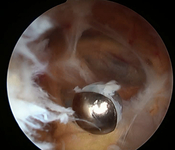
Synovitis within cyst
From the collection of Dr John D. Kelly IV; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Popliteal cyst
Preoperative T2-weighted MRI showing posterior fluid collection communicating with posterior medial joint in a patient with a popliteal cyst secondary to pigmented villonodular synovitis
Adapted from Tosti R, Kelly JD 4th. Pigmented villonodular synovitis presenting as a Baker cyst. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2011;40:528-531; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
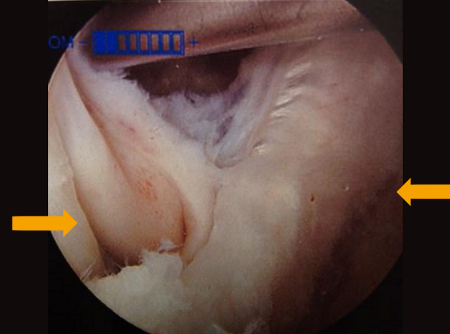
Popliteal cyst
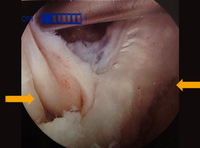
Interval of medial gastrocnemius and semimembranosus viewed with arthroscope
From the collection of Dr John D. Kelly IV; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
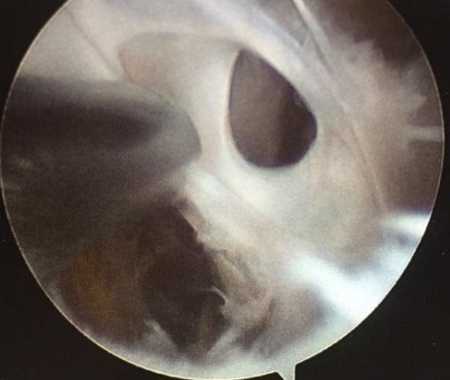
Popliteal cyst
Septae within a popliteal cyst
From the collection of Dr John D. Kelly IV; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
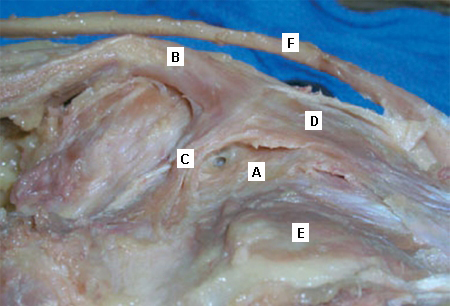
Popliteal cyst
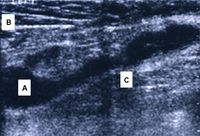
Anatomical dissection of the posteromedial knee capsule. The weak area (A) is identified between the two expansions of the semimembranosus muscle (B), the oblique popliteal ligament (C), and the expansion over the sheath of the popliteus muscle (D). The semitendinosus muscle (E) and popliteus muscle (F) are also indicated
Adapted from Labropoulos N, Shifrin DA, Paxinos O. New insights into the development of popliteal cysts. Br J Surg. 2004;91:1313-1318; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
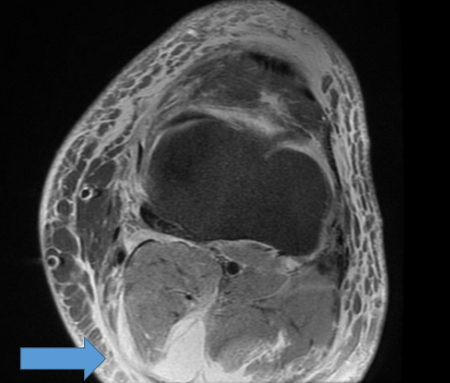
Popliteal cyst
Ruptured popliteal cyst dissection into gastrocnemius
From the collection of Dr John D. Kelly IV; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Popliteal cyst
Popliteal cyst lying in its most common location in the posteromedial popliteal fossa (A), dissecting through the deep fascia (B) and the medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle (C)
Adapted from Labropoulos N, Shifrin DA, Paxinos O. New insights into the development of popliteal cysts. Br J Surg. 2004;91:1313-1318; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
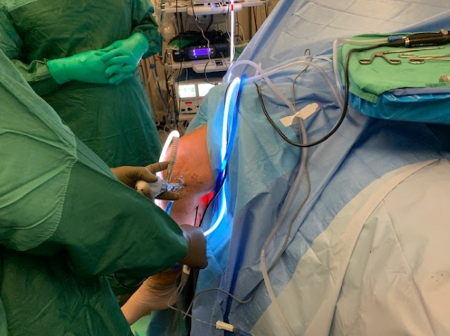
Popliteal cyst
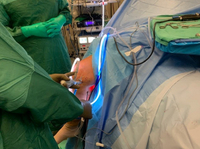
Arthroscopic resection of a popliteal cyst
From the collection of Dr John D. Kelly IV; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Popliteal cyst
Arthroscopic resection of a popliteal cyst
From the collection of Dr John Kelly IV; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
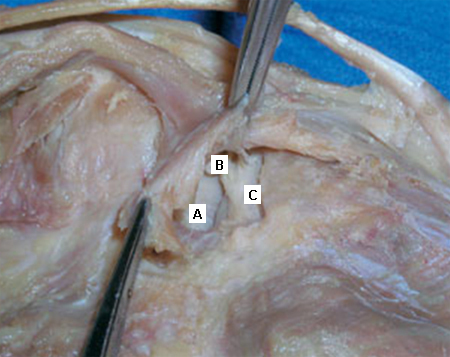
Popliteal cyst
Deep dissection of the posteromedial capsule. The two expansions of the semimembranosus muscle have been elevated, exposing the weak area of the capsule between the posterior cruciate ligament (A) and the posterior horn of the medial meniscus (B) that gives entry to the knee joint. The medial femoral condyle is also visible (C)
Adapted from Labropoulos N, Shifrin DA, Paxinos O. New insights into the development of popliteal cysts. Br J Surg. 2004;91:1313-1318; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
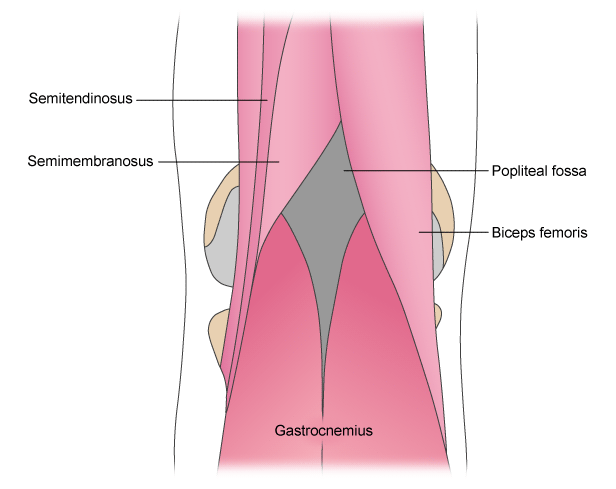
Popliteal cyst
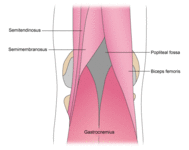
Muscles surrounding the popliteal fossa (view of posterior aspect of right knee)
Adapted by BMJ Evidence Centre from Gray's Anatomy
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer