History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
presence of risk factors
Risk factors include blunt chest wall trauma, physical abuse (particularly in children), osteoporosis, and participation in sports such as rowing and golf.
pain
Rib fractures produce chest wall pain that can often reduce ventilation by impairing chest wall movement.
dyspnoea
Chest wall pain can reduce ventilation by impairing chest wall movement.
Other diagnostic factors
uncommon
signs of impaired oxygenation
Impaired oxygenation can be due to impaired chest wall movement following chest wall pain or be indicative of underlying pneumothorax, haemothorax, or pulmonary contusion.
Rib fractures impair adequate ventilation, resulting in atelectasis, poor oxygenation, and respiratory compromise.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan showing large left-sided pneumothoraxFrom the collection of Dr Paul Novakovich; used with permission [Citation ends].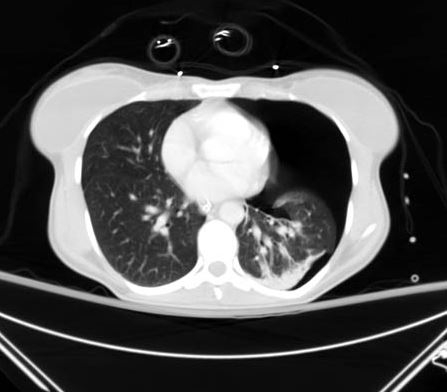 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR depicting the same pneumothorax as shown on CTFrom the collection of Dr Paul Novakovich; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CXR depicting the same pneumothorax as shown on CTFrom the collection of Dr Paul Novakovich; used with permission [Citation ends].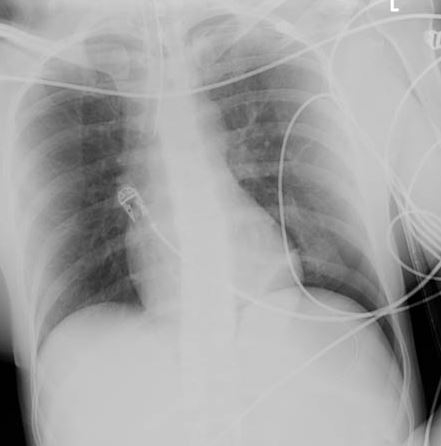
paradoxical chest wall motion
Paradoxical chest wall motion with inspiration or expiration is a sign of a flail chest. A flail chest results when multiple ipsilateral ribs are fractured in 2 or more places, resulting in an unstable segment of the chest wall. Flail chest is often accompanied by other injuries, and carries an increased risk of life-threatening pneumothorax, pulmonary contusion, and haemothorax, with an overall mortality of at least 5%.[38]
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer