Tests
1st tests to order
clinical diagnosis
Test
Frostbite is primarily a clinical diagnosis, where patients present with typical findings in association with cold exposure.
Imaging is not required for the diagnosis of frostbite but can be used to assess the severity of the injury and determine the prognosis.
Result
features of frostbite
Tests to consider
technetium-99m pertechnetate scintigraphy
Test
Measures tissue perfusion.
Provides a sensitive and specific assessment of the extent of deep tissue injury.
Some studies have found good correlation between scintigraphy findings at 48 hours and both intraoperative findings and ultimate prognosis.[2][3]
Can also be used to assess response to therapy.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: (A) Technetium-99m scans of the hands of a patient with frostbite. The terminal digits have reduced signal (especially in the left hand), suggesting that substantial tissue necrosis has occurred. (B) Clinical picture after a 5-day iloprost infusion showing the close correlation between the initial technetium-99m scans and the subsequent clinical appearanceHallam M-J, BMJ 2010;341:c5864 [Citation ends].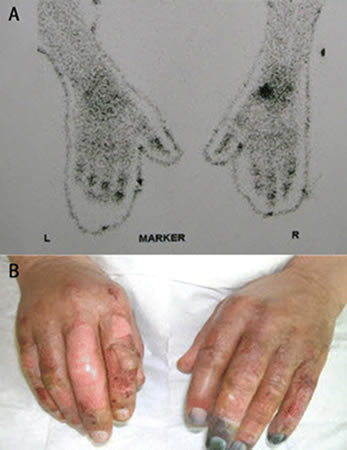
Result
poor perfusion of the bony tissue of the affected extremity
magnetic resonance angiography of affected extremity
Test
Allows direct visualization of vessels and tissues.
Easier to access than technetium-99m scans, so growing trend toward use of this modality.[14]
May be useful to predict tissue viability and guide earlier surgical amputation.[4][28]
May also have a role in guiding experimental therapies such as treatment with iloprost or recombinant tissue plasminogen activator.[4]
Result
visualization of occluded vessels, demarcation of ischemic tissue
plain radiography
Test
Only indicated if an associated fracture or joint dislocation is suspected.
Result
associated fracture or joint dislocation
Emerging tests
thermography and duplex imaging
Test
Poor perfusion is associated with a poor prognosis for the affected limb.
Result
visualization of perfused regions
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer