Tests
1st tests to order
WBC count
Test
Could be useful when IAA is suspected. Although WBC count is commonly elevated, a normal count does not exclude the diagnosis. Leukopenia is more common in older and immunocompromised patients.
Result
elevated with increased proportion of granulocytes (left shift), persistent leukocytosis or bandemia, or leukopenia
drainage culture
Test
Obtaining a culture once IAA has been identified and drained is particularly important in higher-risk patients, and patients with hospital-acquired IAA, to identify potential resistant or opportunistic pathogens.[2]
Result
detection and confirmation of pathogenic etiologic organisms
abdominal CT scan
Test
Easily identifies IAA. CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis with oral and intravenous contrast is very helpful to identify IAA and anastomotic leak, and to differentiate fluid collection from a bowel loop. Identifying an air-fluid collection or visualizing a leak into the fluid collection is usually diagnostic. Rim enhancement aids the diagnosis but cannot differentiate an abscess from an organized loculated fluid collection. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Abscess completely replacing pancreas and extending into portal hilum, with multiple gas bubbles and large air/fluid levelFrom the collection of Dr Ali F. Mallat and Dr Lena M. Napolitano; used with permission [Citation ends].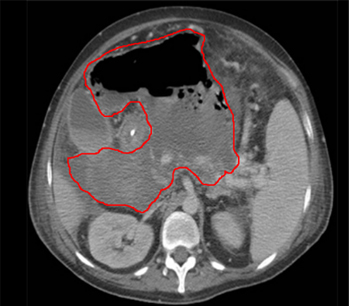 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Intra-abdominal abscess with small air bubble, secondary to perforated diverticulitisFrom the collection of Dr Ali F. Mallat and Dr Lena M. Napolitano; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Intra-abdominal abscess with small air bubble, secondary to perforated diverticulitisFrom the collection of Dr Ali F. Mallat and Dr Lena M. Napolitano; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan showing intra-abdominal abscess with small air bubbleFrom the collection of Dr Ali F. Mallat and Dr Lena M. Napolitano; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan showing intra-abdominal abscess with small air bubbleFrom the collection of Dr Ali F. Mallat and Dr Lena M. Napolitano; used with permission [Citation ends]. Avoid the use of noncontrast-enhanced CT imaging alongside contrast enhanced imaging; the addition of unenhanced CT does not provide additional diagnostic information and exposes patients to unnecessary radiation.[23][24]
Avoid the use of noncontrast-enhanced CT imaging alongside contrast enhanced imaging; the addition of unenhanced CT does not provide additional diagnostic information and exposes patients to unnecessary radiation.[23][24]
Result
visualization of IAA
Tests to consider
serum CRP
Test
Elevated CRP is consistent with an inflammatory state.
Result
may be elevated
serum erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Test
Elevated ESR is consistent with an inflammatory state.
Result
may be elevated
Gram stain of abscess fluid
Test
Obtaining a Gram stain once IAA has been identified and drained is particularly important in higher-risk patients, and patients with hospital-acquired IAA, to identify potential resistant or opportunistic pathogens.[2]
Result
positive for pathogenic organism
serum glucose
Test
Useful for managing diabetic patients with IAA, although treating the hyperglycemia before draining the abscess may be difficult. In addition, when patients become increasingly hyperglycemic with increasing insulin demands, systemic infection should be suspected, including intra-abdominal infection and IAA.
Result
elevated if diabetes present
abdominal ultrasound
Test
May be a useful aid in characterizing an intrahepatic abscess but its sensitivity is less than that of CT in IAA. Ultrasound may be useful as an initial diagnostic evaluation or when a patient cannot be moved to a CT scanner due to hemodynamic instability. Some studies have reported false positives for IAA using ultrasonography in patients with Crohn disease.[25]
Result
visualization of IAA
abdominal MRI scan
Test
May be useful in evaluating pregnant patients with acute abdominal and pelvic pain, and patients with hepatic pathology. CT scan should be the first-line diagnostic test in all other patients.[28]
Result
visualization of IAA
Emerging tests
endoscopic ultrasound
Test
Has been used for evaluating and draining IAA adjacent to the gastrointestinal tract, with the largest experience being with pancreatic fluid collections. Other accessible areas include the pelvis and perirectal space, and the subphrenic and perihepatic spaces. Endoscopic ultrasound requires specialized expertise; data regarding its safety and effectiveness in draining IAA are preliminary. However, endoscopic ultrasound may be useful in critically ill patients requiring bedside procedures or for IAA not amenable to other conventional therapies.[26] The experience remains limited to case reports.
Result
visualization of IAA
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer