Differentials
Common
Corneal ulcer
History
contact lens wear (especially extended wear) is frequently associated; painful, red eye with watery or mucoid ocular discharge; rarely frank purulence; acute to subacute onset
Exam
fluorescein staining of corneal epithelial defect with surrounding corneal infiltration; periorbital redness and swelling in severe cases requires urgent ophthalmologist consultation
1st investigation
Other investigations
Dry eye syndrome (tear dysfunction syndrome)
History
intermittent visual blurring; may be worse in morning or evening; gritty ocular sensation; light sensitivity without true photophobia; may not be relieved by artificial tear use; often history of corneal disease and/or contact lens wear
Exam
may be normal without use of a slit lamp; ocular surface irregularity
1st investigation
- tear breakup time:
<10 seconds
More
Other investigations
- Schirmer test with anesthesia:
<10 millimeters in 5 minutes
More
Dry age-related macular degeneration
History
acute or chronic painless loss of vision; distortion in central vision; age >50 years; smoker; thin; white people affected more than people of other races
Exam
distorted central acuity; normal peripheral vision; intraretinal lipids on fundoscopy
1st investigation
- fluorescein angiogram:
drusen, loss of retinal pigment epithelium
More
Other investigations
Posterior uveitis
History
painful onset with clouding of vision; occurs slowly; flashes and floaters; photophobia; pain with eye movement; correlation of recent systemic infection or autoimmune disease
Exam
tender red eye; possible nodular lesions on sclera; cloudy/obscured view of retina
1st investigation
- CBC with differentials:
elevated WBC count
More
Other investigations
- B-scan ultrasound:
vitreous opacity; retinal elevation
More
Cataract
History
typically painless; progressive loss of vision (may be sudden/rapid); symptoms may be asymmetric; patient may discover vision loss on covering one eye
Exam
redness; relative afferent pupillary defect and/or fundus abnormalities; blurred vision; may be difficult to visualize the fundus
1st investigation
- potential acuity meter:
better acuity close up than at distance
More
Other investigations
Nondiabetic myopic lens shift
History
chronic progression of distance vision deterioration
Exam
blurred vision; vision may improve with use of a pinhole; near vision better than distance vision
1st investigation
- retinoscopy:
may see oil droplet cataract in lens
More
Other investigations
Wet age-related macular degeneration
History
acute or chronic painless loss of vision; distortion in central vision; age >50 years; smoker; thin; white people affected more than people of other races
Exam
distorted central acuity, normal peripheral vision, subretinal hemorrhage, or lipid on fundoscopy
1st investigation
- fluorescein angiogram:
choroidal neovascularization
More
Other investigations
Vitreous hemorrhage
History
sudden onset of floaters followed by diffuse vision loss; monocular; usually painless; strong association with retinal neovascularization; associated with diabetes and sickle cell disease; may occur after trauma
Exam
severe vision loss; no afferent pupillary defect; possible cells in anterior chamber; blood in vitreous humor with poor view of fundus
1st investigation
- blood sugar:
elevated or normal
More
Retinal venous occlusion
History
acute monocular loss of portion of visual field (often inferior); central vision may vary from being normal (with branch occlusion) to worse than 20/400 (with central occlusion); positive risk factors include hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease
Exam
decreased visual acuity; loss of peripheral field; no eye redness; intraretinal hemorrhage and lipids; dilated retinal veins
1st investigation
- fluorescein angiogram:
slow-filling veins
More
Other investigations
- lipid panel:
elevated LDLs and triglycerides; reduced HDLs
More - echocardiogram:
valvular or intramural thrombi
More - prothrombin time:
elevated or normal
More - partial thromboplastin time:
elevated or normal
More - international normalized ratio:
elevated or normal
More - clotting panel:
may be abnormal in young patients
More
Retinal arterial occlusion
History
acute monocular loss of portion of visual field (often inferior); likely to have central vision loss; positive risk factors include hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease; rarely, accidental injection of cosmetic facial filler into retinal artery
Exam
decreased visual acuity; loss of peripheral field; no eye redness; intraretinal hemorrhage; loss of arteriolar filling; dilated retinal veins
1st investigation
- fluorescein angiogram:
slow-filling arterioles
More
Other investigations
- lipid panel:
elevated LDLs and triglycerides; reduced HDLs
More - echocardiogram:
valvular or intramural thrombi
More - prothrombin time:
elevated or normal
More - partial thromboplastin time:
elevated or normal
More - international normalized ratio:
elevated or normal
More - clotting panel:
may be abnormal in young patients
More
Stroke
History
sudden onset of homonymous visual field loss or binocular central vision loss; painless; prior amaurosis fugax or transient ischemic attack; other neurologic symptoms include weakness, numbness, tingling, ataxia, slurred speech; may be accompanied by sensory or motor deficits but may be isolated; evolution over hours to days, usually with spontaneous improvement but without complete resolution; vascular disease such as atherosclerotic coronary artery disease or atherosclerotic peripheral vascular disease frequently also exists
Exam
complete or incomplete homonymous hemianopia, congruity varies with location of stroke (more posterior equates to more congruous); visual field defect may be absolute or scotomatous, may be present only with red test object; ophthalmologic exam normal except for afferent pupillary defect if optic tract involved; decreased visual acuity only if posterior or bilateral occipital infarction; homonymous hemianopia with left temporal and right nasal field loss indicates right-hand-sided lesions; homonymous hemianopia with right temporal and left nasal field loss indicates left-hand-sided lesions; loss of macular vision usually indicates bilateral occipital lobe infarction with damage to both occipital poles
1st investigation
- CT head without contrast:
shows area of infarction and hemorrhage
More
Other investigations
- MRI head with contrast:
area(s) of restricted diffusion on diffusion-weighted imaging, shows area of infarction and hemorrhage
More - perimetry (static or kinetic):
delineates extent and depth of field loss in homonymous hemianopia
More - CBC:
abnormal in hemorrhagic stroke
More - prothrombin time:
abnormal in hemorrhagic stroke
More - partial thromboplastin time:
abnormal in hemorrhagic stroke
More - homocysteine:
may be elevated
More - carotid duplex scan:
atherosclerotic carotid occlusive disease
More - magnetic resonance angiography:
vertebrobasilar or carotid occlusive disease
More - transesophageal echocardiogram:
possible thrombi identified
More
Migraine headache or migraine aura without headache (acephalgic migraine)
History
homonymous positive visual phenomenon; scintillating scotoma with fortification spectrum (expanding zigzag lines) developing over 20 to 30 minutes before spontaneous resolution; patient may report photophobia or phonophobia; may not be followed by headache
Exam
objective examination usually normal
1st investigation
- no initial test:
clinical diagnosis
Other investigations
- MRI head with gadolinium contrast:
normal
More
Pituitary tumor
History
sudden or subacute onset of central or peripheral vision loss; painless; progressive; may have galactorrhea, decreased libido, heat/cold intolerance, increasing size of hands/feet, and/or headache
Exam
bitemporal hemianopia; monocular or binocular loss of central acuity; afferent pupillary defect (if vision loss is asymmetric); ocular motility limitation from cranial nerve paresis
1st investigation
- automated perimetry:
bitemporal field defect confirmed
More
Other investigations
- MRI head and orbits:
sellar and/or suprasellar lesion
More
Diabetic retinopathy
History
longstanding (>10 years) diabetes with/without poor glycemic control; diabetes may be undiagnosed; vision loss rarely sudden; often asymmetric
Exam
decreased visual acuity; poorly reactive pupils (from autonomic neuropathy); iris neovascularization; retinal neovascularization; macular edema; tractional retinal detachment; may notice microaneurysms, dot-hemorrhages, blot-hemorrhages, flame-shaped hemorrhages, retinal or macular edema, hard exudates, cotton wool spots, venous loops, venous bleeding, or other intraretinal microvascular abnormalities
1st investigation
- ocular coherence tomography:
macular thickening or edema
More
Uncommon
Corneal hydrops
History
keratoconus and/or high myopic astigmatism; eye rubbing or Down syndrome (both associated with keratoconus); acute swelling, pain; acute vision loss with or without red eye
Exam
central corneal clouding with clear periphery; normal intraocular pressure; poor view of fundus because of cornea
1st investigation
- corneal topography:
irregular astigmatism with steepening of inferior cornea
More
Other investigations
Traumatic vision loss
History
sharp or blunt trauma to eye, orbit, or head; increased suspicion with loss of consciousness; history may be difficult to obtain
Exam
conscious patients: decreased visual acuity; poor color vision; afferent pupillary defect; conjunctival chemosis or hemorrhage; prolapsed ocular contents; hyphema; retinal hemorrhage and/or vitreous hemorrhage
1st investigation
- CT head and orbits:
fractures, foreign bodies, loss of globe contour may imply rupture
More
Other investigations
Optic neuritis
History
affects females more (female-to-male ratio is 3:2); typical age range is 15 to 45 years; usually painful especially with eye movement; subacute symptoms (days); prior neurologic symptoms (including paresthesias, Uhthoff phenomenon, and weakness) raise suspicions for demyelinating disease such as multiple sclerosis
Exam
decreased visual acuity; loss of color vision; visual field defect; relative afferent pupillary defect; normal optic disk (retrobulbar disease); disk swelling (papillitis)
1st investigation
- MRI head and orbits:
white matter lesions in demyelinating disease, optic nerve enhancement
More
Other investigations
- CBC with differentials:
elevated WBC count in infectious or inflammatory causes
More - syphilis serology:
positive in cases of syphilis
More - Lyme disease serology:
positive in cases of Lyme disease
More - tuberculosis serology:
positive in cases of tuberculosis
More - angiotensin-converting enzyme:
positive in cases of sarcoidosis
More
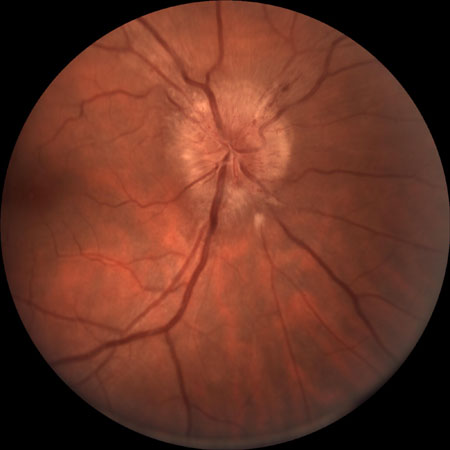
Papilledema
History
headache; transient visual obscuration; diplopia; slow progressive vision loss
Exam
bilateral optic disk swelling; visual field loss; loss of color vision
1st investigation
- MRI head and/or MR venography brain:
mass lesion, venous sinus thrombosis, meningeal enhancement, hydrocephalus, or normal
More
Other investigations
- lumbar puncture:
elevated opening pressure, chemistry or organisms present in cerebrospinal fluid
More
Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON)
History
more common in males; onset often in late teens or early 20s; heavy tobacco and/or alcohol use associated; family history of vision loss (usually in maternal lineage); sudden loss of central acuity, usually with good peripheral vision
Exam
central scotoma, typically with preserved peripheral vision; relative afferent pupillary defect; loss of color vision
1st investigation
- genetic testing:
LHON mutation present
More
Other investigations
Acute angle-closure glaucoma
History
very painful red eye with diffuse vision loss; possibly severe headache; possibly severe abdominal pain (may be the predominant symptom due to severity); may be preceded by similar but less severe attacks
Exam
tender red eye with cloudy cornea; poor view of fundus; pupil mid-dilated and fixed
1st investigation
Other investigations
Retinal detachment
History
flashes and floaters; curtain or veil over vision; sudden onset of painless vision loss; central vision may be involved; progression of field loss can be over hours to days
Exam
relative afferent pupillary defect; lower intraocular pressure on affected side; visual field defect by confrontation
1st investigation
Other investigations
- B-scan ultrasound:
retinal detachment; occasionally retinal break
More
Postoperative endophthalmitis
History
painful, red eye with acute vision loss in a patient with a recent history of cataract surgery or any history of intraocular surgery or injection
Exam
signs of inflammation, with hyperemia, chemosis and corneal edema, and hypopyon
1st investigation
- vitreous and aqueous samples for microbiology:
may reveal causative organism
More
Other investigations
- B-scan ultrasound:
may confirm vitreous involvement
More
Central retinal artery occlusion
History
sudden loss of central and peripheral vision in one eye; painless; may have had prior amaurosis fugax
Exam
severe monocular vision loss; relative afferent pupillary defect; Hollenhorst plaque in central retinal artery; "cherry red spot" in macula
1st investigation
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR):
normal for central retinal artery occlusion due to thromboembolism
More
Other investigations
- C-reactive protein (CRP):
normal for central retinal artery occlusion due to thromboembolism
More - fluorescein angiogram:
marked delay in retinal arteriolar filling
More - CBC:
anemia and thrombocytopenia possible
More - lipid panel:
elevated LDLs and triglycerides; reduced HDLs
More - echocardiogram:
valvular or intramural thrombi
More - prothrombin time:
elevated or normal
More - partial thromboplastin time:
elevated or normal
More - international normalized ratio:
elevated or normal
More - clotting panel:
may be abnormal in young patients
More
Pituitary apoplexy
History
severe headache with acute or subacute vision loss and onset of double vision; diplopia (may be absent if vision loss is so severe that diplopia cannot be appreciated); altered mental status
Exam
limited motility of one or both eyes; ptosis; poorly reactive and/or dilated pupils; optic nerve hemorrhages
1st investigation
- CT head:
may reveal hemorrhage in sella turcica lesion
More
Arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy/giant cell arteritis
History
sudden and profound vision loss; may have had prior amaurosis fugax; painless; may have headache; jaw claudication; proximal muscle weakness; anorexia and weight loss; incidence increases with age (more so at >80 years)
Exam
severe visual loss (often unable to see hand motions or worse); visual field defect; relative afferent pupillary defect; pale optic nerve swelling in affected eye with small optic nerve in fellow eye; optic nerve hemorrhages may be present
1st investigation
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR):
elevated in GCA
More - CRP:
elevated in GCA
More - CBC:
patients with GCA may have a normochromic, normocytic anemia with a normal WBC count and elevated platelet count; mild leukocytosis may occur
More - vascular ultrasonography:
mural inflammatory changes in GCA
More - temporal artery biopsy:
histopathology typically shows granulomatous inflammation in GCA
More
Other investigations
- high-resolution MRI:
mural inflammation or luminal changes of crania or extracranial arteries in patients with suspected GCA
More
Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
History
sudden loss of part of visual field in one eye (often inferior eye); painless; may have headache; may be noted on waking; 75% of affected people are >50 years; history of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor use for erectile dysfunction (which may potentially be associated with an increased risk of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy)
Exam
visual field defect; relative afferent pupillary defect; optic nerve swelling in affected eye with small optic nerve in fellow eye; optic nerve hemorrhages may be present
1st investigation
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate:
normal
More
Other investigations
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
History
painless monocular vision loss; no precipitating factors; lasts between 15 seconds and several minutes; vision lost in part of or all of field; sudden onset; remains unchanged until resolution; may also occur as binocular homonymous field loss; risk factors include hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia
Exam
normal unless event occurs during examination; if event occurs during the examination, expect decreased vision, field loss, afferent pupillary defect, or transient arterial flow abnormalities
1st investigation
- lipid panel:
elevated LDLs and triglycerides
More
Other investigations
Cancer-associated retinopathy
History
history of cancer, but may be the presenting symptom of systemic disease; flashes and/or floaters; other photopsias; nyctalopia (poor night vision)
Exam
blurred vision; preserved central acuity with loss of peripheral vision; pigmentary retinopathy in one or both eyes; fundus exam may be normal; poor pupillary reaction in severe disease
1st investigation
- electroretinogram:
markedly diminished rod function
More
Other investigations
- automated or kinetic perimetry:
constriction
More
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer