Tests
1st tests to order
transthoracic echo with color Doppler and contrast injection
Test
Performed as a screening test when clinical suspicion of condition is low.
Intravenous access is obtained, typically in an antebrachial vein or femoral vein.
Two 10 mL syringes are attached to a 3-way stopcock. About 9.5 mL of normal saline and 0.5 mL of air are drawn into a syringe and then rapidly agitated via the stopcock and the other syringe just prior to intravenous injection.
Echo images are continuously recorded over several cardiac cycles and the sequence is repeated several times with provocative maneuvers.
If upper extremity injection fails to show crossover despite a high suspicion of PFO, lower extremity injection may be used as this can be more sensitive.[20]
Result
color flow at the interatrial septum and crossover of microbubbles from right atrium to left atrium after intravenous injection of agitated saline
transesophageal echo with color Doppler and contrast injection
Test
Performed in cases where a definitive diagnosis is sought; the transthoracic echo is either equivocal or negative; there is uncertainty as to whether the patient has atrial septal defect or PFO; and diagnosis is likely to alter management. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Transesophageal echo showing a 2D image of the interatrial septum with location of the PFOFrom the collection of Kul Aggarwal, MD [Citation ends].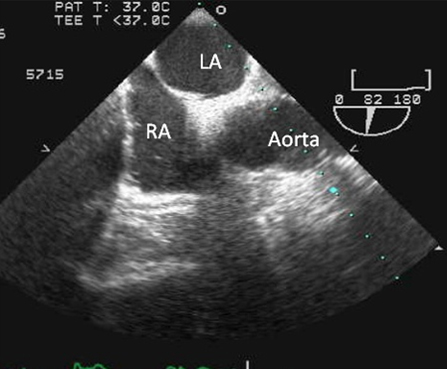 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Transesophageal echo with intravenous injection of agitated saline showing contrast crossing through PFO into left atriumFrom the collection of Kul Aggarwal, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Transesophageal echo with intravenous injection of agitated saline showing contrast crossing through PFO into left atriumFrom the collection of Kul Aggarwal, MD [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Transesophageal echo with color flow Doppler showing presence of PFOFrom the collection of Kul Aggarwal, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Transesophageal echo with color flow Doppler showing presence of PFOFrom the collection of Kul Aggarwal, MD [Citation ends].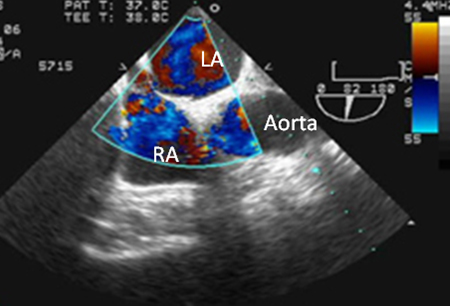
Result
visualization of defect, color flow at the interatrial septum and crossover of microbubbles from right atrium to left atrium after intravenous injection of agitated saline
Tests to consider
intracardiac echo
Test
Not routinely used as a diagnostic procedure for PFO because of its high cost.
Performed in conjunction with percutaneous closure of PFO.[21]
Advantage is elimination of need for deeper sedation and discomfort associated with a transesophageal echo.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Intracardiac echo showing a catheter placed across the PFO into the left atriumFrom the collection of Kul Aggarwal, MD [Citation ends].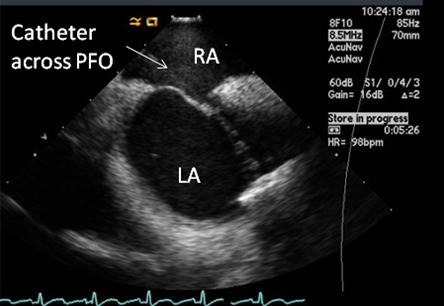
Result
visualization of PFO
ultrasound lower extremity
Test
Useful if suspected paradoxical embolism.
Result
deep venous thrombosis
MRI lower extremity
Test
Useful if suspected paradoxical embolism.
Result
deep venous thrombosis
tilt-table transesophageal echo
Test
Diagnosis of platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome is best made by tilt-table transesophageal echo (TEE). A diagnosis of PFO is established if an inserted TEE probe shows right-to-left shunting across the PFO resulting in hypoxemia in an upright position, and if there is a resolution of shunting and hypoxemia when the patient is in the recumbent position.
Result
right-to-left shunting and hypoxemia in an upright position; resolution in the recumbent position
Emerging tests
transcranial Doppler
Test
Modality not in common clinical use.
May be used in centers with particular expertise and where echo images are suboptimal.
Result
microbubbles in the cranial circulation immediately after intravenous saline
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer