Tests
1st tests to order
Gram and acid-fast stains
Test
The first test performed when Nocardia infection is suspected.
Gram stain allows differentiation of Nocardia from mycobacteria. Although it is less sensitive than Gram stain, modified acid-fast stain allows distinction between Nocardia and Actinomyces.[7] Should be done to confirm a suspicious positive sample on Gram stain. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Expectorated sputum specimen: modified acid-fast staining showing Nocardia speciesFrom the collection of Dr Jorge Garbino [Citation ends].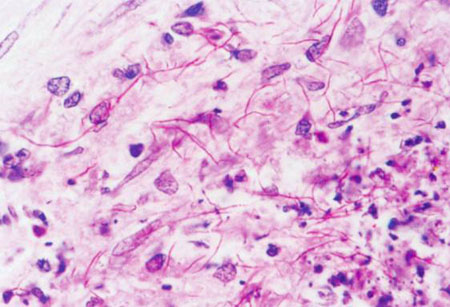 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Expectorated sputum specimen: Ziehl-Neelsen staining to compare the different morphology of Mycobacterium and NocardiaFrom the collection of Dr Jorge Garbino [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Expectorated sputum specimen: Ziehl-Neelsen staining to compare the different morphology of Mycobacterium and NocardiaFrom the collection of Dr Jorge Garbino [Citation ends].
Result
beaded, branching filaments
culture
Test
Nocardia species can grow on most nonselective media used routinely for bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial culture.[20] However, the laboratory should be alerted when Nocardia is suspected, because cultures may take several weeks to become positive. Moreover, special measures should be taken to optimize recognition and recovery of the organism. The presence of aerial hyphae will differentiate the genus Nocardia from other related genera including Rhodococcus, Gordonia, Corynebacterium, and Mycobacterium. Colony morphology of Nocardia is variable, depending on the involved species.[8]
Result
colonies show a chalky-white or cotton ball appearance
matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS)
biochemical species typing
Test
Once the microorganism has been isolated, multiple laboratory tests can be used to differentiate the species.
Biochemical species typing may be employed to achieve this. A combination of tests are used to identify Nocardia isolates to the species level.[60]
Result
species complex or species level
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based techniques
chest x-ray
Test
Should be performed because pulmonary presentation is the most frequent form of the disease. However, there is no specific radiologic pattern for pulmonary nocardiosis.[21][52]
Patients colonized with an invasive pulmonary Nocardia infection usually have previous pulmonary abnormalities such as tuberculosis sequelae, bronchiectasis, or emphysema.
Previous chest x-rays are useful to compare clinical evolution and presence of new abnormalities.
Result
alveolar consolidation, cavities, nodules, pleural effusion
CT head
Test
Brain abscesses are the most frequent presentation in patients with neurologic involvement by Nocardia.[54][61][55] They can also mimic malignancy, or bacterial or fungal infection.[55]
Head imaging (CT or MRI) should be ordered for all patients with confirmed or suspected Nocardia infection, even if no neurologic symptoms are present.[43][54][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Disseminated nocardiosis: CT scan with brain abscesses in an immunosuppressed patientFrom the collection of Dr Jorge Garbino [Citation ends].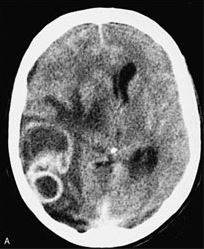
Result
abscesses
Tests to consider
thoracic CT scan
Test
More detailed information than in chest x-ray. Very useful when opportunistic infection is suspected before performing a bronchoalveolar lavage. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Pulmonary nocardiosis: CT scan with nodular lesions in an immunosuppressed patientFrom the collection of Dr Jorge Garbino [Citation ends].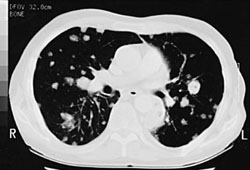
Result
consolidation, cavities, nodules, pleural effusion
MRI head
Test
If possible MRI should be ordered for all immunocompromised patients with confirmed or suspected Nocardia infection, even if no neurologic symptoms are present.[54]
Result
abscesses
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer