The clinical and radiographic findings in pulmonary, disseminated, and cutaneous nocardiosis are nonspecific. They may be mistaken for a variety of other bacterial infections, including actinomycosis and tuberculosis, as well as fungal infections and malignancies affecting the lungs, skin, and brain.[7]Yildiz O, Doganay M. Actinomycoses and Nocardia pulmonary infections. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2006 May;12(3):228-34.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16582679?tool=bestpractice.com
Historical and physical features
Nocardiosis must be suspected in immunocompromised patients with subacute or chronic pneumonia, or in patients with central nervous system (CNS) or skin and soft tissue lesions. Alertness to the possibility of nocardiosis can expedite the diagnostic workup, especially in patients with predisposing factors. Symptoms of pulmonary disease are typically nonspecific and can include fever and cough with sputum production. Patients with CNS disease usually have one or more brain abscesses and so may present with focal neurologic signs of increased intracranial pressure (i.e., nausea, vomiting, headache, confusion, and reduced consciousness). Patients with cutaneous disease often have skin ulcers or abscesses.[43]Margalit I, Lebeaux D, Tishler O, et al. How do I manage nocardiosis? Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Apr;27(4):550-8.
https://www.clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.com/article/S1198-743X(20)30779-5/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33418019?tool=bestpractice.com
Laboratory testing
The diagnosis of nocardiosis requires isolation and identification of the organisms from a clinical specimen. Because Nocardia colonies may take up to 2 weeks to appear, it is important to notify the laboratory when infection is suspected. Measures can then be taken to optimize recognition and recovery of the organism. Nocardia can disseminate to virtually any organ, so clinical samples can vary. Because most cases are pulmonary, the most frequent samples are from sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), or other respiratory specimens. Other samples may be from skin biopsies, aspiration from deep subcutaneous fluid collections, cerebrospinal fluid, and biopsy smears.[20]Corti ME, Villafane-Fioti MF. Nocardiosis: a review. Int J Infect Dis. 2003 Dec;7(4):243-50.
https://www.ijidonline.com/article/S1201-9712(03)90102-0/pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14656414?tool=bestpractice.com
Nocardia is rarely seen as a contaminant in the laboratory, so each isolate must be carefully evaluated.[44]Saubolle MA, Sussland D. Nocardiosis: review of clinical and laboratory experience. J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Oct;41(10):4497-501.
https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/jcm.41.10.4497-4501.2003
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14532173?tool=bestpractice.com
Serology is usually not useful, because no single serologic technique can detect all clinically relevant species. Moreover, antibody response is usually impaired in immunocompromised patients.[8]Brown-Elliott BA, Brown JM, Conville PS, et al. Clinical and laboratory features of the Nocardia spp. based on current molecular taxonomy. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Apr;19(2):259-82.
https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/cmr.19.2.259-282.2006
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16614249?tool=bestpractice.com
Gram and acid-fast stains
Microscopic and macroscopic examination of specimens submitted for culture is the first step in providing a diagnosis.[8]Brown-Elliott BA, Brown JM, Conville PS, et al. Clinical and laboratory features of the Nocardia spp. based on current molecular taxonomy. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Apr;19(2):259-82.
https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/cmr.19.2.259-282.2006
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16614249?tool=bestpractice.com
Staining with modified acid-fast stain, and especially Gram stain, is particularly important to provide a rapid presumptive diagnosis while awaiting the results of the culture.[21]Martínez R, Reyes S, Menendez R. Pulmonary nocardiosis: risk factors, clinical features, diagnosis and prognosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2008 May;14(3):219-27.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18427245?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Expectorated sputum specimen: modified acid-fast staining showing Nocardia speciesFrom the collection of Dr Jorge Garbino [Citation ends].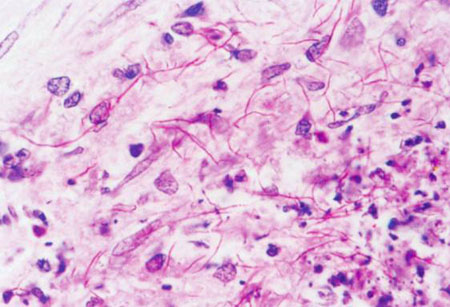
Most Nocardia strains are acid-fast in direct smears if a weak acid is used for discoloration. Gram and modified acid-fast stains must be considered in the initial evaluation of a possible case of nocardiosis.
Samples may be collected again if the initial specimens are negative but there is a high suspicion of infection.
Tuberculosis can be differentiated because the mycobacterium does not stain well with either Gram or modified acid-fast stains and is microscopically different. Actinomyces can be differentiated from Nocardia as it is not detected by modified acid-fast stain.[7]Yildiz O, Doganay M. Actinomycoses and Nocardia pulmonary infections. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2006 May;12(3):228-34.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16582679?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Expectorated sputum specimen: Ziehl-Neelsen staining to compare the different morphology of Mycobacterium and NocardiaFrom the collection of Dr Jorge Garbino [Citation ends].
Cultures
Nocardia species can grow on most nonselective media used routinely for the culture of bacteria, fungi, and mycobacteria. In general, the colonies have a chalky-white or cotton ball appearance because of the presence of abundant aerial filaments.[20]Corti ME, Villafane-Fioti MF. Nocardiosis: a review. Int J Infect Dis. 2003 Dec;7(4):243-50.
https://www.ijidonline.com/article/S1201-9712(03)90102-0/pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14656414?tool=bestpractice.com
In specimens such as sputum that contain mixed flora, Nocardia colonies can easily be obscured by other bacteria that grow more rapidly. The colony yield can be increased by the use of selective media such as Thayer-Martin agar with antibiotics, but the suspicion of nocardiosis must be communicated to the laboratory to optimize recognition and recovery of the organism. Growth of Nocardia species may take 48 hours to several weeks, but typical colonies are usually seen after 3 to 5 days.[45]Ashdown LR. An improved screening technique for isolation of Nocardia species from sputum specimens. Pathology. 1990 Jul;22(3):157-61.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2243728?tool=bestpractice.com
Species typing
Once the microorganism has been isolated, multiple laboratory tests can be used to differentiate the species. Species can be initially identified by biochemical species typing, molecular techniques, or matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS).
Species typing is essential because different species have different resistance profiles and this information is crucial to adjust antibiotic treatment.[8]Brown-Elliott BA, Brown JM, Conville PS, et al. Clinical and laboratory features of the Nocardia spp. based on current molecular taxonomy. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Apr;19(2):259-82.
https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/cmr.19.2.259-282.2006
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16614249?tool=bestpractice.com
[46]Hagerman A, Rodríguez-Nava V, Boiron P, et al. Imipenem-resistant Nocardia cyriacigeorgica infection in a child with chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Microbiol. 2011 Mar;49(3):1185-7.
https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/jcm.02073-10
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21177900?tool=bestpractice.com
[47]Lai CC, Liu WL, Ko WC, et al. Multicenter study in Taiwan of the in vitro activities of nemonoxacin, tigecycline, doripenem, and other antimicrobial agents against clinical isolates of various Nocardia species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 May;55(5):2084-91.
https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/aac.01808-10
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21343461?tool=bestpractice.com
Other molecular diagnostics
PCR-based techniques can be used to identify Nocardia species on samples from BAL and other clinical specimens.[48]Couble A, Rodríguez-Nava V, de Montclos MP, et al. Direct detection of Nocardia spp. in clinical samples by a rapid molecular method. J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Apr;43(4):1921-4.
https://journals.asm.org/doi/full/10.1128/jcm.43.4.1921-1924.2005
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15815019?tool=bestpractice.com
[49]Rouzaud C, Rodriguez-Nava V, Catherinot E, et al. Clinical assessment of a Nocardia PCR-based assay for diagnosis of nocardiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2018 May 25;56(6):e00002-18.
https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/jcm.00002-18
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29563199?tool=bestpractice.com
Next-generation sequencing of clinical samples including tissue, BAL fluid, and blood is an emerging approach for the rapid diagnosis of nocardiosis, including species identification.[50]Vasishta S, Sullivan T. Pulmonary nocardiosis in a heart transplant recipient diagnosed with plasma next-generation sequencing. Transpl Infect Dis. 2022 Jun;24(3):e13841.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35466489?tool=bestpractice.com
[51]Weng SS, Zhang HY, Ai JW, et al. Rapid detection of Nocardia by next-generation sequencing. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Feb 18:10:13.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2020.00013/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32133300?tool=bestpractice.com
Imaging
There is no specific radiologic pattern for pulmonary or disseminated nocardiosis. However, some radiographic features have been reported more frequently and can suggest the diagnosis.
Chest x-ray and computed tomography (CT) chest: multifocal consolidation, with the addition of cavitation in approximately one third of patients; pulmonary nodules; and pleural effusions.[21]Martínez R, Reyes S, Menendez R. Pulmonary nocardiosis: risk factors, clinical features, diagnosis and prognosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2008 May;14(3):219-27.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18427245?tool=bestpractice.com
[52]Smilack JD. Images in clinical medicine. Pulmonary and disseminated nocardiosis. N Engl J Med. 1999 Sep 16;341(12):885.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10486420?tool=bestpractice.com
[53]Liu B, Zhang Y, Gong J, et al. CT findings of pulmonary nocardiosis: a report of 9 cases. J Thorac Dis. 2017 Nov;9(11):4785-90.
https://jtd.amegroups.org/article/view/16507/13847
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268550?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Pulmonary nocardiosis: CT scan with nodular lesions in an immunosuppressed patientFrom the collection of Dr Jorge Garbino [Citation ends].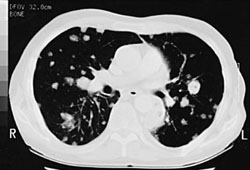
CT, or preferably magnetic resonance imaging, of the brain should always be performed to exclude neurologic involvement in immunocompromised patients with nocardiosis, or immunocompetent patients with pulmonary or disseminated disease.[43]Margalit I, Lebeaux D, Tishler O, et al. How do I manage nocardiosis? Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Apr;27(4):550-8.
https://www.clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.com/article/S1198-743X(20)30779-5/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33418019?tool=bestpractice.com
[54]Cecchini D, Ambrosioni JC, Gomez A, et al. Disseminated nocardiosis caused by Nocardia abscessus in an HIV-infected patient: first reported case. AIDS. 2005 Aug 12;19(12):1330-1.
https://journals.lww.com/aidsonline/fulltext/2005/08120/disseminated_nocardiosis_caused_by_nocardia.15.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16052092?tool=bestpractice.com
Brain abscesses may mimic other conditions, such as malignancy, or bacterial or fungal infection.[55]Kennedy KJ, Chung KH, Bowden FJ, et al. A cluster of nocardial brain abscesses. Surg Neurol. 2007 Jul;68(1):43-9; discussion 49.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17586220?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Disseminated nocardiosis: CT scan with brain abscesses in an immunosuppressed patientFrom the collection of Dr Jorge Garbino [Citation ends].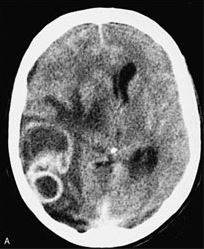
Surgical biopsy
Although the diagnosis can frequently be confirmed with noninvasive samples such as sputum, surgical procedures are occasionally needed to obtain specimens and exclude or confirm Nocardia etiology. This may be particularly important for neurologic involvement in immunocompromised patients, in whom the spectrum of microorganisms can be broader than in immunocompetent patients.[38]Ono M, Kobayashi Y, Shibata T, et al. Nocardia exalbida brain abscess in a patient with follicular lymphoma. Int J Hematol. 2008 Jul;88(1):95-100.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18498026?tool=bestpractice.com
[54]Cecchini D, Ambrosioni JC, Gomez A, et al. Disseminated nocardiosis caused by Nocardia abscessus in an HIV-infected patient: first reported case. AIDS. 2005 Aug 12;19(12):1330-1.
https://journals.lww.com/aidsonline/fulltext/2005/08120/disseminated_nocardiosis_caused_by_nocardia.15.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16052092?tool=bestpractice.com
[55]Kennedy KJ, Chung KH, Bowden FJ, et al. A cluster of nocardial brain abscesses. Surg Neurol. 2007 Jul;68(1):43-9; discussion 49.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17586220?tool=bestpractice.com
If the diagnosis is uncertain, brain biopsy may be considered for patients with cerebral abscesses.[54]Cecchini D, Ambrosioni JC, Gomez A, et al. Disseminated nocardiosis caused by Nocardia abscessus in an HIV-infected patient: first reported case. AIDS. 2005 Aug 12;19(12):1330-1.
https://journals.lww.com/aidsonline/fulltext/2005/08120/disseminated_nocardiosis_caused_by_nocardia.15.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16052092?tool=bestpractice.com
[56]Chakrabarti P, Nandi SS, Todi SK. Nocardia brain abscess in a diabetic patient. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2008 Jan-Mar;51(1):151-3.
https://www.ijpmonline.org/article.asp?issn=0377-4929;year=2008;volume=51;issue=1;spage=151;epage=153;aulast=Chakrabarti
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18417891?tool=bestpractice.com
[57]Vialle R, Aghakhani N, Otayza F, et al. Nocardia farcinica brain abscess: clinical and specific radiological findings and management. Report of two cases in immunononcompromised patients [in French]. Neurochirurgie. 2002 Dec;48(6):516-21.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12595808?tool=bestpractice.com



