Tests
1st tests to order
serum potassium
Test
Hypokalemia occurs due to potassium loss in stool.
Hypokalemia is part of the clinical syndrome for VIPoma.
Result
reduced (often <3 mEq/L)
serum bicarbonate
Test
Low bicarbonate levels occur due to electrolyte losses in stool.
Low bicarbonate levels may result in non-anion gap metabolic acidosis, which can be confirmed by arterial blood gas analysis.
Metabolic acidosis is part of the clinical syndrome for VIPoma.
Result
reduced
serum calcium
serum glucose
Test
Hyperglycemia occurs due to vasoactive intestinal peptide stimulation of glycogenolysis.
May affect 20% to 50% of patients.[30]
Result
elevated
vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) radioimmunoassay
Test
VIPoma is characterized by profuse watery diarrhea, hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis, and hypochlorhydria or achlorhydria, in the presence of elevated serum VIP. The only pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor to secrete VIP is VIPoma.[17]
VIP levels are measured by radioimmunoassay in symptomatic fasting patients (ideally during a bout of diarrhea). If VIP levels are normal, the test should be repeated because VIP secretion from the tumor may be episodic.[22]
VIPoma patients usually have markedly elevated levels of VIP (reference value <75 picograms/mL).[9] One review of case reports and case series reported serum VIP levels ranging from 293 to 1500 picograms/mL.[9]
Result
fasting serum VIP >75 picograms/mL may indicate the presence of an enteropancreatic tumor; >200 picograms/mL is strongly suggestive of VIPoma
liver function tests
Test
May be abnormal in the presence of hepatic metastasis.
Result
normal or abnormal
Tests to consider
arterial blood gas analysis
Test
Arterial blood gas analysis can be used to confirm metabolic acidosis (due to bicarbonate loss in stool).
Result
low pH; low HCO₃
gastric pH monitoring
chromogranin A
Test
Generalized marker that is secreted by a broad variety of neuroendocrine tumors. Can aid in confirming the diagnosis if VIP levels are normal but concerns regarding neuroendocrine tumor persist.[23]
Result
elevated
pancreatic polypeptide
Test
Generalized marker that is secreted by a broad variety of neuroendocrine tumors. Can aid in confirming the diagnosis if VIP levels are normal but concerns regarding neuroendocrine tumor persist.[23]
Result
elevated
contrast-enhanced CT scan of abdomen
Test
VIPomas are usually solitary tumors, >3 cm in diameter at diagnosis. Therefore, most can be located by multiphase abdominal contrast-enhanced CT scan.[26]
Hypervascular lesions are most commonly found in the body/tail segments of the pancreas and appear somewhat spherical or ovoid.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Computed tomography image of VIPoma near the tail of the pancreasFrom the collection of Charles J. Yeo, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].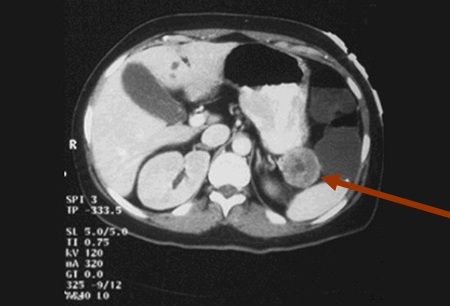
Result
hypervascular lesion
contrast-enhanced MRI of abdomen
Test
Multiphase MRI of the abdomen effectively locates VIPomas, and is warranted if radiation exposure is to be avoided (e.g., pregnancy).[26]
MRI is superior to CT scan in identifying hepatic metastasis.[26]
Hypervascular lesions are most commonly found in the body/tail segments of the pancreas and appear somewhat spherical or ovoid.
Result
hypervascular lesion
somatostatin receptor PET-CT/MRI
Test
If imaging from CT and MRI is inconclusive, then functional somatostatin receptor-based imaging techniques should be considered if available.
Somatostatin receptors are expressed in 80% to 90% of VIPomas.[9]
PET-CT/MRI employing novel somatostatin receptor PET tracers (e.g., 68Ga-DOTATATE; 64Cu-DOTATATE; 68Ga-DOTATOC) has increased sensitivity for detecting neuroendocrine tumors compared with conventional CT, MRI, and scintigraphy.[26][27][28][29]
Somatostatin receptor-based imaging techniques are particularly useful for staging and guiding treatment.[26][27] These modalities can identify patients with sufficient tumor somatostatin receptor expression who may benefit from treatment with somatostatin analogs.[26][27]
Result
primary or metastatic lesion
somatostatin receptor scintigraphy
Test
If imaging from CT and MRI is inconclusive, then functional somatostatin receptor-based imaging techniques should be considered if available.
Somatostatin receptors are expressed in 80% to 90% of VIPomas.[9]
Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy (using a radiolabeled somatostatin analog, e.g., octreotide) can confirm the location of the tumor and detect occult hepatic metastasis. It has increased sensitivity for detecting neuroendocrine tumors (including metastases) compared with CT and MRI.[26][27] However, this imaging modality has been mostly replaced by more advanced imaging techniques (e.g., somatostatin receptor PET/CT).
Somatostatin receptor-based imaging techniques are particularly useful for staging and guiding treatment.[26][27] These modalities can identify patients with sufficient tumor somatostatin receptor expression who may benefit from treatment with somatostatin analogs.[26][27]
Result
uptake of radiotracer by primary tumor and metastasis
endoscopic ultrasound
Test
Useful in cases with small tumors (rare). Endoscopic ultrasound can allow for a definitive diagnosis via ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of the mass.[24]
Result
hypoechoic lesion in pancreas
operative exploration
Test
Most tumors are easily visualized and palpated at pancreatic exploration.
Result
tumor visualization or palpation
intraoperative ultrasound
Test
Intraoperative ultrasound can be used during operative exploration to localize tumors if they are not visualized or palpated at pancreatic exploration.
Result
hypoechoic lesion in pancreas
biopsy
Test
In patients with surgically resectable disease, preoperative biopsy is not indicated. For unresectable disease obtaining a tissue diagnosis is recommended with endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration. Pathologic evaluation focuses on Ki-67 and mitosis per high power field to determine tumor grade and prognosis.[17]
Result
VIPoma tumor cells, immunohistochemistry: stain positive for VIP, somatostatin, neuron-specific enolase, chromogranin A, synaptophysin and cytokeratin
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer