Differentials
Common
Fever
History
fever
Exam
elevated temperature >100.4°F (38.0°C)
1st investigation
- none:
clinical diagnosis
Other investigations
Heavy physical exertion
History
recent strenuous exercise
Exam
no specific findings
1st investigation
- repeat urinalysis after 2 days' rest:
no proteinuria
Other investigations
Urinary tract infection
History
dysuria; cloudy foul-smelling urine; urinary urgency; urinary frequency
Exam
flank tenderness (if pyelonephritis); bladder tenderness on palpation
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
>5-10 white blood cells per high-power field; bacteria visualized; nitrites present
- urine culture:
>100,000 colonies/mL
Other investigations
Urologic hemorrhage
History
recent instrumentation or trauma to urologic system
Exam
gross hematuria
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
+ blood
More - serum creatinine:
usually normal
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
usually normal
Other investigations
- CT abdomen:
normal or renal/bladder mass
- renal ultrasound:
normal or renal/bladder mass
- cystoscopy:
normal or may reveal bladder source and allows therapeutic intervention
Orthostatic proteinuria
History
usually children and adolescents
Exam
no specific findings
1st investigation
- split urine collection:
proteinuria during the day and not at night
More
Other investigations
Minimal change disease
History
most common in children and older people but occurs at all ages; often sudden onset with marked edema; may be associated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), interferon, lithium, lymphoma, bee stings, stem cell transplant
Exam
marked edema; BP often normal to low
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
bland sediment, usually nephrotic-range proteinuria
- serum creatinine:
normal
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
normal
Other investigations
- renal biopsy:
normal-appearing glomeruli under light microscopy with effacement of podocyte foot processes under electron microscopy
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
History
more common in black people and in patients with HIV infection; can be secondary to hypertension, diabetes, prior renal injury, obesity, bisphosphonates, heroin use
Exam
edema; hypertension
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
may have mild hematuria; subnephrotic- to nephrotic-range proteinuria
- serum creatinine:
elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
decreased
- renal biopsy:
glomeruli with focal areas of sclerosis
Other investigations
- HIV testing:
normal or positive
More
Membranous nephropathy
History
more common in older adults; may be associated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), gold, penicillamine, adenocarcinoma, systemic lupus erythematosus, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, syphilis, stem cell transplant
Exam
edema; often hypertensive
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
may have mild hematuria; subnephrotic- to nephrotic-range proteinuria
- serum creatinine:
normal or elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
normal or decreased
- renal biopsy:
glomeruli demonstrate increased mesangial matrix with thickened basement membranes; subepithelial immune deposits with occasional mesangial and subepithelial deposits
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
History
idiopathic is rare; generally history of another disease such as systemic lupus erythematosus, hepatitis C, postinfectious glomerulonephritis, endocarditis, cryoglobulinemia, thrombotic microangiopathy
Exam
edema; often hypertensive; may have evidence of arthritis/rash/other end-organ involvement with systemic lupus erythematosus; murmur with endocarditis; tea-colored urine with postinfectious glomerulonephritis
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
often with hematuria, may have red blood cell casts; subnephrotic- to nephrotic-range proteinuria
- serum creatinine:
normal or elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
normal or decreased[69]
- renal biopsy:
glomeruli demonstrate lobulated tufts with increased mesangial matrix, endothelial cell proliferation, and thickened basement membranes; subendothelial and mesangial deposits
IgA nephropathy
History
most common glomerulonephritis worldwide; high incidence in Asian populations; history of gross hematuria associated with upper respiratory infection; history of Crohn disease or celiac disease; more common in males
Exam
rarely edema and hypertension; often discovered incidentally while evaluating microscopic hematuria; may have purpuric skin lesions
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
typically subnephrotic-range proteinuria
- serum creatinine:
usually normal
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
usually normal
- renal biopsy:
glomeruli range from mild increase in mesangial matrix to crescent glomerulonephritis; mesangial deposits that stain for IgA
Systemic lupus erythematosus
History
history of rash, photosensitivity, oral ulcers, arthritis, serositis, renal disease, neurologic changes (psychosis, seizures), hematologic disease
Exam
malar rash; arthritis; edema; hypertension; oral ulcers; pleural effusion; neuropathy; Raynaud phenomenon
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
may have hematuria, red blood cell casts, and pyuria; subnephrotic- to nephrotic-range proteinuria
- renal biopsy:
biopsy findings range from mild mesangial proliferation to crescentic glomerulonephritis; may also result in a membranous nephropathy or interstitial nephritis
- antinuclear antibody:
positive
- serum creatinine:
normal or elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
normal or decreased
Postinfectious glomerulonephritis
History
recent history of infection; can occur with virtually any infectious agent; classic description is poststreptococcal; Staphylococcus aureus superantigens can result in rapid acute kidney injury
Exam
edema; hypertension; tea-colored urine in some cases
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
hematuria and red blood cell casts; typically subnephrotic-range proteinuria
- serum creatinine:
normal or elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
normal or decreased
- renal biopsy:
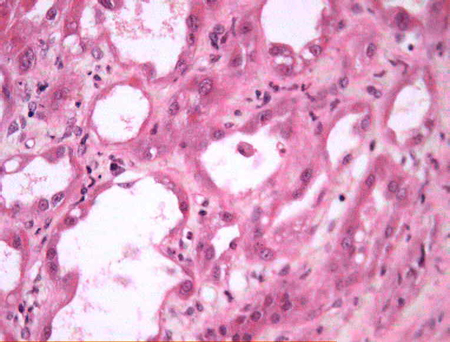
glomeruli have large subepithelial hump-like deposits; crescents and endocapillary proliferation are common, and glomeruli may have a membranoproliferative appearance
Acute tubular injury
History
recent nephrotoxic injury such as hypotension, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, zoledronic acid, oral phosphate bowel preparations, intravenous contrast, mechanical ventilation, ischemia
Exam
no specific findings
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
typically acellular with granular muddy-brown casts; minimal proteinuria; renal tubular epithelial (RTE) cells, RTE casts, waxy casts
- serum creatinine:
elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
decreased
Other investigations
- renal biopsy:
proximal tubular injury, loss of brush border, vacuolization of tubular epithelial cells
More
Interstitial nephritis
History
exposure to typical offending medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics, allopurinol, proton pump inhibitors; uveitis in the tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome; infectious agents (e.g., viruses); systemic disease (e.g., sarcoidosis, Sjogren disease)
Exam
may have rash and fever; anterior uveitis in tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
pyuria; WBC cast; may have hematuria; subnephrotic-range proteinuria
- CBC:
eosinophilia
More - serum creatinine:
elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
decreased
Other investigations
- renal biopsy:
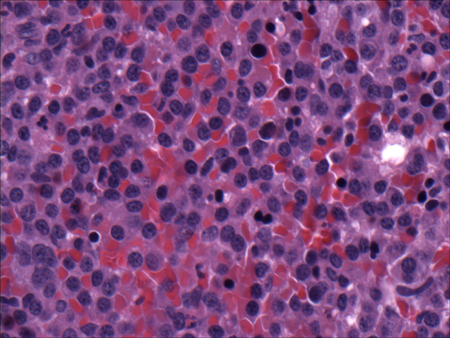
interstitial nephritis with eosinophils
More
Urinary tract obstruction
History
history of benign prostatic hyperplasia, kidney stones, urinary retention, gynecologic cancer; may have decreased, normal, or increased urine output; flank or suprapubic pain
Exam
palpable bladder may be present; enlarged prostate on rectal exam
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
typically acellular; minimal proteinuria
More - renal ultrasound:
distended bladder with benign prostatic hyperplasia; hydronephrosis/hydroureter with ureteral obstruction
- serum creatinine:
normal or elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
normal or decreased
Metabolic syndrome
History
overweight; history of hypertension, insulin resistance/diabetes, dyslipidemia
Exam
BP ≥130/85 mmHg; waist ≥40 inches in men or 35 inches in women
1st investigation
- lipid profile:
triglyceride ≥150 mg/dL; HDL <40 mg/dL in men or <50 mg/dL in women
- fasting blood sugar:
≥126 mg/dL or HbA1c ≥48 mmol/mol
- serum creatinine:
normal or elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
normal or decreased
Other investigations
Diabetic nephropathy
History
increases with duration of diabetes; retinopathy is typically present
Exam
retinopathy; neuropathy; often hypertensive with macrovascular complications
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
usually >1 g proteinuria
More - serum creatinine:
normal or elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
normal or decreased
- renal biopsy:
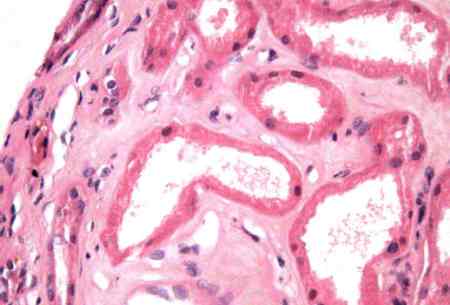
increased mesangial matrix with Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules
Other investigations
Hypertension
History
long-standing history of hypertension
Exam
evidence of hypertensive end-organ damage (e.g., retinopathy, left ventricular hypertrophy)
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
usually subnephrotic-range proteinuria
- serum creatinine:
normal or elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
normal or decreased
Other investigations
- echocardiogram:
normal or left ventricular hypertrophy
More - renal biopsy:
evidence of hypertensive vascular changes and nephrosclerosis
Medium- and small-vessel vasculitis
History
multiorgan disorder; rash, neuropathy, headache, stroke, change in mental status, shortness of breath, hemoptysis, abdominal pain, acute renal failure
Exam
specific organ involvement dictates findings; typically multiple systems are involved simultaneously
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
medium-vessel vasculitis: typically acellular and minimal proteinuria; small-vessel vasculitis: hematuria, red blood cell casts, and usually subnephrotic-range proteinuria
- serum creatinine:
normal or elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
normal or decreased
- renal biopsy:
small-vessel vasculitis produces a crescentic glomerulonephritis without significant endothelial proliferation or marked immune complex deposition
- angiography:
normal or polyarteritis nodosa (PAN)
More
Rhabdomyolysis (myoglobinuria)
History
muscle pain; recent crush injury; prolonged immobility, or viral infection; use of drugs such as statins and cocaine; inborn errors of muscle metabolism may present in young adults
Exam
muscle tenderness; dark urine
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
heme pigments without red blood cells; subnephrotic-range proteinuria
- serum creatinine:
elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
decreased
- creatine kinase:
usually >5000 to 10,000 U/L
Other investigations
- urine myoglobin:
normal or positive
More
Uncommon
Pregnancy
History
worsening of pre-existing chronic kidney disease; development of new-onset hypertension and/or edema during pregnancy (e.g., preeclampsia); visual disturbances; upper abdominal pain; headache; possible thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)-hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
Exam
hypertension; edema; bruising/petechiae (with TTP-HUS)
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
subnephrotic- to nephrotic-range proteinuria; bland sediment with preeclampsia; may have hematuria in TTP-HUS
- uric acid:
usually >6 mg/dL in preeclampsia
- BUN and creatinine:
may be elevated
- peripheral blood smear:
schistocytes; anemia; thrombocytopenia if TTP-HUS
Other investigations
- renal biopsy:
glomerular endotheliosis in preeclampsia; glomerular thrombosis can be seen, although renal biopsy is often not obtained due to thrombocytopenia
Amyloidosis
History
chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, restrictive heart disease, liver failure, and familial Mediterranean fever; plasma cell dyscrasia such as multiple myeloma or monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
Exam
edema; hypertension; may have carpal tunnel syndrome; capillary fragility; autonomic insufficiency
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
hematuria; subnephrotic- to nephrotic-range proteinuria
- renal biopsy:
glomerular amyloid deposits
More - serum creatinine:
usually normal
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
usually normal
- protein electrophoresis:
a monoclonal protein is typically evident on serum and urine electrophoresis
Other investigations
- bone marrow biopsy:
may reveal evidence of plasma cell dyscrasia
More
Light and heavy chain deposition diseases
History
plasma cell dyscrasia such as multiple myeloma or monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
Exam
edema; hypertension; autonomic insufficiency
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
may have hematuria and subnephrotic- to nephrotic-range proteinuria
- serum creatinine:
usually elevated in multiple myeloma
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
usually decreased in multiple myeloma
- renal biopsy:
glomerular and tubular deposits of light chains
More - protein electrophoresis:
monoclonal protein, elevated kappa or lambda light chain levels
More - serum free light chains:
increased concentrations of free light chains in serum
More
Other investigations
- bone marrow biopsy:
normal or plasma cell dyscrasia
More
Fibrillary and immunotactoid glomerulopathy
History
plasma cell dyscrasia such as multiple myeloma or monoclonal gammopathy; hepatitis C; some patients have underlying lymphoma
Exam
edema; hypertension
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
hematuria; subnephrotic- to nephrotic-range proteinuria
- serum creatinine:
usually elevated in multiple myeloma
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
usually decreased in multiple myeloma
- renal biopsy:
deposits of fibrils visualized by electron microscopy
More - protein electrophoresis:
normal or monoclonal protein
More
Other investigations
Antiglomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) disease (Goodpasture syndrome)
History
rapidly progressive renal failure, hemoptysis, hematuria; often has positive smoking history
Exam
crackles; may have gross hematuria
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
hematuria; proteinuria typically minimal to <2 g
- anti-GBM antibody:
positive (≥3 U/mL)
- chest radiograph:
bilateral air space opacities
More - serum creatinine:
elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
decreased
- renal biopsy:
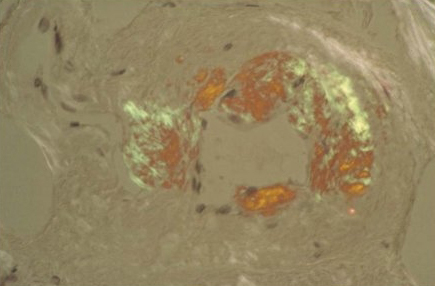
crescentic, nonproliferative glomerulonephritis; linear IgG glomerular basement membrane staining
Other investigations
Fanconi syndrome
History
can be inherited; may have underlying multiple myeloma, heavy metal exposure, or medications such as tenofovir
Exam
microcephaly, hypogonadism, and café au lait spots with congenital disease; adult-onset symptoms specific to underlying etiology
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
low-molecular-weight proteinuria/subnephrotic-range proteinuria; glycosuria; proximal renal tubular acidosis; phosphaturia
- serum electrolytes:
hypophosphatemia; hypokalemia; nonanion gap acidosis
- serum creatinine:
usually normal
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
usually normal
Cystic kidney disease
History
chronic kidney disease in childhood with nephronophthisis; may have flank pain or hematuria with polycystic kidney disease (PKD); cerebral hemorrhage/stroke in PKD
Exam
palpable kidneys in PKD; retinitis pigmentosa in some forms of nephronophthisis; polydactyly in Bardet-Biedl syndrome
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
usually acellular; minimal proteinuria
- serum creatinine:
often normal
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
often normal
- ultrasound:
small cystic kidneys with nephronophthisis; enlarged cystic kidneys with PKD
Other investigations
Hypercalciuria
History
usually asymptomatic; may have history of kidney stones; if also hypercalcemic, may have nausea, constipation, psychosis, polyuria, weakness
Exam
if hypercalcemic, may have change in mental status, generalized weakness
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
may have hematuria; subnephrotic-range proteinuria
More - serum creatinine:
often normal
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
often normal
- urine calcium excretion:
>300 mg in men and >250 mg in women
Other investigations
- renal ultrasound:
may reveal evidence of nephrocalcinosis
Dent disease
History
X-linked recessive: typically only males are affected; polyuria and nocturia in childhood; kidney stones; chronic kidney disease; rickets; nephrocalcinosis
Exam
few physical findings
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
low-molecular-weight/subnephrotic-range proteinuria; may have hematuria; hypercalciuria; glycosuria
More - serum creatinine:
usually elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
usually decreased
Other investigations
- CLC-5 gene testing:
gene mutation
More
Aristolochic acid nephropathy
History
has been associated with aristolochic acid ingestion, which is a component of some Chinese herbs and weight loss medications and is a part of wheat used for bread in the Balkan region
Exam
few physical findings; may have gross hematuria with underlying urologic malignancy
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
may have mild hematuria and pyuria; proteinuria generally <2 g
- serum creatinine:
usually elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
usually decreased
- renal biopsy:
severe cortical interstitial fibrosis with glomerular sparing; general absence of inflammatory infiltrate
Other investigations
Light chain cast nephropathy
History
plasma cell dyscrasia, such as multiple myeloma or monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance; rapid onset of renal failure
Exam
edema; hypertension
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
typically acellular; nephrotic-range proteinuria
- renal biopsy:
light chain casts within the renal tubules without evidence of glomerular deposition or amyloid
- serum creatinine:
usually elevated in multiple myeloma
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
usually decreased in multiple myeloma
- protein electrophoresis:
a monoclonal protein is typically evident on serum and urine electrophoresis
Other investigations
- bone marrow biopsy:
may reveal evidence of plasma cell dyscrasia
More
Fabry disease
History
X-linked genetic deficiency of alpha-galactosidase-A; burning sensation of the hands with exercise and heat, eye disease, peripheral and coronary arterial disease, congestive heart failure, hypohidrosis, gastrointestinal dysmotility, renal failure, and fever
Exam
corneal clouding; hypertension; poor circulation; angina; angiokeratomas; hypohidrosis; obesity; telangiectasia; angiokeratomas; corneal deposits
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
subnephrotic- to nephrotic-range proteinuria
- leukocyte alpha-galactosidase A level:
<4% of normal
- serum creatinine:
usually elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
usually decreased
Other investigations
- skin biopsy:
accumulation of glycolipid
- renal biopsy:
accumulation of glycolipid and foam cells
More
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
History
recent Escherichia coli infection; diarrhea; in cases of atypical HUS, there is history of HUS/thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; positive family history; history of complement regulatory protein mutations; prior bone marrow transplant; associated with medications such as cyclosporine, gemcitabine, and bevacizumab (vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor); pregnancy or postpartum state
Exam
edema; hypertension; petechial rash or purpura; fever
1st investigation
Other investigations
- stool culture to detect E coli O157:H7 or O104:H4:
translucent colonies on sorbitol-MacConkey agar (these can be further investigated with antisera to the antigens)
- renal biopsy:
glomerular thrombosis can be seen, although renal biopsy is often not obtained due to thrombocytopenia
- complement mutation analysis:
may detect mutations in ≥1 members of complement pathway
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
History
recent infection; mental status changes ranging from headache and confusion to seizures; history of TTP; positive family history; prior bone marrow transplant; associated with medications such as cyclosporine, clopidogrel, and gemcitabine
Exam
edema; hypertension, petechial rash or purpura; fever; focal neurologic deficits, and coma
1st investigation
Other investigations
- renal biopsy:
glomerular thrombosis can be seen, although renal biopsy is often not obtained due to thrombocytopenia
Scleroderma renal crisis
History
usually within first 5 years of scleroderma diagnosis with diffuse skin involvement; patients often taking prednisone; new-onset hypertension and rapidly worsening renal function; may have gastrointestinal dysmotility and pulmonary hypertension
Exam
often marked hypertension (often abrupt onset); masked facies of scleroderma; tapered digits with tight skin
1st investigation
- creatinine:
rapidly rising
- urinalysis:
may be acellular or with mild hematuria; proteinuria typically minimal to <2 g
More
Other investigations
- renal biopsy:
demonstrates onion-skinned vascular lesions; may have evidence of thrombotic microangiopathy
Heavy metal poisoning
History
history of industrial/environmental exposure; old paint and moonshine are common sources for lead poisoning; may have neuropathy, hypertension, abdominal pain, psychiatric symptoms, gout, rash
Exam
gout, neuropathy, developmental delay, hyperkeratosis, hypertension
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
often acellular; subnephrotic-range proteinuria
- urine heavy metal testing:
positive
- serum creatinine:
usually elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
usually decreased
Other investigations
- renal biopsy:
nonspecific findings of interstitial fibrosis
Idiopathic nodular glomerulosclerosis
History
history of smoking and obesity
Exam
obesity, edema
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
acellular, nephrotic-range proteinuria
- serum creatinine:
usually elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
usually decreased
Other investigations
- renal biopsy:
nodular glomerulosclerosis
Proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal IgG deposits
History
history of monoclonal gammopathy
Exam
edema
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
subnephrotic-range proteinuria with hematuria
- serum creatinine:
usually elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
usually decreased
- serum immunoglobulins:
monoclonal spike
Other investigations
- renal biopsy:
granular nonorganized deposits on electron microscopy
Polymyositis
History
history of muscle pain and weakness
Exam
muscle weakness
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
subnephrotic-range proteinuria
- antisynthetase antibodies:
anti-Jo1 positive
- creatine kinase:
elevated
- serum creatinine:
normal or elevated
- estimated glomerular filtration rate:
normal or decreased
Other investigations
- MRI:
muscle edema and inflammation
- muscle biopsy:
cellular infiltrate with the fascicle
Renal vein thrombosis
History
most common in patients with nephrotic syndrome (primarily membranous nephropathy), antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, and other inherited prothrombotic defects; extrinsic compression of the renal vein by retroperitoneal fibrosis or aortic aneurysm; history of trauma or severe dehydration; in children presents with acute flank pain
Exam
hematuria, edema
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
hematuria; subnephrotic- to nephrotic-range proteinuria
- BUN and creatinine:
elevated if bilateral or unilateral thrombosis is present in the setting of chronic kidney disease
- LDH:
may be elevated
Other investigations
- selective renal venography:
shows renal vein occlusion
- MRI, CT, or Doppler ultrasound:
shows renal vein occlusion
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer