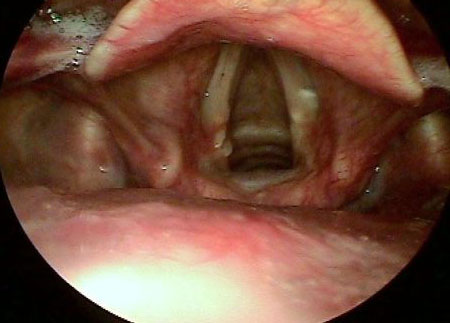
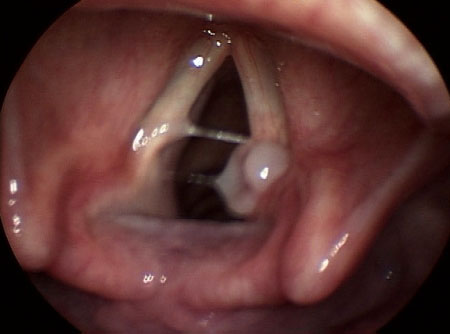
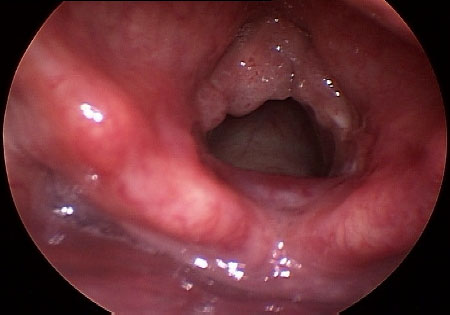
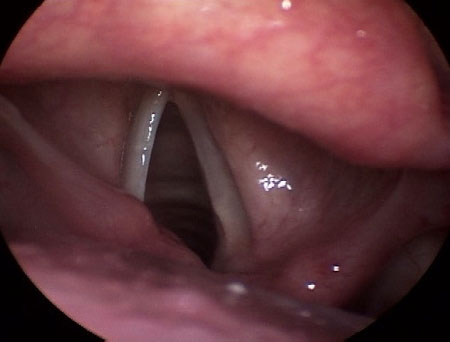
Differentials
Common
Muscle tension dysphonia
History
adult presenting with throat discomfort, neck tenderness, vocal fatigue, possible voice loss, and dysphagia; possible associated upper respiratory infection (URI), phonotrauma, GERD, laryngopharyngeal reflux, asthma, known allergies, sinusitis, neuromuscular abnormalities, depression, anxiety, stress, and/or recent psychological trauma
Exam
tension and tenderness of cervical, laryngeal (extrinsic muscles), and neck muscles; signs of associated condition
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
voice near normal; variable-to-severe voice loss; poor breath support; low pitch; inappropriate intensity
- acoustic assessment:
variable depending on severity
- aerodynamic assessment:
variable depending on severity
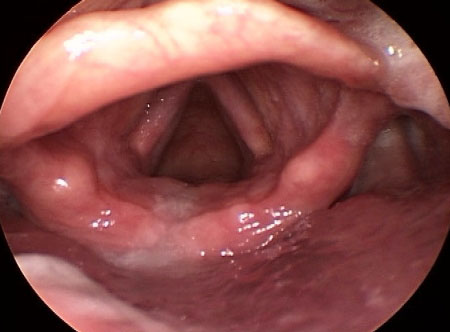
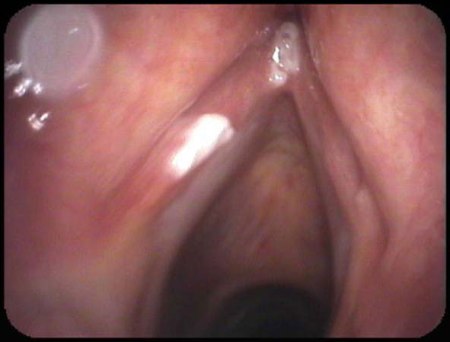
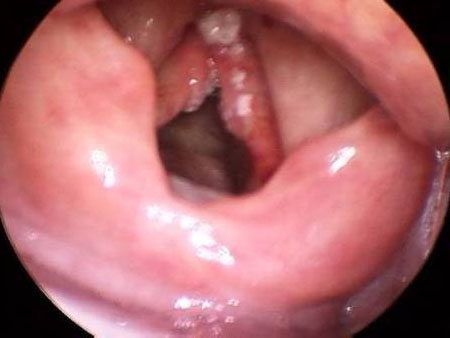
- videostroboscopy:
anteroposterior and/or lateral muscle tension; vocal fold hypoadduction; glottic gap
Other investigations
Acute laryngitis
History
acute onset of breathiness, vocal weakness, and fatigue following a respiratory infection (bacterial, viral, fungal), tuberculosis, laryngopharyngeal reflux, phonotrauma, or exposure to environmental irritants or noxious agents occurring at any age
Exam
head and neck exam unremarkable
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
breathiness, vocal weakness, and fatigue
- acoustic assessment:
lower pitch with vocal fold edema; higher pitch with vocal fold stiffness
- aerodynamic assessment:
variable phonatory airflow pressure
- videostroboscopy:
edema and erythema with possible ulcerative change to mid-membranous vocal fold
More
Other investigations
Chronic laryngitis
History
roughness, altered pitch and volume, and voice breaks following prolonged history of recurrent respiratory infections (bacterial, viral, fungal), tuberculosis, episodic sore throats, globus, chronic cough and throat clearing, and painful swallowing; possible associated exposure to environmental irritants, noxious agents or gastric acid (laryngopharyngeal reflux), and/or phonotrauma
Exam
head and neck exam unremarkable
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
variable roughness, pitch, and loudness with possible voice breaks
- acoustic assessment:
increased frequency of perturbation and amplitude perturbation; decreased fundamental frequency
- aerodynamic assessment:
normal, elevated, or variable phonatory airflow pressure
- videostroboscopy:
diffuse glottic and subglottic edema and erythema with possible ulcerative change on vocal process and mid-membranous vocal fold; asymmetry and aperiodicity of vocal fold vibration; excessive thick sticky exudate
More
Other investigations
Reflux laryngitis
History
altered vocal pitch, chronic cough and throat clearing with excess throat mucus or postnasal drip; dysphagia to solids, liquids, or pills, and coughing after eating or lying down; breathing difficulty or choking episodes, globus and heartburn (in <50% of cases); secondary to laryngopharyngeal reflux; occurs at any age
Exam
head and neck exam unremarkable
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
lower or higher pitch; coughing; throat clearing
- acoustic assessment:
variable fundamental frequency, amplitude and signal-to-noise ratio
- aerodynamic assessment:
variable phonatory airflow pressure
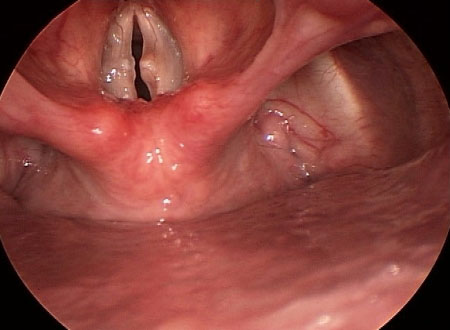
- videostroboscopy:
subglottic, vocal fold, or diffuse laryngeal edema; ventricular obliteration; erythema/hyperemia; posterior commissure hypertrophy; granuloma/granulation tissue; thick endolaryngeal mucus
More
Other investigations
- dual probe pH and impedance:
pH is <4.0, >0% of the time when supine and >1.2% when upright
More
Vocal fold nodule
History
gradual or acute onset of hoarseness and breathiness, and difficulty with high pitch related to phonotrauma, dehydration, or respiratory infection; possible associated laryngopharyngeal reflux occurring at any age
Exam
head and neck exam unremarkable
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
breathiness; difficulty with high pitch; variable degree of hoarseness
- acoustic assessment:
frequency and loudness normal or reduced
- aerodynamic assessment:
normal or increased phonatory subglottic pressure
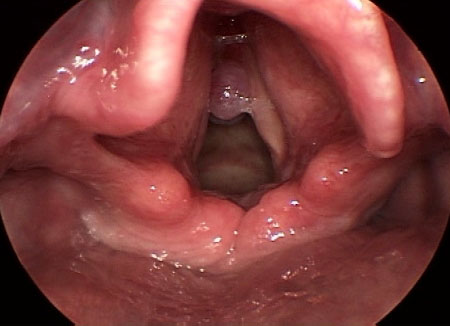
- videostroboscopy:
hourglass vocal fold closure; aperiodicity of vocal fold vibration; anteroposterior and/or lateral hyperfunction during phonation
More
Other investigations
Vocal fold cyst
History
gradual or acute onset of breathiness, vocal fatigue, restricted vocal range, and low pitch related to phonotrauma, dehydration, and respiratory illness; typically in adolescents and adults
Exam
head and neck exam unremarkable
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
breathiness; vocal fatigue; restricted vocal range and lower pitch
- acoustic assessment:
aperiodicity of vocal fold vibration, altered fundamental frequency and loudness
- aerodynamic assessment:
increased phonatory airflow and subglottic pressure
- videostroboscopy:
absence or reduction of mucosal wave and amplitude; vocal fold closure hourglass, incomplete or with posterior gap
More
Other investigations
Vocal fold polyp
History
gradual or acute onset of roughness, breathiness, loss of high pitch, and restricted dynamic range related to phonotrauma, dehydration, and respiratory illness
Exam
head and neck exam unremarkable
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
roughness; breathiness; loss of high pitch; restricted dynamic range
- acoustic assessment:
altered fundamental frequency and intensity
More - aerodynamic assessment:
increased phonatory airflow and subglottic pressure
- videostroboscopy:
asymmetry of vocal fold movement; aperiodicity of vocal fold vibration; reduced amplitude; decreased or increased mucosal wave
More
Other investigations
Fibrous mass
History
roughness, restricted vocal range with loss of high pitch, pain, and vocal fatigue related to repeated or chronic phonotrauma occurring at any age
Exam
head and neck exam unremarkable
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
variable degrees of roughness; loss of high pitch; vocal fatigue; restricted vocal range
- acoustic assessment:
altered fundamental frequency and loudness
More - aerodynamic assessment:
increased phonatory airflow and subglottic pressures
- videostroboscopy:
aperiodicity of vocal fold vibration; incomplete or hourglass vocal fold closure; decreased mucosal wave
More
Other investigations
Vocal fold scar or sulcus
History
breathiness, roughness, voice breaks, reduced pitch and loudness, thin and weak voice quality, vocal fatigue, and/or voice loss related to prolonged phonotrauma, laryngeal microsurgery, or laryngeal radiation for head and neck cancer
Exam
head and neck exam unremarkable
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
breathiness; roughness; increased fundamental frequency; thin and weak voice quality; vocal fatigue; voice loss
- acoustic assessment:
decreased signal-to-noise ratio; decreased phonation time
- aerodynamic assessment:
increased phonatory airflow and subglottic pressure
- videostroboscopy:
incomplete glottic closure; decreased mucosal wave and amplitude
More
Other investigations
Reinke edema
History
smoker presenting with roughness, vocal fatigue, and low-pitched voice; possible history of laryngopharyngeal reflux and phonotrauma
Exam
head and neck exam unremarkable
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
lower pitch; roughness; vocal fatigue
- acoustic assessment:
decreased fundamental frequency
- aerodynamic assessment:
decreased phonatory airflow; normal or increased subglottic pressure
More - videostroboscopy:
increased mass or vocal fold cover; increased or decreased mucosal wave; complete glottic closure; decreased amplitude
More
Other investigations
Presbylarynx
History
patients ages >60 years complain of difficulty making themselves heard, altered pitch (increased in men, decreased in women), roughness, breathiness, tremulousness, and changes in their singing voice
Exam
head and neck exam unremarkable
1st investigation
- perceptual:
pitch: increased in men, decreased in woman; roughness; breathiness; tremulousness; asthenia
- acoustic:
increased perturbation; decreased signal-to-noise ratio
- aerodynamic:
increased phonatory airflow pressure
- videostroboscopy:
vocal fold bowing; spindle-shaped closure; bilateral prominence of vocal process
More
Other investigations
Essential tremor
History
slowly worsening tremulous voice with fluctuation of vocal pitch and volume (at least a 3-year history of tremor); symptoms worsen in demanding speaking situations or with increased emotion and stress; possible family history of tremor
Exam
6- to 8-Hz tremor of hands, voice, and sometimes head not resolved on movement; vocal tremor more evident with connected speech than with singing or sustained phonation
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
fluctuations of pitch and/or loudness on sustained phonation
- acoustic assessment:
normal to reduced fundamental frequency and intensity; elevated jitter and shimmer; decreased phonation time and noise-to-harmonic ratio
- aerodynamic assessment:
normal
- videostroboscopy:
rhythmic movement of palate, pharynx, and vocal folds
More
Other investigations
- laryngeal EMG:
rhythmic waxing and waning activation of muscle activity
More
Uncommon
Granuloma with/without contact ulcer
History
pain, globus, coughing, throat clearing, mild roughness, and voice breaks associated with phonotrauma, acid irritation (laryngopharyngeal reflux), or intubation
Exam
head and neck exam unremarkable
1st investigation
Other investigations
Recurrent respiratory papilloma
History
gradually worsening hoarseness over several months; biphasic and inspiratory stridor (progressive if involvement of subglottis) occurring in the first 10 years of life or adulthood; less commonly presents with aphonia, chronic cough, recurrent pneumonia, failure to thrive, dysphagia, acute respiratory distress, and stridor; previous history of treatment for asthma, croup, allergies, vocal fold nodules, or bronchitis is common in children
Exam
head and neck exam unremarkable
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
mild hoarseness to aphonia; inspiratory or biphasic stridor
- acoustic assessment:
increased fundamental frequency due to vocal fold stiffness; reduced signal-to-noise ratio
More - aerodynamic assessment:
increased subglottic pressure
More - videostroboscopy:
white cluster(s) of tissue stippled evenly with vascular features
More
Other investigations
Hypokinetic dysarthria
History
poor awareness of voice changes secondary to sensory deficits of Parkinson disease, but may complain of breathiness, hoarseness, vocal fatigue, quiet and monotonous speech, difficulty with pitch variation, slurred speech, altered rate of speech with short rushes of speech, and impaired intelligibility; other symptoms include loss of sense of smell, walking difficulties, and tremor
Exam
characterized by rigidity (cogwheel), resting tremor (4-6 Hz), and bradykinesia (masked facies, shuffling gait, and decreased arm swing)
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
low vocal intensity and fundamental frequency
- acoustic assessment:
reduced pitch range and loudness; monotone vocal production; decreased phrase length; faster or slower speech; impaired speech intelligibility; short rushes of speech
- aerodynamic assessment:
increased phonatory airflow
More - videostroboscopy:
vocal fold bowing and incomplete glottic closure (poor laryngeal valving); anterior/posterior glottic gaps during phonation
More
Other investigations
Unilateral vocal fold paralysis/paresis
History
difficulty swallowing, shortness of breath, breathiness, weak and quiet voice, loss of high notes, and increased vocal effort and fatigue related to recent history of surgery (thoracic, cervical, skull base) or intubation; possible neurologic symptoms of stroke, brainstem lesion, or bulbar palsy; unexplained weight loss in malignancy
Exam
surgical scars; neurologic signs of stroke, brainstem lesion, or bulbar palsy; unilateral oral and facial weakness; possible cachexia, and regional cervical lymphadenopathy
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
breathiness; diplophonia; aphonia; loss of loudness and high notes; high fundamental frequency; weak cry and cough; stridor; increased vocal effort and fatigue
More - acoustic assessment:
reduced frequency and intensity; loss of pitch control; breathiness; vocal fatigue
More - aerodynamic assessment:
increased airflow and subglottic pressure
- videostroboscopy:
immobile left or right arytenoid complex; vocal fold motion impairment
More
Bilateral vocal fold paralysis/paresis
History
difficulty swallowing, shortness of breath, breathiness, weak and quiet voice, loss of high notes, and increased vocal effort and fatigue related to recent history of thyroidectomy or intubation; possible neurologic symptoms of stroke or brainstem lesion; unexplained weight loss in malignancy; possible history of sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, amyloidosis, or radiation therapy for head and neck cancer
Exam
surgical scars; neurologic signs of stroke, brainstem lesion, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; bilateral oral and facial weakness; possible cachexia and regional cervical lymphadenopathy
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
stridor; difficulty breathing; breathiness; diplophonia; aphonia; loss of loudness and high notes; high fundamental frequency; weak cry and cough; stridor; increased vocal effort and fatigue
More - acoustic assessment:
reduced frequency and intensity; loss of pitch control; breathiness; vocal fatigue
More - aerodynamic assessment:
increased airflow and subglottic pressure
- videostroboscopy:
immobile left and right arytenoid complex; vocal fold motion impairment.
More
Adductor spasmodic dysphonia
History
gradual progression - or, more rarely, sudden onset - after viral illness or heavy voice use; possible family history of neurologic disorders; typical onset at around age 30 years; possible associated tremor
Exam
task-specific movement abnormality; dystonia tremor (6-8 Hz); evidence of other focal dystonias (writer's cramp, blepharospasm, torticollis)
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
strained and strangled voice quality; increased vocal effort; vocal fatigue; voice breaks
- acoustic assessment:
aperiodic segments; phonatory breaks; frequency shifts
- aerodynamic assessment:
increased airflow and subglottic pressure
More - videostroboscopy:
involuntary vocal fold adduction during connected speech
More
Other investigations
- high speed digital laryngeal imaging:
laryngeal spasm
- laryngeal EMG:
abnormal delay between onset of electrical and acoustic activity
More
Abductor spasmodic dysphonia
History
gradual progression - or, more rarely, sudden onset - after viral illness or heavy voice use; possible family history of neurologic disorders; typical onset at around age 30 years; possible associated tremor
Exam
dystonia tremor (6-8 Hz); evidence of other focal dystonias (writer's cramp, blepharospasm, torticollis)
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
intermittent breathy breaks during connected speech; prolonged voiceless speech sounds
- acoustic assessment:
aperiodic segments; phonatory breaks; frequency shifts; reduced loudness; prolonged voice onset time
- aerodynamic assessment:
increased average airflow; variation in subglottic pressure
- videostroboscopy:
involuntary abduction of vocal folds during connected speech
More
Other investigations
- high speed digital laryngeal imaging:
laryngeal spasm
- laryngeal EMG:
abnormal delay between onset of electrical and acoustic activity
More
Leukoplakia
History
mild dysphonia to aphonia, breathiness, raspy voice quality, and possible otalgia in patient with a history of tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption; possible history of previous radiation therapy or laryngopharyngeal reflux
Exam
head and neck exam may be normal; possible regional cervical lymphadenopathy and/or white patches on the tongue, buccal mucosa, and/or palate
1st investigation
- perceptual assessment:
mild dysphonia to aphonia; breathiness; raspy voice quality; decreased fundamental frequency
- acoustic assessment:
increased perturbation; decreased signal-to-noise ratio
- aerodynamic assessment:
phonatory airflows may be increased
More - videostroboscopy:
keratotic erythroplakia or leukoplakia; vocal fold stiffness at site of lesion
More
Other investigations
- biopsy:
atypical cytologic features in squamous epithelium without histopathologic evidence of malignancy
More
Vocal fold cancer
History
symptoms depend on tumor size, location, and progression and include dysphonia and aphonia, difficulty breathing, stridor, dysphagia, otalgia, and unexplained weight loss with history of tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption
Exam
head and neck exam may reveal regional cervical lymphadenopathy; mirror exam will identify location and macroscopic extent of tumor within larynx
1st investigation
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer