Tests
1st tests to order
ECG
Test
Positive findings confirm the diagnosis of NSVT. Evidence of ischemic heart disease and left ventricular hypertrophy should be sought. Baseline ECG may demonstrate QT interval prolongation, evidence of Brugada syndrome, or arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. T-wave inversion, although nonspecific, may suggest structural cardiac disease.[38][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Nonsustained ventricular tachycardiaFrom the collection of Dr F. Kusumoto; used with permission [Citation ends].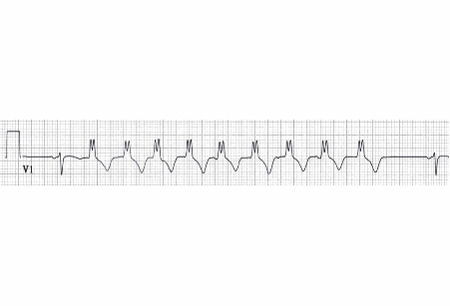
Result
wide QRS complex (≥120 milliseconds), rate >100 bpm lasting for ≥3 beats, spontaneously resolving in <30 seconds
electrolyte panel
Test
Electrolyte abnormalities may trigger NSVT in patients with or without cardiac disease.[2]
Result
normal; hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, or hypomagnesemia
troponin
Test
Clinical suspicion for ischemia should prompt testing of myocardial biomarker assays, as they provide useful confirmatory information.
Result
may be elevated in myocardial infarction
CK-MB
Test
Clinical suspicion for ischemia should prompt testing of myocardial biomarker assays, as they provide useful confirmatory information.
Result
may be elevated in myocardial infarction
Tests to consider
24-hour ambulatory ECG monitoring
Test
Useful in selected patients to determine extent of arrhythmia burden. Also helps to establish whether correlation between NSVT and symptoms is required.
Can also be very useful for identifying presence of idiopathic sustained VTs, particularly those arising from the outflow tracts.
Result
frequency and severity of NSVT
echocardiogram
Test
Safe and inexpensive tool to evaluate for structural cardiac abnormalities such as valvular heart disease, which in advanced stages can cause NSVT and is treatable. Echocardiogram is also useful to quantify systolic function and detect the presence of an underlying cardiomyopathy.
Result
compromised left ventricular function; evidence of structural heart disease, or hypertrophic or idiopathic cardiomyopathy
cardiac catheterization
Test
May be appropriate early test for patients presenting with symptoms of myocardial infarction, because early reperfusion decreases overall prevalence of NSVT.[9] Also helpful in determining if patient has ischemic or nonischemic cardiac disease.
Result
may show coronary artery obstruction
cardiac MRI with gadolinium
Test
Useful in investigating patients with suspected structural cardiac disease. Particularly helpful in establishing the presence of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, especially wall motion abnormalities in the right ventricle. Guidelines recommend considering a cardiac MRI in patients with newly documented NSVT and suspected structural heart disease (other than coronary artery disease) after initial evaluation.[2]
Result
scar, fibrofatty infiltration of myocardium, other evidence of infiltrative cardiomyopathy
electrophysiologic testing
Test
Testing may provide important clues for the cause of wide complex tachycardias due to NSVT, especially in patients with no identifiable structural abnormalities on previous testing. Useful in patients after myocardial infarction including those with inducible VT and ejection fraction <40% and with ejection fraction <30% to 35% without inducible VT, especially if QRS is prolonged.[31] A useful diagnostic and therapeutic tool for selected patients with symptomatic NSVT, with idiopathic VTs, or where NSVT or frequent premature ventricular contractions are thought to be a cause of cardiomyopathy.
Result
distinguishes VT from SVT with aberration; establishes mechanism of VT in patients with apparently structurally normal heart
stress testing
Test
Useful in establishing the presence of coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients who have risk factors for CAD, but may be asymptomatic. The patient's pretest probability of CAD should be scored and used to guide the choice of investigations. Often stress testing with imaging (nuclear or echocardiogram) is required for more definitive identification of underlying ischemia.
Result
may show cardiac ischemia
genetic screening
Test
Consultation with a cardiologist or medical geneticist may be helpful in determining which patients would benefit most from genetic screening. Cascade genetic testing of family members may be warranted.[2][23][35][36][37]
Result
may show mutations associated with long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome, and catecholaminergic polymorphic VT
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer