Tests
1st tests to order
serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
Test
Elevation of ALT and AST levels, between 1 and 4 times the upper limit of normal values, occurs in 50% to 90% of patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD).[43] Results rarely exceed 300 IU/L.[44] Patients with any type of MASLD may have normal LFTs.[37][45]
The AST:ALT ratio (AAR) in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is typically <1.[46] This differs from acute alcohol-related hepatitis, where the ratio is usually >2. Ratio reversal in patients with MASH (AAR >1) may be an indicator of more advanced liver fibrosis.[36][47]
Result
normal or elevated
total bilirubin
Test
Usually only begins to elevate with decompensated disease.
Result
normal or elevated
alkaline phosphatase
Test
Up to twice the upper limit of normal.
Result
normal or elevated
gamma glutamyl transferase
Test
A level >96.5 U/L increases the risk for presence of advanced fibrosis in MASLD.[57]
Result
normal or elevated
CBC
Test
Anemia and thrombocytopenia due to hypersplenism usually seen after the development of cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Platelet count is a component of the NAFLD Fibrosis Index and FIB-4 scores, which estimate the risk of advanced fibrosis. NAFLD Fibrosis Score Opens in new window Fibrosis 4 Score (FIB-4) Opens in new window
Result
anemia or thrombocytopenia
metabolic panel
Test
Mild hyponatremia is commonly seen in patients with cirrhosis. Due to increased levels of antidiuretic hormone. Portends a worse prognosis in patients with cirrhosis.[58][59]
Serum creatinine and BUN may be elevated because it is common for renal function to decline as liver disease advances.
European guidelines mandate screening all patients diagnosed with MASLD for type 2 diabetes mellitus.[40]
Result
abnormal
lipid panel
Test
Fasting lipid panel shows hypertriglyceridemia in 20% to 80% of patients; many patients with MASH will have low HDL as part of metabolic syndrome. As liver disease becomes more severe, it is not uncommon for cholesterol levels to decrease.
Result
elevated total cholesterol, LDL, triglyceride, and low HDL
prothrombin time and INR
Test
Indication of impaired or decompensated liver synthetic function.
Result
normal or elevated
serum albumin
Test
Low albumin is an indication of impaired liver synthetic function.
Result
normal or decreased
autoimmune liver disease screen
Test
Autoimmune markers (including antinuclear antibody, smooth muscle antibody, anti-liver kidney microsomal antibody, and quantitative immunoglobulins) should be requested to exclude autoimmune liver disease. One retrospective review suggested that positive low-titer antinuclear antibody is relatively common in patients with MASH (34%); antismooth muscle antibody is seen in 6% of cases.[60] In patients with suspected MASLD and antinuclear antibody positivity at titers greater than 1:160 or anti-smooth muscle antibody positivity at titers greater than 1:40, a liver biopsy may be considered to exclude the presence of autoimmune hepatitis.[48]
Result
variable
iron studies
hepatitis B surface antigen, surface antibody, and core antibody
Test
To exclude chronic hepatitis B as the cause of liver disease.
Result
negative
hepatitis C virus antibody
Test
To exclude chronic hepatitis C as the cause of liver disease.
Result
negative
alpha-1 antitrypsin level and phenotype
Test
To exclude alpha-1 antitrypsin as the cause of liver dysfunction.
Result
normal
liver ultrasound
Test
Initial imaging test for suspected SLD. Findings include 1) diffuse hyperechoic echotexture (bright liver); 2) increased liver echotexture compared with kidneys; 3) vascular blurring; and 4) deep attenuation. Controlled attenuation parameter, an ultrasound-based technique, provides a point-of-care semi-quantitative assessment of SLD.[3] Transient elastography measured controlled attenuation parameter (TE-CAP) has good diagnostic accuracy to grade steatosis and can be used in clinical practice.[33]
Result
abnormal echotexture
Tests to consider
fasting insulin
Test
Level greater than the upper limit of normal for the assay used (approximately 60 picomoles/L) is considered evidence of insulin resistance. Should be measured in all nondiabetic patients with MASLD or MASH regardless of BMI.
Result
elevated
homeostatic model assessment (HOMA) calculation
Test
A method used to quantify insulin resistance and beta-cell function. Calculated as glucose (mg/dL) × insulin (microunits/mL)/405. A score of ≥2 is consistent with insulin resistance.
Should be calculated on all nondiabetic patients with MASLD or MASH regardless of BMI.
Result
variable
abdominal MRI
Test
MRI liver may be requested if SLD is suspected but is not detected using ultrasound.[8] MRI protein density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) correlates well with biopsy-proven SLD and is more accurate than ultrasound for identifying SLD.[53][54] MRI-PDFF can quantify steatosis.[3] MRI-PDFF is superior to blood-based noninvasive tests and should be used in the assessment of hepatic steatosis in adults with MASLD, where available.[33]
Result
increased liver fat content
elastography
Test
For the identification of advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis, the leading biomarker is liver stiffness. Ultrasound shear wave elastography is a noninvasive technique for assessing liver stiffness. Tissue stiffness is deduced from analysis of shear waves that are generated by high-intensity ultrasound pulses.[55] Magnetic resonance elastography is an alternative technique for assessing liver stiffness. It is more accurate than ultrasound shear wave elastography for identifying fibrosis and cirrhosis, and performs better in people with obesity.[52][54][55]
Result
increased liver stiffness
liver biopsy
Test
Liver biopsy is the gold standard for confirming the diagnosis of MASLD.[48] It is also the most sensitive and specific means of providing important prognostic information. Usually reserved for patients where there is diagnostic uncertainty or who are at increased risk of having steatohepatitis or advanced fibrosis.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A wedge biopsy of the liver from a 52-year-old female organ donor; the biopsy shows moderate mixed micro- and macrovesicular steatosis; there is no significant lobular inflammation or necrosis (hematoxylin and eosin, [H&E] stain, x 200)From the collection of Kapil B. Chopra, MD [Citation ends].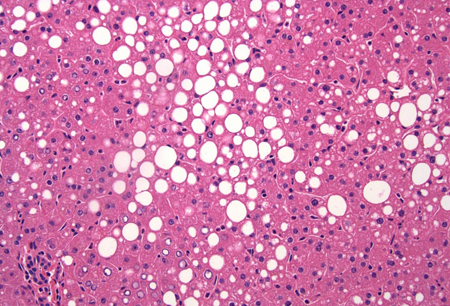 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A case of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis; the biopsy shows ballooning degeneration of the hepatocytes (middle right) and spotty lobular inflammation in addition to mixed micro- and macrovesicular steatosis (H&E, x 200)From the collection of Kapil B. Chopra, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A case of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis; the biopsy shows ballooning degeneration of the hepatocytes (middle right) and spotty lobular inflammation in addition to mixed micro- and macrovesicular steatosis (H&E, x 200)From the collection of Kapil B. Chopra, MD [Citation ends].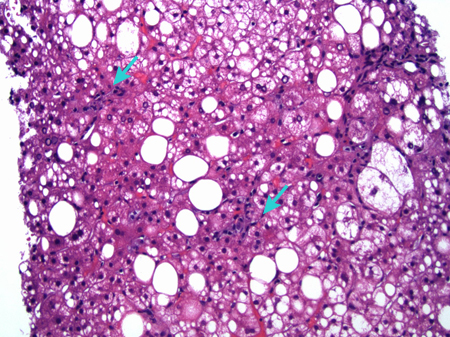 The most widely used scoring system stages steatosis 0 to 3, and grades fibrosis from 0 to 4.[4]
The most widely used scoring system stages steatosis 0 to 3, and grades fibrosis from 0 to 4.[4]
Result
variable (e.g., steatosis, inflammation, hepatocyte ballooning degeneration, fibrosis)
ceruloplasmin
Test
To screen for Wilson disease in appropriate age groups (<40 years).
Result
normal
HFE gene mutation testing
Test
To exclude hereditary hemochromatosis in patients with elevated serum ferritin.
Result
normal
anti-M2 mitochondrial antibody
Test
May be performed to exclude primary biliary cholangitis in patients with elevated alkaline phosphatase and no biliary dilatation on ultrasound.[44]
Result
negative
Emerging tests
cytokeratin-18 fragments
Test
Biomarkers may be able to detect the degree of liver injury without the need for liver biopsy. Cytokeratin-18 fragments indicate hepatocyte apoptosis and may distinguish MASH from simple fatty liver.[62]
Result
elevated
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer