Tests
1st tests to order
CT head (without contrast) or MRI head
Test
CT head (without contrast) or MRI head should be ordered initially in all patients.[18] A CT scan provides sufficient information in the majority of cases, demostrating the size and shape of the ventricles. However, an MRI scan has the benefit of avoiding exposure to ionizing radiation.
May show disproportionate central atrophy, resulting in larger ventricles with relative preservation of cortical sulci in the atrophic process.[19]
Neuroimaging is not diagnostic by itself, but is necessary to exclude other pathology.
An obstructive lesion excludes diagnosis.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Normal CT scan in patient with levodopa-unresponsive gait apraxia, emphasizing that the condition is not necessarily a radiologic diagnosisPersonal collection of Richard Adam Grünewald [Citation ends].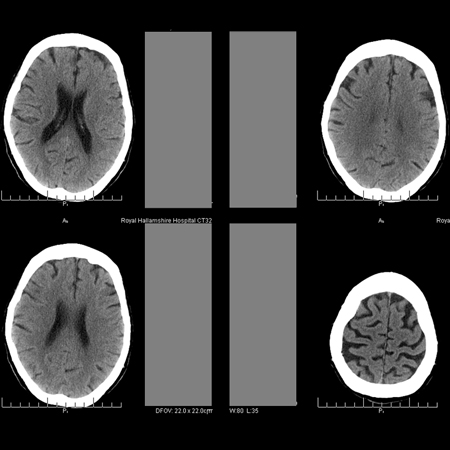 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI fluid attenuation inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequence showing periventricular high signal (leukoaraiosis) and central and peripheral brain atrophyPersonal collection of Richard Adam Grünewald [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: MRI fluid attenuation inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequence showing periventricular high signal (leukoaraiosis) and central and peripheral brain atrophyPersonal collection of Richard Adam Grünewald [Citation ends].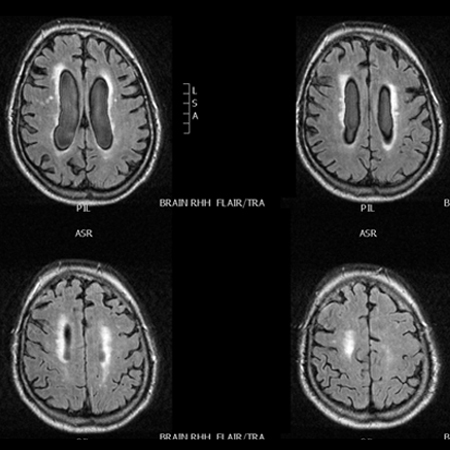
Result
normal; or mild to moderate ventricular enlargement, periventricular leukomalacia (i.e., damage to the white matter around the cerebral ventricles), cerebral infarction, relative preservation of cortical gyri and sulci, aqueduct flow void, reduced diameter of the corpus callosum and decreased callosal angle
levodopa challenge
Test
Should be ordered in all patients with suspected Parkinson disease.[20]
Patient is given a therapeutic trial of levodopa and asked to note subjective improvement in gait symptoms. If symptoms are responsive, a diagnosis of NPH can be ruled out.
If there is any doubt about response, a formal challenge test should be considered. A timed walk is recorded on video, followed by administration of levodopa, then the timed walk is repeated after 1 to 3 hours and the result compared with the initial timed walk. Positive response to the drug is represented by a clinically useful improvement in walking speed (approximately >20%). Patient should also be asked to report any subjective improvement.
Levodopa challenge should only be undertaken after an overnight withdrawal of all dopaminergic drugs.
Result
no response to therapy
Tests to consider
lumbar puncture
Test
Should be considered in any patient with levodopa-unresponsive gait apraxia, unless they are considered unsuitable for a corrective surgical procedure after an assessment of the benefits and risk of surgery, or a definitive alternative diagnosis is established.
Reveals normal (or not significantly elevated) cerebrospinal fluid pressure.[18] Values outside this range are incompatible with diagnosis.
Result
opening pressure: 7 to 25 cm water (5-18 mmHg)
lumbar puncture with large-volume cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tap
Test
Should be considered in any patient with levodopa-unresponsive gait apraxia.
Involves removal of 30 to 60 mL of CSF via lumbar puncture.
Supports diagnosis, and indicates an increased likelihood of response to CSF diversion procedure, if there is improvement in gait symptoms, shown by a recorded, timed walk (and/or other tests if appropriate) before and 1 to 3 hours after the procedure.
Although the sensitivity of the test is uncertain, it is thought to be of high specificity.
Considered diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic.
Result
improvement in gait symptoms after procedure
prolonged external lumbar drainage
Test
Usually reserved for patients with equivocal results after large-volume cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tap, or if there is a high index of suspicion of diagnosis but no response to large-volume CSF tap.
Involves placing catheter in lumbar CSF space for 2 to 4 days and removing 150 to 250 mL of CSF per day.
Supports diagnosis if there is an improvement in gait symptoms, shown by a recorded, timed walk (and/or other tests if appropriate) before and 1 to 3 hours after the procedure.
May have higher sensitivity than a single, large-volume CSF tap, but the evidence for this procedure is sparse.
Available in specialized centers only.
Result
improvement in gait symptoms after procedure
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) infusion procedure
Test
Usually reserved for patients with equivocal results after large-volume CSF tap, or if there is a high index of suspicion of diagnosis but no response to large-volume CSF tap.
In the Katzman test, a pump infuses saline through a needle in the lumbar subarachnoid space. The impedance is calculated as the difference in the final steady state pressure reached and the initial pressure, divided by the infusion rate.
Alternative methods involve bolus injections of volumes of saline into the subarachnoid space, or rely on recording the time pressure curve during continuous saline infusion.
The results of these tests are variable and center-specific, but the technique of CSF impedance measurement has been assessed as potentially valuable.[23]
Available in specialized centers only.
Result
variable: elevated outflow resistance predicts which patients will respond most favorably to shunting
continuous intracranial pressure monitoring
Test
One prospective cohort study (n=131) of patients undergoing surgery for NPH reported that 93% of patients with increased intracranial pressure (ICP) pulsatility (ICP wave amplitude >4 mmHg on average and >5 mmHg in >10% of recording time) responded to shunt surgery, whereas 10% of patients without increased ICP pulsatility responded to shunt surgery.[24] Another prospective study found that high ICP pulse amplitude had a sensitivity of 84.4%, specificity of 88%, positive predictive value of 94.7%, and negative predictive value of 61.8% for predicting shunt responders.[25]
There is a small risk of superficial wound infection and ventriculitis associated with this procedure.
Result
normal or high pulse amplitude
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer