Images and videos
Images
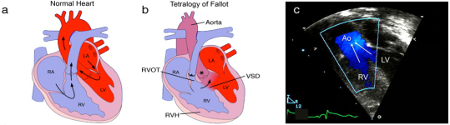
Tetralogy of Fallot
Anatomy and pathophysiology of tetralogy of Fallot (TOF): normal heart structure (a) promotes unidirectional flow of deoxygenated blood (blue) into the lungs and oxygenated blood (red) into the aorta; in TOF (b) pulmonary stenosis and narrowing of the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) impedes the flow of deoxygenated blood into the lungs, and both the ventricular septal defect (VSD) and overriding aorta (*) promote the flow of deoxygenated blood into the systemic circulation, to produce cyanosis (sometimes referred to as “blue baby” syndrome), right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) is also present; (c) a Doppler echocardiogram shows mixing of deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle (RV) and oxygenated blood from the left ventricle (LV) as blood is pumped out the over-riding aorta (Ao) in a patient with TOF (RA=right atrium, LA=left atrium)
Multimedia Library of Congenital Heart Disease, Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA, editor Robert Geggel, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Tetralogy of Fallot
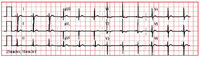
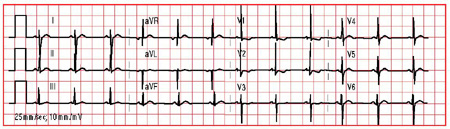
ECG in tetralogy of Fallot showing right ventricular hypertrophy
From the collection of Dr Jeffrey Gossett; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer