Case history
Case history #1
A girl is born at term after a normal pregnancy and delivery. On examination she is noted to be hypotonic with hyperextensible joints, small ears, and a small mouth. She has a protruding tongue, a broad neck, an upward slant to the eyes with epicanthal folds, and a single palmar crease.
Case history #2
The result of an amniocentesis in a pregnant 39-year-old mother reveals a chromosomal karyotype of 47,XX,+21.
Other presentations
Down syndrome (DS) is typically diagnosed during the newborn period based on the characteristic physical presentation. However, the diagnosis may be challenging in certain racial/ethnic groups or in individuals with mosaicism. Children with DS and darker eye color may not have noticeable Brushfield spots. Some features, for example, the presence of a protruding tongue or extra nuchal skin, are not always present.[2] Children with DS diagnosed after the newborn period may present with developmental delay, hypotonia with hyperextensible joints, or DS-associated medical conditions (e.g., atrioventricular septal defects, hearing loss, or Hirschsprung disease). [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Girl with Down syndromeFrom the personal collection of Dr Jeannie Visootsak; photo used with parental consent [Citation ends].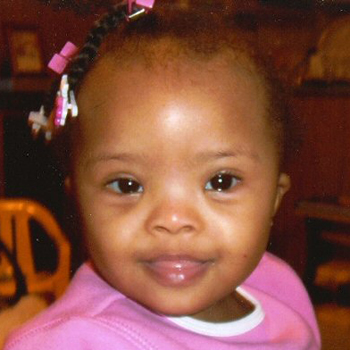 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Boy with mosaic Down syndrome, diagnosed at 18 monthsFrom the personal collection of Dr Jeannie Visootsak; photo used with parental consent [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Boy with mosaic Down syndrome, diagnosed at 18 monthsFrom the personal collection of Dr Jeannie Visootsak; photo used with parental consent [Citation ends].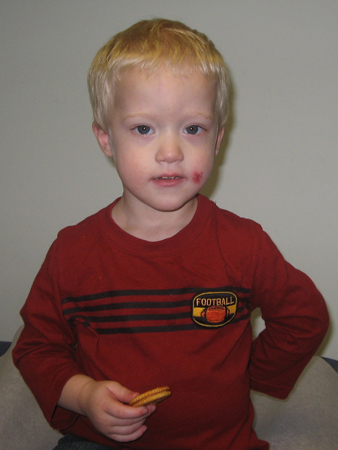
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer