Criteria
Prader score for genital atypia
Genital ambiguity can be evaluated by the Prader score in newborns.[20]The scores range on a scale of 1 to 5 (I to V). The genitalia can be scored from slightly virilized (score of 1) to indistinguishable from a male (score of 5). [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Prader Score: degree of virilization of the external genitalia of females as proposed by Prader. In type I, the only abnormality is a slight enlargement of the clitoris. In type V, there is a markedly enlarged phallus with a penile urethraPermission granted by Helvetica Paediatrica Acta [Citation ends].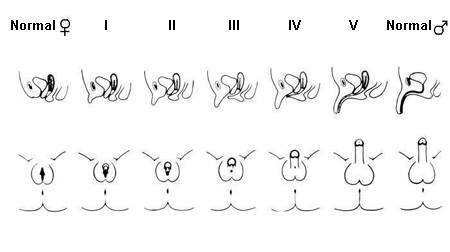
Hormonal criteria: nomogram ACTH stimulations test standard
Hormonal standards for a diagnostic ACTH-stimulation test are determined by plots on a logarithmic scale of baseline versus ACTH-stimulated 17-hydroxyprogesterone concentrations resulting in a regression line with 3 distinguishable groups.[15] These nomograms clearly distinguish patients with classical 21-hydroxylase deficiency from those with milder symptomatic and asymptomatic nonclassical disease.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Nomogram relating baseline to ACTH-stimulated serum concentrations of 17-hydroxyprogesterone. The scales are on log^10. A regression line for all data points is shownPermission granted by The Endocrine Society [Citation ends].
Ferriman-Gallwey score for hirsutism
This scoring system quantifies the extent of hair growth in 9 key anatomic sites. Hair growth is graded using a scale from zero (no terminal hair) to 4 (maximal growth), for a maximum score of 36. A score of 8 or more indicates the presence of hirsutism. The degree of facial and body hair excess can be objectively scored by this method.[21]
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer