History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
pain on swallowing
Usually not severe, but on occasion may result in significantly reduced intake, which may necessitate admission to the hospital.[18]
fever (>100.5°F [>38°C])
tonsillar exudate
Patients with acute tonsillitis, particularly when it is caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, often have purulent exudate on the tonsillar surface.[1][5] Tonsillar exudate is one of the Centor criteria.[20] Three of four Centor criteria make bacterial infection more likely. However, tonsillar exudates are also prominent in infectious mononucleosis.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tonsillitis caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcusFrom the collection of Dr Eleftherios Margaritis [Citation ends].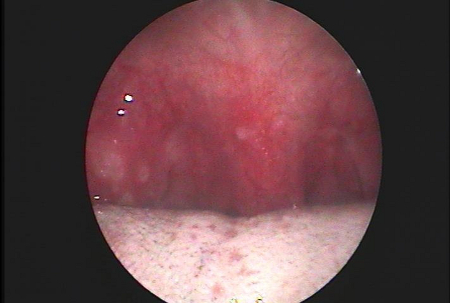
Other diagnostic factors
common
sudden onset of sore throat
A sudden onset of sore throat is suggestive of an infectious process.[18]
headache
A nonspecific symptom of the acute infective process.
abdominal pain
May lead occasionally to the false diagnosis of gastroenteritis and (rarely) may even mimic an acute abdomen.[18]
nausea and vomiting
A nonspecific symptom but one that may lead to a false diagnosis of gastroenteritis, if very prominent.[18]
presence of cough or runny nose
Suggests viral upper respiratory infection. Absence of cough is a Centor criteria.[20] Three of four Centor criteria make bacterial infection more likely.
tonsillar erythema
Common sign on presentation.
tonsillar enlargement
Common sign on presentation.
enlarged anterior cervical lymph nodes
Risk factors
weak
age between 5 and 15 years
contact with infected people in enclosed spaces (e.g., child care centers, schools, prison)
Tonsillitis, whether viral or bacterial, is an infectious condition and can be spread by exposure to an infected person.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer