Tests
1st tests to order
serum calcium level
Test
Levels will be low or normal in vitamin D deficiency.
Result
normal or low
serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level
Test
Commonly low with vitamin D deficiency from various causes, especially in the setting of limited sunlight exposure and malabsorption.
A 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration of <25 nanomol/L (<10 nanogram/mL) is the threshold regarded internationally as defining the risk of osteomalacia.[17][47]
Result
low
serum phosphate level
Test
Levels tend to be low in patients with primary renal phosphate wasting or may coexist with other renal tubular defects, such as hypouricemia, aminoaciduria, and glycosuria in patients with Fanconi syndrome.
Result
low
serum BUN and creatinine
Test
In patients with renal failure, this ratio will be elevated.
Result
ratio elevated
intact PTH
Test
PTH is high in vitamin D deficiency, renal failure, and hypocalcemia. PTH levels tend to decline with vitamin D and calcium supplementation.[53]
All patients suspected of osteomalacia should receive this test.
Result
high
serum alkaline phosphatase
Test
Serum alkaline phosphatase levels are high in the majority of patients with osteomalacia, except in those patients with hypophosphatasia.
Result
high
24-hour urinary calcium
Test
A 24-hour urinary calcium measurement is useful in confirming vitamin D-deficient states as a cause of osteomalacia.
Result
low
Tests to consider
bone x-rays
Test
Looser pseudofractures (also known as milkman fractures) associated with sclerotic borders, which lie perpendicular to the cortical margins of bone, are a pathognomonic finding in osteomalacia. They are often bilateral and symmetric and are found at the femoral neck, on the medial part of the femoral shaft, or at the pubic and ischial rami.[52][54]
Other possible findings include resorption of the subperiosteal region of the phalanges, bone cysts, resorption of the distal ends of long bones (namely, proximal femur, tibia, humerus, and the distal clavicle), reduced bone density with thinning of the cortex, osteopenia and coarse trabeculae, codfish vertebrae or soft tissue calcification, and amyloid deposition (chronic kidney disease-mineral bone disorder [CKD-MBD]).
Osteosclerosis (increased bone density) occurs in patients with CKD-MBD. The Rugger-Jersey sign may be seen where alternating parallel sclerotic bands and radiolucent bands appear on x-ray of the spine.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Radiograph of the femoral shaft in a patient with osteomalacia demonstrating a “pseudofracture” (also known as Looser zone) on the medial aspect of the mid-femoral shaftFrom the collection of Bridget Sinnott, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].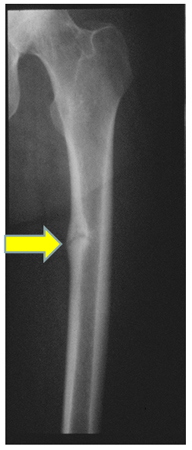
Result
may see characteristic findings of long-standing secondary hyperparathyroidism; reversible with treatment of the underlying disorder
24-hour urinary phosphate
Test
Urinary phosphate levels are high in patients with primary renal phosphate wasting or Fanconi syndrome and in oncogenic osteomalacia.
Result
high
dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry
Test
Dual-energy, x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) reveals a low bone mass in both osteoporosis and osteomalacia. Osteomalacia presents as osteoporosis on DXA in up to 70% of cases, and therefore DXA cannot distinguish these disease entities.[50]
Result
low bone density
iliac crest biopsy with double tetracycline labeling
Test
Iliac crest biopsy using double tetracycline labeling is the definitive diagnostic test; however, due to the invasive nature, it is rarely performed.[30][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Photomicrography of a normal transilial bone biopsy demonstrating mineralized osteoid (shown in purple)From the collection of Bridget Sinnott, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].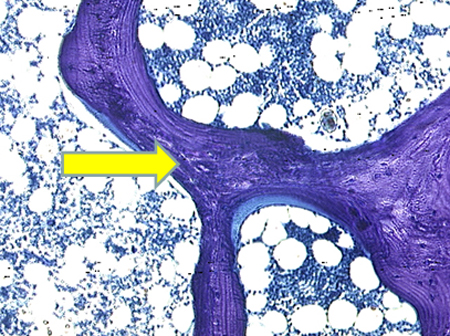 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Photomicrography of a transilial bone biopsy in a patient with osteomalacia demonstrating unmineralized osteoid (shown in purple). The width of the osteoid seams is substantially increasedFrom the collection of Bridget Sinnott, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Photomicrography of a transilial bone biopsy in a patient with osteomalacia demonstrating unmineralized osteoid (shown in purple). The width of the osteoid seams is substantially increasedFrom the collection of Bridget Sinnott, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].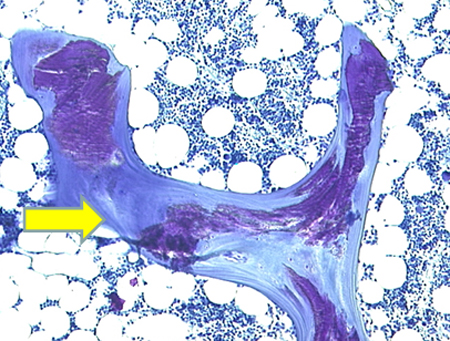
Result
reduced distance between tetracycline bands; unmineralized matrix appears as widened osteoid seam (>15 microns); increased osteoid volume >10%
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer