IgA nephropathy (IgAN) can only be diagnosed with a kidney biopsy.[40]Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Glomerular Diseases Work Group. KDIGO 2021 clinical practice guideline for the management of glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 2021 Oct;100(4s):S1-S276.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2021.05.021
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34556256?tool=bestpractice.com
No combination of clinical, serologic, and immunologic parameters can be used to replace the kidney biopsy.
Clinical evaluation
Visible hematuria is reported by about half of patients and is usually preceded by an upper respiratory tract infection (synpharyngitic nephritis) or gastroenteritis. Visible hematuria is usually painless but may occasionally be accompanied by loin pain and dysuria. Rarely, patients develop acute kidney injury, resulting from heavy glomerular hematuria leading to tubular occlusion and damage by red blood cells. This phenomenon is usually reversible, although incomplete recovery of kidney function may occur.
Approximately one third of patients have invisible hematuria and mild proteinuria. Less than 10% present with the nephrotic syndrome or a rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN).[8]Barratt J, Feehally J. IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Jul;16(7):2088-97.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15930092?tool=bestpractice.com
[41]Coppo R, D'Amico G. Factors predicting progression of IgA nephropathies. J Nephrol. 2005 Sep-Oct;18(5):503-12.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16299675?tool=bestpractice.com
[42]Szeto CC, Lai FM, To KF, et al. The natural history of immunoglobulin a nephropathy among patients with hematuria and minimal proteinuria. Am J Med. 2001 Apr 15;110(6):434-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11331053?tool=bestpractice.com
Patients aged between 20 and 30 years are more commonly diagnosed than other age groups.[13]Knoppova B, Reily C, King RG, et al. Pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy: current understanding and implications for development of disease-specific treatment. J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 29;10(19):4501.
https://www.doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194501
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34640530?tool=bestpractice.com
[14]Penfold RS, Prendecki M, McAdoo S, et al. Primary IgA nephropathy: current challenges and future prospects. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2018;11:137-48.
https://www.doi.org/10.2147/IJNRD.S129227
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29695925?tool=bestpractice.com
IgAN affects males more than females with a ratio of at least 2:1 in North America and western Europe, but the sexes are equally affected in Asia.[37]Galla JH. IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1995 Feb;47(2):377-87.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7723227?tool=bestpractice.com
Although IgAN is commonly sporadic, familial cases have been reported.[16]Gharavi AG, Yan Y, Scolari F, et al. IgA nephropathy, the most common cause of glomerulonephritis, is linked to 6q22-23. Nat Genet. 2000 Nov;26(3):354-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11062479?tool=bestpractice.com
[17]Bisceglia L, Cerullo G, Forabosco P, et al. Genetic heterogeneity in Italian families with IgA nephropathy: suggestive linkage for two novel IgA nephropathy loci. Am J Hum Genet. 2006 Dec;79(6):1130-4.
http://www.cell.com/ajhg/fulltext/S0002-9297(07)63477-6
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17186473?tool=bestpractice.com
[18]Paterson AD, Liu XQ, Wang K, et al. Genome-wide linkage scan of a large family with IgA nephropathy localizes a novel susceptibility locus to chromosome 2q36. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007 Aug;18(8):2408-15.
http://jasn.asnjournals.org/content/18/8/2408.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17634434?tool=bestpractice.com
[19]Karnib HH, Sanna-Cherchi S, Zalloua PA, et al. Characterization of a large Lebanese family segregating IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007 Mar;22(3):772-7.
https://academic.oup.com/ndt/article/22/3/772/1899254
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17172253?tool=bestpractice.com
IgAN may also be identified during investigation of patients with established chronic kidney disease and hypertension (approximately 20% of cases). Less common presentations include nephrotic syndrome (<5% cases); RPGN characterized by edema, hypertension, hematuria, and kidney failure (<5% cases); and malignant hypertension (<1% cases).[8]Barratt J, Feehally J. IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Jul;16(7):2088-97.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15930092?tool=bestpractice.com
[9]Donadio JV, Grande JP. IgA nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2002 Sep 5;347(10):738-48.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12213946?tool=bestpractice.com
Malignant hypertension commonly presents with chest pain (angina or myocardial infarction), shortness of breath (pulmonary edema), or neurologic symptoms (headaches, visual disturbances, altered mental state, seizures).[8]Barratt J, Feehally J. IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Jul;16(7):2088-97.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15930092?tool=bestpractice.com
[9]Donadio JV, Grande JP. IgA nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2002 Sep 5;347(10):738-48.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12213946?tool=bestpractice.com
All patients with IgAN should be assessed for secondary causes (e.g., underlying HIV or viral hepatitis infection, inflammatory bowel disease, autoimmune disease, liver cirrhosis, or features suggesting IgA-dominant infection-related glomerulonephritis or IgA vasculitis).[40]Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Glomerular Diseases Work Group. KDIGO 2021 clinical practice guideline for the management of glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 2021 Oct;100(4s):S1-S276.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2021.05.021
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34556256?tool=bestpractice.com
Laboratory evaluation
There are no specific laboratory or serologic diagnostic tests for IgAN.
Urine microscopy is likely to show erythrocyturia with dysmorphic erythrocytes consistent with glomerular bleeding. Rarely red cell casts may also be seen.
Proteinuria is commonly present, with approximately 60% of patients having <1 g/day and up to 10% of patients presenting with nephrotic-range proteinuria.[8]Barratt J, Feehally J. IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Jul;16(7):2088-97.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15930092?tool=bestpractice.com
[37]Galla JH. IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1995 Feb;47(2):377-87.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7723227?tool=bestpractice.com
Kidney function (serum creatinine and estimated glomerular filtration rate) is routinely checked at diagnosis and regularly during follow-up to monitor the course of the disease.
Complement levels (C3 and C4) are usually within normal limits and should only be ordered to exclude other causes of kidney disease where appropriate.[9]Donadio JV, Grande JP. IgA nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2002 Sep 5;347(10):738-48.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12213946?tool=bestpractice.com
[43]Barratt J, Feehally J, Smith AC. Pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy. Semin Nephrol. 2004 May;24(3):197-217.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15156526?tool=bestpractice.com
[44]Davin JC, Ten Berge IT, Weening JJ. What is the difference between IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis? Kidney Int. 2001 Mar;59(3):823-34.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11231337?tool=bestpractice.com
Kidney and skin biopsy
A diagnosis of IgAN can only be made by kidney biopsy, which will confirm mesangial IgA deposition either by immunofluorescence or immunoperoxidase studies. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Immunofluorescence staining for IgA showing strong granular staining in the mesangium globally (anti-IgA immunofluorescence, x200)Courtesy of Drs Hwei Yee Lee, Cristine Ding, and Yong Howe Ho (Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore) [Citation ends].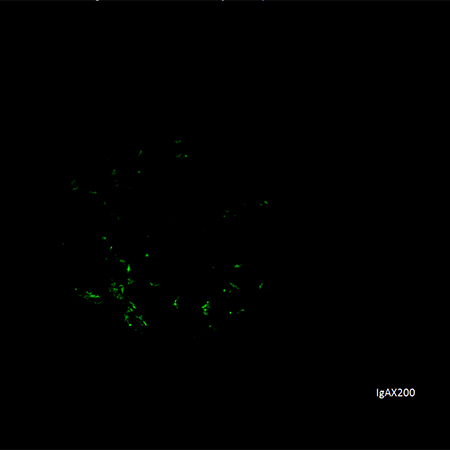 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Electron dense deposits in mesangial and paramesangial regions (electron micrograph, x1000)Courtesy of Drs Hwei Yee Lee, Cristine Ding, and Yong Howe Ho (Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore) [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Electron dense deposits in mesangial and paramesangial regions (electron micrograph, x1000)Courtesy of Drs Hwei Yee Lee, Cristine Ding, and Yong Howe Ho (Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore) [Citation ends].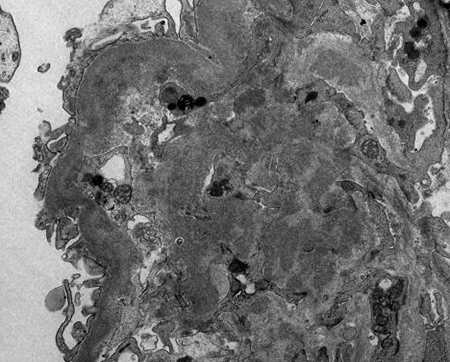
Indications for kidney biopsy vary from center to center. In general, it is indicated in any patient with consistently impaired kidney function and/or persistent protein excretion of >1 g/day, but not for isolated invisible hematuria.
Skin biopsy is only performed when IgA vasculitis is suspected and has no role in diagnosing IgAN. In IgA vasculitis, there may be evidence of dermal capillary deposits of IgA, C3, properdin, and fibrin.[45]Haas M. Histologic subclassification of IgA nephropathy: a clinicopathologic study of 244 cases. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997 Jun;29(6):829-42.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9186068?tool=bestpractice.com
[46]Iseki K, Miyasoto F, Uehara H, et al. Outcome study of renal biopsy patients in Okinawa, Japan. Kidney Int. 2004 Sep;66(3):914-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15327381?tool=bestpractice.com
[47]Li LS, Liu ZH. Epidemiologic data of renal diseases from a single unit in China: analysis based on 13,519 renal biopsies. Kidney Int. 2004 Sep;66(3):920-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15327382?tool=bestpractice.com
[48]Hasbargen JA, Copley JB. Utility of skin biopsy in the diagnosis of IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 1985 Aug;6(2):100-2.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3927716?tool=bestpractice.com
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Electron dense deposits in mesangial and paramesangial regions (electron micrograph, x1000)Courtesy of Drs Hwei Yee Lee, Cristine Ding, and Yong Howe Ho (Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore) [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Electron dense deposits in mesangial and paramesangial regions (electron micrograph, x1000)Courtesy of Drs Hwei Yee Lee, Cristine Ding, and Yong Howe Ho (Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore) [Citation ends].