Tests
1st tests to order
ECG
Test
If sinus rhythm is present, a key finding is tall, peaked P-waves (>2.5 mm in II, III, V1) of right atrial enlargement in the absence of RVH.[11] Atrial fibrillation is present in up to 40% to 70% of patients with rheumatic tricuspid stenosis (TS).[3][4][5]
Result
sinus rhythm versus atrial fibrillation
chest x-ray
Test
Findings are nonspecific.
Result
cardiomediastinal silhouette may be normal in size to mildly enlarged, right atrial enlargement and prominence of right heart border may be appreciated; presence of single or multiple pulmonary opacities may indicate pulmonary embolization and abscess formation from vegetations in the right heart with infective endocarditis
2D transthoracic echocardiogram
Test
Normal appearing valve by 2D echocardiogram does not exclude TS. Doppler echocardiography also needs to be performed. The presence of an abnormally appearing tricuspid valve with normal appearing mitral and aortic valves should prompt consideration for carcinoid heart disease and dissuade the clinician from rheumatic heart disease as the etiology. Right atrial enlargement with dilated systemic and hepatic veins is consistent with more severe TS.
Result
thickened, fused, and doming tricuspid valve leaflets, restricted leaflet motion, reduced diameter of valve orifice, right atrial enlargement with dilated systemic and hepatic veins
Doppler transthoracic echocardiogram
Test
Transthoracic echocardiogram with Doppler has largely replaced cardiac catheterization as a means to diagnose TS and correlates well with hemodynamic data obtained during catheterization.[38][39] Valve area has not correlated well with severity and has not been validated for clinical use. In the presence of moderate to severe tricuspid regurgitation, the valve area can be underestimated. A calculated valve area based on continuity equation <4.0 to 4.9 cm² is clinically significant TS. Others have indicated that a valve area <1 cm², a pressure gradient of ≥5 mmHg or >7 to 10 mmHg (depending on definition), and a pressure half time of >190 msec indicates severe TS.[31][32][33][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Echocardiogram with color Doppler reveals flow acceleration across the tricuspid valve and spectral Doppler reveals a mean TV gradient of 6 mmHgFrom the personal collection of Martin Bocks; used with permission [Citation ends].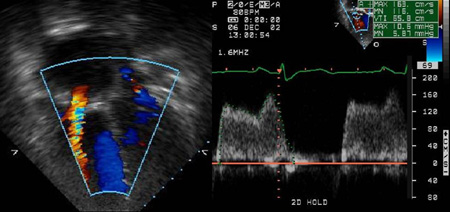
Result
elevated mean tricuspid valve gradient >2 mmHg, prolonged slope of antegrade flow; peak velocity across tricuspid valve >0.7 m/second
liver function tests
Test
Specificity for TS is poor. A normal value may also be obtained.
Result
mild elevation of aminotransferases may be present secondary to chronic hepatic venous congestion
blood biochemistry
Test
Minor metabolic abnormalities may be present depending on the extent of disease, such as elevated BUN and creatinine in renal insufficiency.
Result
abnormalities
CBC
Test
Polycythemia may suggest chronic hypoxemia secondary to diminished pulmonary blood flow or right-to-left shunting at the atrial level. Leukocytosis may indicate infective endocarditis.
Result
polycythemia in chronic hypoxemia or leukocytosis in infective endocarditis
blood cultures
Test
Bacterial or fungal cultures may indicate infective endocarditis.
Result
positive in infective endocarditis
24-hour urinary excretion of 5-hydroxy-indole acetic acid (5-HIAA)
Test
Twenty-four-hour urinary excretion of 5-HIAA is 10-fold higher than normal level in patients with carcinoid heart disease.[18]
Result
elevated in carcinoid heart disease
Tests to consider
cardiac catheterization
Test
Simultaneous right atrial and right ventricular pressures must be obtained over 8 to 10 cardiac cycles while breath-holding after normal inspiration. Tricuspid valve gradient can be provoked with normal saline bolus infusions.
Result
transvalvular mean diastolic gradient ≥2 mmHg indicates TS and a gradient ≥5 mgHg or >7 to 10 mmHg (depending on definition) is considered severe
cardiac MRI
3D transthoracic echocardiogram
Test
May provide better anatomical imaging and more consistent estimations of valve area. May also be useful in identifying valve abnormalities in carcinoid heart disease.[35]
Result
may provide better anatomical imaging and more consistent estimations of valve area
cardiac CT angiography (CTA)
Test
May detect valve or paravalvular abnormalities not detected on echocardiogram.[2]
Result
valve abnormalities in nonvegetative endocarditis, paravalvular abscesses, periprosthetic valve complications
[18F] fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)-PET/CT
Test
May be used to confirm diagnosis of endocarditis with or without positive blood cultures.[2]
Result
evidence of infective endocarditis, involved structures, embolic disease
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer