Criteria
Ankle-brachial index (ABI)
This is a ratio of the blood pressure at the ankle compared with the arm while resting:[2]
1.00 to 1.40 is normal
0.91 to 0.99 indicates borderline
≤0.90 is abnormal
>1.40 indicates noncompressible vasculature
Society for Vascular Surgery lower extremity threatened limb classification system: risk stratification based on wound, ischemia, and foot infection (WIfI)[50]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: WoundMills JL Sr, Conte MS, Armstrong DG, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Threatened Limb Classification System: risk stratification based on wound, ischemia, and foot infection (WIfI). J Vasc Surg. 2014 Jan;59(1):220-34;e1-2. [Citation ends].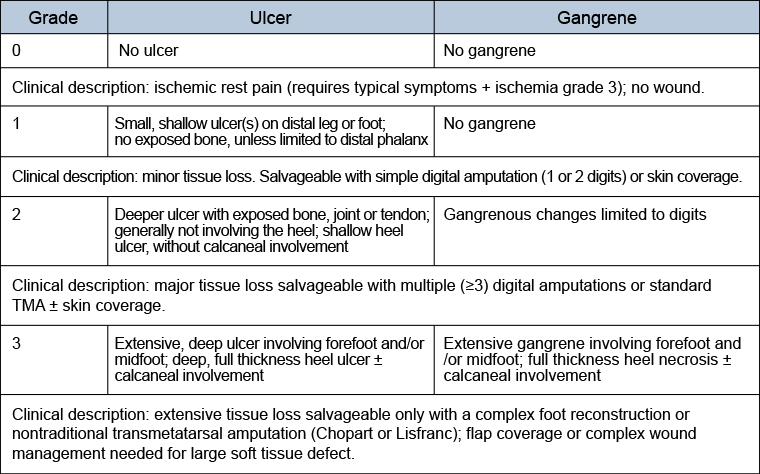 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ischemia (ABI: ankle-brachial index; TP: toe pressure; TcPO2: transcutaneous oximetry)Mills JL Sr, Conte MS, Armstrong DG, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Threatened Limb Classification System: risk stratification based on wound, ischemia, and foot infection (WIfI). J Vasc Surg. 2014 Jan;59(1):220-34;e1-2. [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ischemia (ABI: ankle-brachial index; TP: toe pressure; TcPO2: transcutaneous oximetry)Mills JL Sr, Conte MS, Armstrong DG, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Threatened Limb Classification System: risk stratification based on wound, ischemia, and foot infection (WIfI). J Vasc Surg. 2014 Jan;59(1):220-34;e1-2. [Citation ends].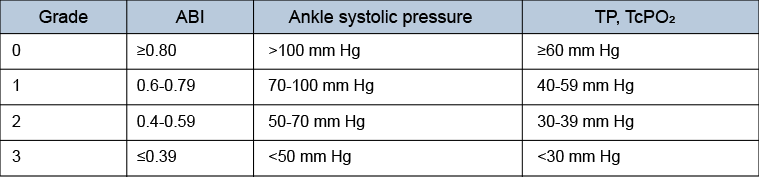 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Foot infection (PACO2: partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide; SIRS: systemic inflammatory response syndrome)Mills JL Sr, Conte MS, Armstrong DG, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Threatened Limb Classification System: risk stratification based on wound, ischemia, and foot infection (WIfI). J Vasc Surg. 2014 Jan;59(1):220-34;e1-2. [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Foot infection (PACO2: partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide; SIRS: systemic inflammatory response syndrome)Mills JL Sr, Conte MS, Armstrong DG, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Threatened Limb Classification System: risk stratification based on wound, ischemia, and foot infection (WIfI). J Vasc Surg. 2014 Jan;59(1):220-34;e1-2. [Citation ends].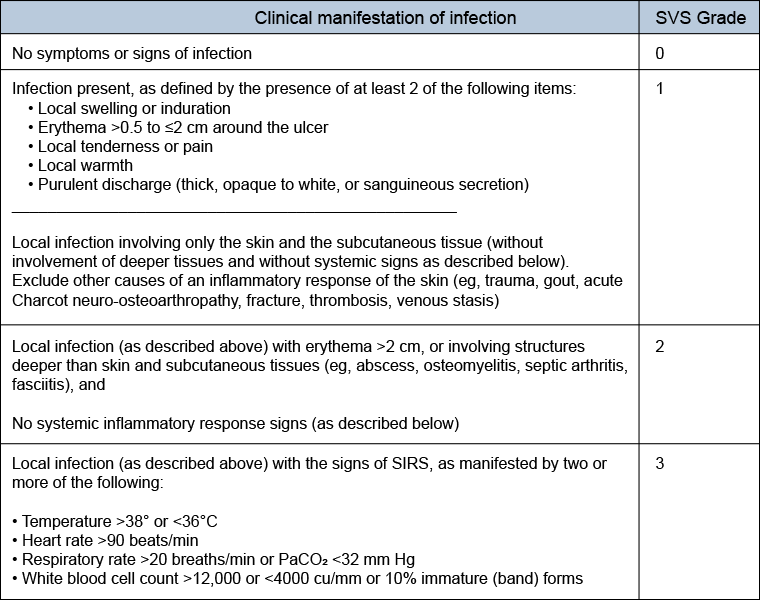 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Clinical stages (major limb amputation risk) based on Wound, Ischemia, and foot Infection (WIfI) classificationMills JL Sr, Conte MS, Armstrong DG, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Threatened Limb Classification System: risk stratification based on wound, ischemia, and foot infection (WIfI). J Vasc Surg. 2014 Jan;59(1):220-34;e1-2. [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Clinical stages (major limb amputation risk) based on Wound, Ischemia, and foot Infection (WIfI) classificationMills JL Sr, Conte MS, Armstrong DG, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Threatened Limb Classification System: risk stratification based on wound, ischemia, and foot infection (WIfI). J Vasc Surg. 2014 Jan;59(1):220-34;e1-2. [Citation ends].
TransAtlantic Inter-Society Consensus (TASC): morphological stratification of iliac lesions[51]
TASC type A iliac lesions:
Single stenosis <3 cm of the common iliac artery (CIA) or external iliac artery (EIA) (unilateral/bilateral)
TASC type B iliac lesions:
Single stenosis 3-10 cm in length, not extending into the common femoral artery (CFA)
Total of 2 stenoses <5 cm long in the CIA and/or EIA and not extending into the CFA
Unilateral CIA occlusion
TASC type C iliac lesions:
Bilateral 5-10 cm long stenosis of the CIA and/or EIA, not extending into the CFA
Unilateral EIA occlusion not extending into the CFA
Bilateral CIA occlusion
TASC type D iliac lesions:
Diffuse, multiple unilateral stenoses involving the CIA, EIA, and CFA (usually >10 cm long)
Unilateral occlusion involving both the CIA and EIA
Bilateral EIA occlusions
Diffuse disease involving the aorta and both iliac arteries
Iliac stenoses in a patient with an abdominal aortic aneurysm or other lesion requiring aortic or iliac surgery
TASC: morphological stratification of femoropopliteal lesions[51]
TASC type A femoropopliteal lesions:
Single stenosis <3 cm of the superficial femoral artery or popliteal artery
TASC type B femoropopliteal lesions:
Single stenosis 3-10 cm in length, not involving the distal popliteal artery
Heavily calcified stenoses ≤3 cm in length
Multiple lesions, each <3 cm (stenoses or occlusions)
Single or multiple lesions in the absence of continuous tibial runoff to improve inflow for distal surgical bypass
TASC type C femoropopliteal lesions:
Single stenosis or occlusion longer than 5 cm
Multiple stenoses or occlusions, each 3-5 cm in length, with or without heavy calcification
TASC type D femoropopliteal lesions:
Complete CFA or superficial femoral artery occlusions or complete popliteal and proximal trifurcation occlusions
TASC: morphological stratification of infrapopliteal lesions[52]
TASC type A infrapopliteal lesions:
Single focal stenosis in the target tibial artery ≤5 cm in length, with occlusion of similar or worse severity in the other tibial arteries.
TASC type B infrapopliteal lesions:
Multiple stenoses, each ≤5 cm in length, or total length ≤10 cm, or single occlusion ≤3 cm in length, with occlusion of similar or worse severity in the other tibial arteries.
TASC type C infrapopliteal lesions:
Multiple stenoses in the target tibial artery and/or single occlusion with total lesion length >10 cm, with occlusion of similar or worse severity in the other tibial arteries.
TASC type D infrapopliteal lesions:
Multiple occlusions involving the target tibial artery with total lesion length >10 cm or dense lesion calcification or nonvisualization of collaterals. The other tibial arteries are occluded or have dense calcification.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer